Abstract
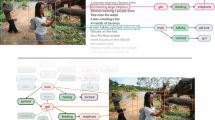
General Purpose Vision (GPV) systems are models that are designed to solve a wide array of visual tasks without requiring architectural changes. Today, GPVs primarily learn both skills and concepts from large fully supervised datasets. Scaling GPVs to tens of thousands of concepts by acquiring data to learn each concept for every skill quickly becomes prohibitive. This work presents an effective and inexpensive alternative: learn skills from supervised datasets, learn concepts from web image search, and leverage a key characteristic of GPVs: the ability to transfer visual knowledge across skills. We use a dataset of 1M+ images spanning 10k+ visual concepts to demonstrate webly-supervised concept expansion for two existing GPVs (GPV-1 and VL-T5) on 3 benchmarks: 5 Coco-based datasets (80 primary concepts), a newly curated series of 5 datasets based on the OpenImages and VisualGenome repositories (\(\sim \)500 concepts), and the Web-derived dataset (10k+ concepts). We also propose a new architecture, GPV-2 that supports a variety of tasks — from vision tasks like classification and localization to vision+language tasks like QA and captioning, to more niche ones like human-object interaction detection. GPV-2 benefits hugely from web data and outperforms GPV-1 and VL-T5 across these benchmarks. Our data, code, and web demo are available at https://prior.allenai.org/projects/gpv2.
A. Kamath, C. Clark and T. Gupta—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Since [24] takes a long time to train when using the web data (over 3 weeks), results for GPV-1 with and without web data are reported after 20 epochs training.
References
Agrawal, H., et al.: Nocaps: novel object captioning at scale. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8947–8956 (2019)
Anderson, P., et al.: Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6077–6086 (2018)
Antol, S., et al.: VQA: visual question answering. In: ICCV (2015)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. ArXiv arXiv:2005.14165 (2020)
Brysbaert, M., Warriner, A., Kuperman, V.: Concreteness ratings for 40 thousand generally known English word lemmas. Behav. Res. Methods 46(3), 904–911 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-013-0403-5
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. ECCV arXiv:2005.12872 (2020)
Chao, Y.W., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Zeng, H., Deng, J.: Learning to detect human-object interactions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (2018)
Chao, Y.W., Wang, Z., He, Y., Wang, J., Deng, J.: HICO: a benchmark for recognizing human-object interactions in images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Chen, H., Gallagher, A., Girod, B.: Describing clothing by semantic attributes. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7574, pp. 609–623. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33712-3_44
Chen, X., Gupta, A.: Webly supervised learning of convolutional networks. In: ICCV (2015)
Chen, X., Shrivastava, A., Gupta, A.: NEIL: extracting visual knowledge from web data. In: ICCV (2013)
Chen, Y.C., et al.: Uniter: learning universal image-text representations. ArXiv arXiv:1909.11740 (2019)
Cho, J., Lei, J., Tan, H., Bansal, M.: Unifying vision-and-language tasks via text generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.02779 (2021)
Divvala, S., Farhadi, A., Guestrin, C.: Learning everything about anything: webly-supervised visual concept learning. In: CVPR (2014)
Dong, W., Socher, R., Li-Jia, L., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16 \(\times \) 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ICLR arXiv:2010.11929 (2021)
Fang, H., Xie, Y., Shao, D., Lu, C.: Dirv: dense interaction region voting for end-to-end human-object interaction detection. In: AAAI (2021)
Farhadi, A., Endres, I., Hoiem, D., Forsyth, D.A.: Describing objects by their attributes. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1778–1785 (2009)
Fergus, R., Fei-Fei, L., Perona, P., Zisserman, A.: Learning object categories from Google’s image search. In: Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2005) Volume 1 2, vol. 2, pp. 1816–1823 (2005)
Golge, E., Duygulu, P.: ConceptMap: mining noisy web data for concept learning. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8695, pp. 439–455. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_29
Goyal, Y., Khot, T., Summers-Stay, D., Batra, D., Parikh, D.: Making the V in VQA matter: elevating the role of image understanding in Visual Question Answering. In: CVPR (2017)
Gu, X., Lin, T.Y., Kuo, W., Cui, Y.: Open-vocabulary object detection via vision and language knowledge distillation (2021)
Guo, S., et al.: Curriculumnet: weakly supervised learning from large-scale web images. ArXiv arXiv:1808.01097 (2018)
Gupta, T., Kamath, A., Kembhavi, A., Hoiem, D.: Towards general purpose vision systems: an end-to-end task-agnostic vision-language architecture. In: CVPR (2022)
Gupta, T., Marten, R., Kembhavi, A., Hoiem, D.: Grit: general robust image task benchmark. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.13653 (2022)
Gupta, T., Schwing, A.G., Hoiem, D.: No-frills human-object interaction detection: factorization, layout encodings, and training techniques. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 9676–9684 (2019)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollar, P., Girshick, R.: Mask R-CNN. In: ICCV (2017)
Hoffman, J., et al.: LSDA: large scale detection through adaptation. In: NIPS (2014)
Jaegle, A., et al.: Perceiver IO: a general architecture for structured inputs & outputs. ArXiv arXiv:2107.14795 (2021)
Jaegle, A., Gimeno, F., Brock, A., Zisserman, A., Vinyals, O., Carreira, J.: Perceiver: general perception with iterative attention. In: ICML (2021)
Jia, C., et al.: Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In: ICML (2021)
Jin, B., Segovia, M.V.O., Süsstrunk, S.: Webly supervised semantic segmentation. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1705–1714 (2017)
Kim, B., Lee, J., Kang, J., Kim, E.S., Kim, H.J.: HOTR: end-to-end human-object interaction detection with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Kim, W., Son, B., Kim, I.: ViLT: vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. ArXiv arXiv:2102.03334 (2021)
Krause, J., et al.: The unreasonable effectiveness of noisy data for fine-grained recognition. ArXiv arXiv:1511.06789 (2016)
Krishna, R., et al.: Visual genome: connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. IJCV 123, 32–73 (2017)
Kumar, N., Berg, A.C., Belhumeur, P.N., Nayar, S.K.: Attribute and simile classifiers for face verification. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 365–372 (2009)
Kuznetsova, A., et al.: The Open Images Dataset V4: unified image classification, object detection, and visual relationship detection at scale. arXiv:1811.00982 (2018)
Lampert, C.H., Nickisch, H., Harmeling, S.: Learning to detect unseen object classes by between-class attribute transfer. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 951–958 (2009)
Li, L.J., Fei-Fei, L.: Optimol: automatic online picture collection via incremental model learning. Int. J. Comput. Vision 88, 147–168 (2007)
Li, L.H., Yatskar, M., Yin, D., Hsieh, C., Chang, K.W.: Visualbert: a simple and performant baseline for vision and language. ArXiv arXiv:1908.03557 (2019)
Li, Q., Wu, J., Tu, Z.: Harvesting mid-level visual concepts from large-scale internet images. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 851–858 (2013)
Li, X., et al.: Oscar: object-semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12375, pp. 121–137. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58577-8_8
Liang, K., Guo, Y., Chang, H., Chen, X.: Visual relationship detection with deep structural ranking. In: AAAI (2018)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. ICCV arXiv:2103.14030 (2021)
Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., Lee, S.: Vilbert: pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Lu, J., Goswami, V., Rohrbach, M., Parikh, D., Lee, S.: 12-in-1: multi-task vision and language representation learning. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10434–10443 (2020)
Lu, J., Goswami, V., Rohrbach, M., Parikh, D., Lee, S.: 12-in-1: multi-task vision and language representation learning. In: CVPR (2020)
Luo, A., Li, X., Yang, F., Jiao, Z., Cheng, H.: Webly-supervised learning for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 103, 107308 (2020)
van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.E.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008)
McCann, B., Keskar, N., Xiong, C., Socher, R.: The natural language decathlon: multitask learning as question answering. ArXiv arXiv:1806.08730 (2018)
Niu, L., Tang, Q., Veeraraghavan, A., Sabharwal, A.: Learning from noisy web data with category-level supervision. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7689–7698 (2018)
Niu, L., Veeraraghavan, A., Sabharwal, A.: Webly supervised learning meets zero-shot learning: a hybrid approach for fine-grained classification. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7171–7180 (2018)
Parikh, D., Grauman, K.: Relative attributes. In: 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 503–510 (2011)
Patterson, G., Hays, J.: Sun attribute database: discovering, annotating, and recognizing scene attributes. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2751–2758 (2012)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision (2021)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: ICML (2021)
Raffel, C., et al.: Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 21, 140:1-140:67 (2020)
Ramakrishnan, S., Agrawal, A., Lee, S.: Overcoming language priors in visual question answering with adversarial regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.03649 (2018)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolo9000: better, faster, stronger. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 6517–6525 (2017)
Sharma, P., Ding, N., Goodman, S., Soricut, R.: Conceptual captions: a cleaned, hypernymed, image alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning. In: ACL (2018)
Shen, S., et al.: How much can clip benefit vision-and-language tasks? ArXiv arXiv:2107.06383 (2021)
Shen, T., Lin, G., Shen, C., Reid, I.D.: Bootstrapping the performance of webly supervised semantic segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1363–1371 (2018)
Shen, Y., et al.: Noise-aware fully webly supervised object detection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11323–11332 (2020)
Sun, G., Wang, W., Dai, J., Van Gool, L.: Mining cross-image semantics for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12347, pp. 347–365. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_21
Tan, H.H., Bansal, M.: Lxmert: learning cross-modality encoder representations from transformers. In: EMNLP/IJCNLP (2019)
Uijlings, J.R.R., Popov, S., Ferrari, V.: Revisiting knowledge transfer for training object class detectors. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1101–1110 (2018)
Ulutan, O., Iftekhar, A.S.M., Manjunath, B.S.: Vsgnet: spatial attention network for detecting human object interactions using graph convolutions. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13614–13623 (2020)
Vedantam, R., Zitnick, C.L., Parikh, D.: Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) pp. 4566–4575 (2015)
Vijayanarasimhan, S., Grauman, K.: Keywords to visual categories: multiple-instance learning forweakly supervised object categorization. In: 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Wang, S., Thompson, L., Iyyer, M.: Phrase-Bert: improved phrase embeddings from Bert with an application to corpus exploration. In: EMNLP (2021)
Wang, S., Joo, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, S.C.: Weakly supervised learning for attribute localization in outdoor scenes. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3111–3118 (2013)
Wang, X.J., Zhang, L., Li, X., Ma, W.Y.: Annotating images by mining image search results. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 30, 1919–1932 (2008)
Whitehead, S., Wu, H., Ji, H., Feris, R.S., Saenko, K., MIT-IBM, U.: Separating skills and concepts for novel visual question answering. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5628–5637 (2021)
Wu, Z., Tao, Q., Lin, G., Cai, J.: Exploring bottom-up and top-down cues with attentive learning for webly supervised object detection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 12933–12942 (2020)
Xu, H., Yan, M., Li, C., Bi, B., Huang, S., Xiao, W., Huang, F.: E2E-VLP: end-to-end vision-language pre-training enhanced by visual learning (2021)
YANG, J., et al.: Webly supervised image classification with self-contained confidence. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12353, pp. 779–795. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58598-3_46
Yatskar, M., Zettlemoyer, L., Farhadi, A.: Situation recognition: visual semantic role labeling for image understanding. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5534–5542 (2016)
Zareian, A., Rosa, K.D., Hu, D.H., Chang, S.F.: Open-vocabulary object detection using captions. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 14388–14397 (2021)
Zhang, A., et al.: Mining the benefits of two-stage and one-stage hoi detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.05077 (2021)
Zhang, P., et al.: Vinvl: making visual representations matter in vision-language models. ArXiv arXiv:2101.00529 (2021)
Zheng, W., Yan, L., Gou, C., Wang, F.: Webly supervised knowledge embedding model for visual reasoning. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) pp. 12442–12451 (2020)
Zhong, X., Ding, C., Qu, X., Tao, D.: Polysemy deciphering network for human-object interaction detection. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12365, pp. 69–85. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58565-5_5
Zou, C., et al.: End-to-end human object interaction detection with hoi transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by ONR award N00014-21-1-2705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kamath, A., Clark, C., Gupta, T., Kolve, E., Hoiem, D., Kembhavi, A. (2022). Webly Supervised Concept Expansion for General Purpose Vision Models. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13696. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20059-5_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20059-5_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20058-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20059-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)