Abstract
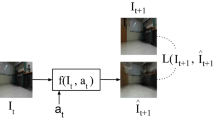
Imitation learning is a widely used policy learning method that enables intelligent agents to acquire complex skills from expert demonstrations. The input to the imitation learning algorithm is usually composed of both the current observation and historical observations since the most recent observation might not contain enough information. This is especially the case with image observations, where a single image only includes one view of the scene, and it suffers from a lack of motion information and object occlusions. In theory, providing multiple observations to the imitation learning agent will lead to better performance. However, surprisingly people find that sometimes imitation from observation histories performs worse than imitation from the most recent observation. In this paper, we explain this phenomenon from the information flow within the neural network perspective. We also propose a novel imitation learning neural network architecture that does not suffer from this issue by design. Furthermore, our method scales to high-dimensional image observations. Finally, we benchmark our approach on two widely used simulators, CARLA and MuJoCo, and it successfully alleviates the copycat problem and surpasses the existing solutions.
C.-C. Chuang and D. Yang—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argall, B.D., Chernova, S., Veloso, M.M., Browning, B.: A survey of robot learning from demonstration. Robot. Auton. Syst. 57(5), 469–483 (2009)
Bansal, M., Krizhevsky, A., Ogale, A.S.: Chauffeurnet: Learning to drive by imitating the best and synthesizing the worst. In: Bicchi, A., Kress-Gazit, H., Hutchinson, S. (eds.) Robotics: Science and Systems XV, University of Freiburg, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 22–26 June 2019 (2019)
Beery, S., Van Horn, G., Perona, P.: Recognition in terra incognita. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11220, pp. 472–489. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01270-0_28
Bojarski, M., et al.: End to end learning for self-driving cars. CoRR abs/1604.07316 (2016)
Brantley, K., Sun, W., Henaff, M.: Disagreement-regularized imitation learning. In: 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2020, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. OpenReview.net (2020)
Chen, D., Koltun, V., Krähenbühl, P.: Learning to drive from a world on rails. CoRR abs/2105.00636 (2021)
Chen, D., Zhou, B., Koltun, V., Krähenbühl, P.: Learning by cheating. In: Kaelbling, L.P., Kragic, D., Sugiura, K. (eds.) 3rd Annual Conference on Robot Learning, CoRL 2019, Osaka, Japan, October 30–November 1, 2019, Proceedings. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 100, pp. 66–75. PMLR (2019)
Codevilla, F., Müller, M., López, A.M., Koltun, V., Dosovitskiy, A.: End-to-end driving via conditional imitation learning. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2018, Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018, pp. 1–9. IEEE (2018)
Codevilla, F., Santana, E., López, A.M., Gaidon, A.: Exploring the limitations of behavior cloning for autonomous driving. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), October 27–November 2 2019, pp. 9328–9337. IEEE (2019)
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., López, A.M., Koltun, V.: CARLA: an open urban driving simulator. In: 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, CoRL 2017, Mountain View, California, USA, 13–15 November 2017, Proceedings. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 78, pp. 1–16. PMLR (2017)
Geirhos, R., et al.: Shortcut learning in deep neural networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2(11), 665–673 (2020)
Geirhos, R., Rubisch, P., Michaelis, C., Bethge, M., Wichmann, F.A., Brendel, W.: Imagenet-trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness. In: 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2019, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. OpenReview.net (2019)
Giusti, A., et al.: A machine learning approach to visual perception of forest trails for mobile robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 1(2), 661–667 (2016)
de Haan, P., Jayaraman, D., Levine, S.: Causal confusion in imitation learning. In: Wallach, H.M., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E.B., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32, Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, NeurIPS 2019, 8–14 December 2019, Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp. 11693–11704 (2019)
Heinze-Deml, C., Meinshausen, N.: Conditional variance penalties and domain shift robustness. Mach. Learn. 110(2), 303–348 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-020-05924-1
Ho, J., Ermon, S.: Generative adversarial imitation learning. In: Lee, D.D., Sugiyama, M., von Luxburg, U., Guyon, I., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 29, Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2016, December 5–10, 2016, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 4565–4573 (2016)
Hu, P., Huang, A., Dolan, J.M., Held, D., Ramanan, D.: Safe local motion planning with self-supervised freespace forecasting. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2021, virtual, 19–25 June 2021, pp. 12732–12741. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2021)
Laskey, M., Lee, J., Fox, R., Dragan, A.D., Goldberg, K.: DART: noise injection for robust imitation learning. In: 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, CoRL 2017, Mountain View, California, USA, 13–15 November 2017, Proceedings. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 78, pp. 143–156. PMLR (2017)
LeCun, Y., Muller, U., Ben, J., Cosatto, E., Flepp, B.: Off-road obstacle avoidance through end-to-end learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 18 [Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2005, 5–8 December 2005, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada], pp. 739–746 (2005)
Levine, S., Koltun, V.: Guided policy search. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2013, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, vol. 28, pp. 1–9. JMLR.org (2013)
Loquercio, A., Kaufmann, E., Ranftl, R., Dosovitskiy, A., Koltun, V., Scaramuzza, D.: Deep drone racing: From simulation to reality with domain randomization. IEEE Trans. Robot. 36(1), 1–14 (2020)
Mandlekar, A., et al.: What matters in learning from offline human demonstrations for robot manipulation. In: Faust, A., Hsu, D., Neumann, G. (eds.) Conference on Robot Learning, 8–11 November 2021, London, UK. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 164, pp. 1678–1690. PMLR (2021)
McCoy, T., Pavlick, E., Linzen, T.: Right for the wrong reasons: Diagnosing syntactic heuristics in natural language inference. In: Korhonen, A., Traum, D.R., Màrquez, L. (eds.) Proceedings of the 57th Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2019, Florence, Italy, July 28–August 2, 2019, Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 3428–3448. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
Minh, V., et al.: Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540), 529–533 (2015)
Mülling, K., Kober, J., Kroemer, O., Peters, J.: Learning to select and generalize striking movements in robot table tennis. Int. J. Robot. Res. 32(3), 263–279 (2013)
Murphy, K.: A survey of POMDP solution techniques. Environment 2, 1–12 (2000)
Niven, T., Kao, H.: Probing neural network comprehension of natural language arguments. In: Korhonen, A., Traum, D.R., Màrquez, L. (eds.) Proceedings of the 57th Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2019, Florence, Italy, July 28–August 2 2019, Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 4658–4664. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019)
Ohn-Bar, E., Prakash, A., Behl, A., Chitta, K., Geiger, A.: Learning situational driving. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020, pp. 11293–11302. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Osa, T., Pajarinen, J., Neumann, G., Bagnell, J.A., Abbeel, P., Peters, J.: An algorithmic perspective on imitation learning. CoRR abs/1811.06711 (2018)
Pomerleau, D.: ALVINN: an autonomous land vehicle in a neural network. In: Touretzky, D.S. (ed.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 1, [NIPS Conference, Denver, Colorado, USA, 1988], pp. 305–313. Morgan Kaufmann (1988)
Ross, S., Gordon, G.J., Bagnell, D.: A reduction of imitation learning and structured prediction to no-regret online learning. In: Gordon, G.J., Dunson, D.B., Dudík, M. (eds.) Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, AISTATS 2011, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 11–13 April 2011. JMLR Proceedings, vol. 15, pp. 627–635. JMLR.org (2011)
Schulman, J., Levine, S., Moritz, P., Jordan, M.I., Abbeel, P.: Trust region policy optimization. CoRR abs/1502.05477 (2015)
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., Klimov, O.: Proximal policy optimization algorithms. CoRR abs/1707.06347 (2017)
Spencer, J.C., Choudhury, S., Venkatraman, A., Ziebart, B.D., Bagnell, J.A.: Feedback in imitation learning: The three regimes of covariate shift. CoRR abs/2102.02872 (2021)
Sun, W., Bagnell, J.A., Boots, B.: Truncated horizon policy search: Combining reinforcement learning & imitation learning. In: 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2018, Vancouver, BC, Canada, April 30–May 3 2018, Conference Track Proceedings. OpenReview.net (2018)
Sun, W., Venkatraman, A., Gordon, G.J., Boots, B., Bagnell, J.A.: Deeply aggrevated: differentiable imitation learning for sequential prediction. In: Precup, D., Teh, Y.W. (eds.) Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2017, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 70, pp. 3309–3318. PMLR (2017)
Todorov, E., Erez, T., Tassa, Y.: MuJoCo: a physics engine for model-based control. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS 2012, Vilamoura, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012, pp. 5026–5033. IEEE (2012)
Wang, D., Devin, C., Cai, Q., Krähenbühl, P., Darrell, T.: Monocular plan view networks for autonomous driving. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS 2019, Macau, SAR, China, 3–8 November 2019, pp. 2876–2883. IEEE (2019)
Wen, C., Lin, J., Darrell, T., Jayaraman, D., Gao, Y.: Fighting copycat agents in behavioral cloning from observation histories. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2020, NeurIPS 2020, 6–12 December 2020, virtual (2020)
Wen, C., Lin, J., Qian, J., Gao, Y., Jayaraman, D.: Keyframe-focused visual imitation learning. In: Meila, M., Zhang, T. (eds.) Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, 18–24 July 2021, Virtual Event. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 139, pp. 11123–11133. PMLR (2021)
Wen, C., Qian, J., Lin, J., Teng, J., Jayaraman, D., Gao, Y.: Fighting fire with fire: avoiding DNN shortcuts through priming. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 23723–23750. PMLR (2022)
Widrow, B., Smith, F.W.: Pattern-recognizing control systems (1964)
Zhang, Z., Liniger, A., Dai, D., Yu, F., Gool, L.V.: End-to-end urban driving by imitating a reinforcement learning coach. CoRR abs/2108.08265 (2021)
Zhou, X., Koltun, V., Krähenbühl, P.: Tracking objects as points. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12349, pp. 474–490. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_28
Acknowledgement
We thank Jiaye Teng, Renhao Wang and Xiangyue Liu for insightful discussions and comments. This work is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the 2030 Innovation Megaprojects “Program on New Generation Artificial Intelligence" (Grant No. 2021AAA0150000), and a grant from the Guoqiang Institute, Tsinghua University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chuang, CC., Yang, D., Wen, C., Gao, Y. (2022). Resolving Copycat Problems in Visual Imitation Learning via Residual Action Prediction. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13699. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19842-7_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19842-7_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19841-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19842-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)