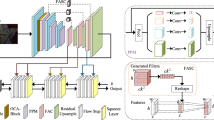
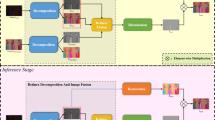
Abstract
Night photography typically suffers from both low light and blurring issues due to the dim environment and the common use of long exposure. While existing light enhancement and deblurring methods could deal with each problem individually, a cascade of such methods cannot work harmoniously to cope well with joint degradation of visibility and sharpness. Training an end-to-end network is also infeasible as no paired data is available to characterize the coexistence of low light and blurs. We address the problem by introducing a novel data synthesis pipeline that models realistic low-light blurring degradations, especially for blurs in saturated regions, e.g., light streaks, that often appear in the night images. With the pipeline, we present the first large-scale dataset for joint low-light enhancement and deblurring. The dataset, LOL-Blur, contains 12,000 low-blur/normal-sharp pairs with diverse darkness and blurs in different scenarios. We further present an effective network, named LEDNet, to perform joint low-light enhancement and deblurring. Our network is unique as it is specially designed to consider the synergy between the two inter-connected tasks. Both the proposed dataset and network provide a foundation for this challenging joint task. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan, K.C., Zhou, S., Xu, X., Loy, C.C.: Investigating tradeoffs in real-world video super-resolution. In: CVPR (2022)
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Do, M.N., Koltun, V.: Seeing motion in the dark. In: ICCV (2019)
Chen, C., Chen, Q., Xu, J., Koltun, V.: Learning to see in the dark. In: CVPR (2018)
Chen, L., Fang, F., Zhang, J., Liu, J., Zhang, G.: OID: outlier identifying and discarding in blind image deblurring. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12370, pp. 598–613. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58595-2_36
Chen, L., Zhang, J., Lin, S., Fang, F., Ren, J.S.: Blind deblurring for saturated images. In: CVPR (2021)
Chen, L., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Lin, S., Fang, F., Ren, J.S.: Learning a non-blind deblurring network for night blurry images. In: CVPR (2021)
Cho, S.J., Ji, S.W., Hong, J.P., Jung, S.W., Ko, S.J.: Rethinking coarse-to-fine approach in single image deblurring. In: CVPR (2021)
Gong, D., et al.: From motion blur to motion flow: a deep learning solution for removing heterogeneous motion blur. In: CVPR (2017)
Guo, C., et al.: Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In: CVPR (2020)
Hu, X., et al.: Pyramid architecture search for real-time image deblurring. In: ICCV (2021)
Hu, Z., Cho, S., Wang, J., Yang, M.H.: Deblurring low-light images with light streaks. In: CVPR (2014)
Jiang, H., Zheng, Y.: Learning to see moving objects in the dark. In: ICCV (2019)
Jiang, Y., et al.: EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision. TIP 30, 2340–2349 (2021)
Ke, J., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Milanfar, P., Yang, F.: MUSIQ: multi-scale image quality transformer. In: ICCV (2021)
Kupyn, O., Budzan, V., Mykhailych, M., Mishkin, D., Matas, J.: DeblurGAN: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Kupyn, O., Martyniuk, T., Wu, J., Wang, Z.: DeblurGAN-V2: deblurring (orders-of-magnitude) faster and better. In: CVPR (2019)
Li, C., et al.: Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: a survey. arXiv:2104.10729 (2021)
Li, C., Guo, C., Loy, C.C.: Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(8), 4225–4238 (2022)
Li, D., et al.: ARVo: learning all-range volumetric correspondence for video deblurring. In: CVPR (2021)
Li, X., Chen, C., Zhou, S., Lin, X., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: Blind face restoration via deep multi-scale component dictionaries. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12354, pp. 399–415. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_23
Liu, J., Xu, D., Yang, W., Fan, M., Huang, H.: Benchmarking low-light image enhancement and beyond. IJCV 129(4), 1153–1184 (2021)
Liu, R., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In: CVPR (2021)
Lore, K.G., Akintayo, A., Sarkar, S.: LLNet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recogn. 61, 650–662 (2017)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: SGDR: stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv:1608.03983 (2016)
Lv, F., Lu, F., Wu, J., Lim, C.: MBLLEN: low-light image/video enhancement using CNNs. In: BMVC (2018)
Ma, C., Yang, C.Y., Yang, X., Yang, M.H.: Learning a no-reference quality metric for single-image super-resolution. CVIU 158, 1–16 (2017)
Maggioni, M., Boracchi, G., Foi, A., Egiazarian, K.: Video denoising, deblocking, and enhancement through separable 4-D nonlocal spatiotemporal transforms. TIP 21(9), 3952–3966 (2012)
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A.C.: Making a “completely blind’’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(3), 209–212 (2012)
Nah, S., et al.: NTIRE 2019 challenge on video deblurring and super-resolution: Dataset and study. In: CVPRW (2019)
Nah, S., Hyun Kim, T., Mu Lee, K.: Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring. In: CVPR (2017)
Niklaus, S., Mai, L., Liu, F.: Video frame interpolation via adaptive separable convolution. In: ICCV (2017)
Rim, J., Lee, H., Won, J., Cho, S.: Real-world blur dataset for learning and benchmarking deblurring algorithms. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12370, pp. 184–201. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58595-2_12
Shen, Z., et al.: Human-aware motion deblurring. In: ICCV (2019)
Su, S., Delbracio, M., Wang, J., Sapiro, G., Heidrich, W., Wang, O.: Deep video deblurring for hand-held cameras. In: CVPR (2017)
Sun, J., Cao, W., Xu, Z., Ponce, J.: Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal. In: CVPR (2015)
Tao, X., Gao, H., Shen, X., Wang, J., Jia, J.: Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring. In: CVPR (2018)
Wang, R., Xu, X., Fu, C.W., Lu, J., Yu, B., Jia, J.: Seeing dynamic scene in the dark: a high-quality video dataset with mechatronic alignment. In: CVPR (2021)
Wang, R., Zhang, Q., Fu, C.W., Shen, X., Zheng, W.S., Jia, J.: Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In: CVPR (2019)
Wang, X., Xie, L., Dong, C., Shan, Y.: Real-ESRGAN: training real-world blind super-resolution with pure synthetic data. In: ICCVW (2021)
Wang, X., et al.: ESRGAN: enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In: Leal-Taixé, L., Roth, S. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11133, pp. 63–79. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11021-5_5
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., Liu, J.: Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. In: BMVC (2018)
Yang, W., Wang, S., Fang, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, J.: From fidelity to perceptual quality: a semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement. In: CVPR (2020)
Yang, W., Wang, W., Huang, H., Wang, S., Liu, J.: Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. TIP 30, 2072–2086 (2021)
Zamir, S.W., et al.: CycleISP: real image restoration via improved data synthesis. In: CVPR (2020)
Zamir, S.W., et al.: Learning enriched features for real image restoration and enhancement. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12370, pp. 492–511. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58595-2_30
Zamir, S.W., et al.: Multi-stage progressive image restoration. In: CVPR (2021)
Zhang, H., Dai, Y., Li, H., Koniusz, P.: Deep stacked hierarchical multi-patch network for image deblurring. In: CVPR (2019)
Zhang, J., et al.: Dynamic scene deblurring using spatially variant recurrent neural networks. In: CVPR (2018)
Zhang, K., Liang, J., Van Gool, L., Timofte, R.: Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution. In: ICCV (2021)
Zhang, K., et al.: Deblurring by realistic blurring. In: CVPR (2020)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A., Shechtman, E., Wang, O.: The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In: CVPR (2018)
Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Ma, J., Liu, W., Zhang, J.: Beyond brightening low-light images. IJCV 129(4), 1013–1037 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Guo, X.: Kindling the darkness: a practical low-light image enhancer. In: ACM MM (2019)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR (2017)
Zheng, C., Shi, D., Shi, W.: Adaptive unfolding total variation network for low-light image enhancement. In: CVPR (2021)
Zhou, S., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Xie, H., Zuo, W., Ren, J.: Spatio-temporal filter adaptive network for video deblurring. In: ICCV (2019)
Zhou, S., Zhang, J., Zuo, W., Xie, H., Pan, J., Ren, J.S.: DAVANet: stereo deblurring with view aggregation. In: CVPR (2019)
Acknowledgment
This study is supported under the RIE2020 Industry Alignment Fund - Industry Collaboration Projects (IAF-ICP) Funding Initiative, as well as cash and in-kind contribution from the industry partner(s).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhou, S., Li, C., Change Loy, C. (2022). LEDNet: Joint Low-Light Enhancement and Deblurring in the Dark. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13666. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20068-7_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20068-7_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20067-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20068-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)