Abstract
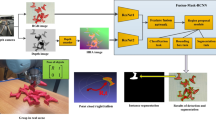
Instance segmentation with unseen objects is a challenging problem in unstructured environments. To solve this problem, we propose a robot learning approach to actively interact with novel objects and collect each object’s training label for further fine-tuning to improve the segmentation model performance, while avoiding the time-consuming process of manually labeling a dataset. Given a cluttered pile of objects, our approach chooses pushing and grasping motions to break the clutter and conducts object-agnostic grasping for which the Singulation-and-Grasping (SaG) policy takes as input the visual observations and imperfect segmentation. We decompose the problem into three subtasks: (1) the object singulation subtask aims to separate the objects from each other, which creates more space that alleviates the difficulty of (2) the collision-free grasping subtask; (3) the mask generation subtask obtains the self-labeled ground truth masks by using an optical flow-based binary classifier and motion cue post-processing for transfer learning. Our system achieves \(70\%\) singulation success rate in simulated cluttered scenes. The interactive segmentation of our system achieves \(87.8\%\), \(73.9\%\), and \(69.3\%\) average precision for toy blocks, YCB objects in simulation, and real-world novel objects, respectively, which outperforms the compared baselines. Please refer to our project page for more information: https://z.umn.edu/sag-interactive-segmentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boerdijk, W., Sundermeyer, M., Durner, M., Triebel, R.: Self-supervised object-in-gripper segmentation from robotic motions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04487 (2020)
Bohg, J.: Interactive perception: Leveraging action in perception and perception in action. IEEE Trans. Rob. 33(6), 1273–1291 (2017)
Byravan, A., Fox, D.: Se3-nets: Learning rigid body motion using deep neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 173–180. IEEE (2017)
Calli, B., Walsman, A., Singh, A., Srinivasa, S., Abbeel, P., Dollar, A.M.: Benchmarking in manipulation research: Using the yale-cmu-berkeley object and model set. IEEE Robotics Autom. Mag. 22(3), 36–52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/MRA.2015.2448951
Chaudhary, K., et al.: Retrieving unknown objects using robot in-the-loop based interactive segmentation. In: 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), pp. 75–80. IEEE (2016)
Chen, Y., Ju, Z., Yang, C.: Combining reinforcement learning and rule-based method to manipulate objects in clutter. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2020)
Coleman, T.F., Moré, J.J.: Estimation of sparse Jacobian matrices and graph coloring problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 20(1), 187–209 (1983)
Dave, A., Tokmakov, P., Ramanan, D.: Towards segmenting anything that moves. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Oct 2019
Deng, Y., et al.: Deep reinforcement learning for robotic pushing and picking in cluttered environment. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 619–626. IEEE (2019)
Eitel, A., Hauff, N., Burgard, W.: Self-supervised transfer learning for instance segmentation through physical interaction. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4020–4026. IEEE (2019)
Eitel, A., Hauff, N., Burgard, W.: Learning to singulate objects using a push proposal network. In: Amato, N.M., Hager, G., Thomas, S., Torres-Torriti, M. (eds.) Robotics Research. SPAR, vol. 10, pp. 405–419. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28619-4_32
Fang, K., Bai, Y., Hinterstoisser, S., Savarese, S., Kalakrishnan, M.: Multi-task domain adaptation for deep learning of instance grasping from simulation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3516–3523. IEEE (2018)
Fitzpatrick, P.: First contact: an active vision approach to segmentation. In: Proceedings 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No. 03CH37453), vol. 3, pp. 2161–2166. IEEE (2003)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.: Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2961–2969 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hermans, T., Rehg, J.M., Bobick, A.: Guided pushing for object singulation. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4783–4790. IEEE (2012)
Huang, B., Han, S.D., Boularias, A., Yu, J.: Dipn: Deep interaction prediction network with application to clutter removal. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4694–4701. IEEE (2021)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Ilg, E., Mayer, N., Saikia, T., Keuper, M., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T.: Flownet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2462–2470 (2017)
Kenney, J., Buckley, T., Brock, O.: Interactive segmentation for manipulation in unstructured environments. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1377–1382. IEEE (2009)
Kiatos, M., Malassiotis, S.: Robust object grasping in clutter via singulation. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1596–1600. IEEE (2019)
Kurenkov, A., et al.: Visuomotor mechanical search: Learning to retrieve target objects in clutter. In: 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 8408–8414. IEEE (2020)
Kuzmič, E.S., Ude, A.: Object segmentation and learning through feature grouping and manipulation. In: 2010 10th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, pp. 371–378. IEEE (2010)
Le Goff, L.K., Mukhtar, G., Le Fur, P.H., Doncieux, S.: Segmenting objects through an autonomous agnostic exploration conducted by a robot. In: 2017 First IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), pp. 284–291. IEEE (2017)
Liang, H., Lou, X., Yang, Y., Choi, C.: Learning visual affordances with target-orientated deep q-network to grasp objects by harnessing environmental fixtures. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2562–2568. IEEE (2021)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Mnih, V., et al.: Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540), 529 (2015)
O Pinheiro, P.O., Collobert, R., Dollár, P.: Learning to segment object candidates. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28 (2015)
Pathak, D., et al.: Learning instance segmentation by interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 2042–2045 (2018)
Rohmer, E., Singh, S.P., Freese, M.: V-rep: A versatile and scalable robot simulation framework. In: 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1321–1326. IEEE (2013)
Russakovsky, O., et al.: Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision 115(3), 211–252 (2015)
Sarantopoulos, I., Kiatos, M., Doulgeri, Z., Malassiotis, S.: Split deep q-learning for robust object singulation. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 6225–6231. IEEE (2020)
Schiebener, D., Ude, A., Asfour, T.: Physical interaction for segmentation of unknown textured and non-textured rigid objects. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4959–4966. IEEE (2014)
Spelke, E.S.: Principles of object perception. Cogn. Sci. 14(1), 29–56 (1990)
Wu, Y., Kirillov, A., Massa, F., Lo, W.Y., Girshick, R.: Detectron2. https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2 (2019)
Xie, C., Xiang, Y., Mousavian, A., Fox, D.: The best of both modes: Separately leveraging rgb and depth for unseen object instance segmentation. In: Conference on Robot Learning, pp. 1369–1378. PMLR (2020)
Xie, C., Xiang, Y., Mousavian, A., Fox, D.: Unseen object instance segmentation for robotic environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 1–17 (2021)
Xu, K., Yu, H., Lai, Q., Wang, Y., Xiong, R.: Efficient learning of goal-oriented push-grasping synergy in clutter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 6(4), 6337–6344 (2021)
Yang, Y., Liang, H., Choi, C.: A deep learning approach to grasping the invisible. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(2), 2232–2239 (2020)
Zeng, A., Song, S., Welker, S., Lee, J., Rodriguez, A., Funkhouser, T.: Learning synergies between pushing and grasping with self-supervised deep reinforcement learning. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4238–4245. IEEE (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Sony Research Award Program and NSF Award 2143730.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yu, H., Choi, C. (2022). Self-supervised Interactive Object Segmentation Through a Singulation-and-Grasping Approach. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13699. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19842-7_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19842-7_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19841-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19842-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)