Abstract
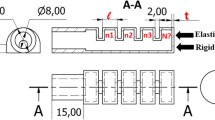
Soft robotic systems are ideally suited for adaptive bioinspired grippers due to their intrinsic properties. The advent of flexible 3D printing materials has made soft robotic actuator designs that were previously difficult or impossible to produce now implementable. In this study, we present an application-oriented comparison of the suitability for the printing of pneumatic actuators of two state-of-the-art 3D printing processes for flexible material, fused deposition modeling (FDM) and material jetting (PolyJet). While the FDM method affects the actuator designs, e.g., by the lack of practicable support material for flexible materials and its nozzle size, PolyJet uses support material but requires a design that allows the removal of it afterward. To compare how the two 3D printer technologies are suited for fabricating bending actuators, we have developed a pneumatic mono-material bending actuator that meets the design requirements to be printed with both printers. The design process itself and the characterization by bending angle and torque provided information about which design concepts could be better implemented with which method. The PolyJet process seems more suited for pneumatic actuators with large chambers and complex overhangs that show a sensitive response in the bending angle, but have low robustness. In contrast, the FDM method appears more suited for actuators with small chambers and complex geometries that feature high robustness and higher absolute tip force. These results form the basis for translating new inspirations from the elastic movements of living nature into our actuators by fully exploiting the advantages of each additive manufacturing process.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kovacs, G., Düring, L., Michel, S., Terrasi, G.: Stacked dielectric elastomer actuator for tensile force transmission. Sens. Actuators, A 155, 299–307 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2009.08.027
Wani, O.M., Zeng, H., Priimagi, A.: A light-driven artificial flytrap. Nat. Commun. 8, 15546 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15546
Kim, S., Laschi, C., Trimmer, B.: Soft robotics: a bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 31(5), 287–294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.03.002
Wei, Y., et al.: A novel, variable stiffness robotic gripper based on integrated soft actuating and particle jamming. Soft Rob. 3(3), 134–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2016.0027
Sun, Y., Liu, Y., Lueth, T.C.: Optimization of stress distribution in tendon-driven continuum robots using fish-tail-inspired method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7(2), 3380–3387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2022.3147456
Wehner, M., et al.: An integrated design and fabrication strategy for entirely soft, autonomous robots. Nature 536(7617), 451–455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19100
Gorissen, B., Reynaerts, D., Konishi, S., Yoshida, K., Kim, J.-W., Volder, M.: Elastic inflatable actuators for soft robotic applications. Adv. Mater. 29, 1604977 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201604977
Sun, T., Chen, Y., Han, T., Jiao, C., Lian, B., Song, Y.: A soft gripper with variable stiffness inspired by pangolin scales, toothed pneumatic actuator and autonomous controller. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 61(2020), 101848 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101848
Esser, F., Steger, T., Bach, D., Masselter, T., Speck, T.: Development of novel foam-based soft robotic ring actuators for a biomimetic peristaltic pumping system. In: Mangan, M., Cutkosky, M., Mura, A., Verschure, P.F.M.J., Prescott, T., Lepora, N. (eds.) Living Machines 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10384, pp. 138–147. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63537-8_12
Esser, F., Krüger, F., Masselter, T., Speck, T.: Development and characterization of a novel biomimetic peristaltic pumping system with flexible silicone-based soft robotic ring actuators. In: Vouloutsi, V., Halloy, J., Mura, A., Mangan, M., Lepora, N., Prescott, T.J., Verschure, P.F.M.J. (eds.) Living Machines 2018. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10928, pp. 157–167. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95972-6_17
Esser, F., Krüger, F., Masselter, T., Speck, T.: Characterization of biomimetic peristaltic pumping system based on flexible silicone soft robotic actuators as an alternative for technical pumps. In: Martinez-Hernandez, U., et al. (eds.) Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems: 8th International Conference, Living Machines 2019, Nara, Japan, proceedings, vol. 11556, pp. 101–113. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24741-6_9
Agerholm, M., Lord, A.: The “artificial muscle” of McKibben. The Lancet 277(7178), 660–661 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(61)91676-2
Schulte, Jr. H.F.: The characteristics of the McKibben artificial muscle. The application of external power in prosthetics and orthotics, pp. 94–115. National Academy of Sciences - National Research Council, Washington, DC (1961)
Temirel, M., Yenilmez, B., Knowlton, S., Walker, J., Joshi, A., Tasoglu, S.: Three-dimensional-printed carnivorous plant with snap trap. 3D Printing Addit. Manuf. 3(4), 244–251 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/3dp.2016.0036
Schaffner, M., Faber, J.A., Pianegonda, L., Rühs, P.A., Coulter, F., Studart, A.R.: 3D printing of robotic soft actuators with programmable bioinspired architectures. Nat. Commun. 9(1), 878 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03216-w
Geer, R., Iannucci, S., Li, S.: Pneumatic coiling actuator inspired by the awns of Erodium cicutarium. Front. Robot. AI 7(7), 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2020.00017
Ilievski, F., Mazzeo, A.D., Shepherd, R.F., Chen, X., Whitesides, G.M.: Soft robotics for chemists. Angew. Chem. 123(8), 1930–1935 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201006464
Demir, K.G., Zhang, Z., Yang, J., Gu, G.X.: Computational and experimental design exploration of 3D-printed soft pneumatic actuators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2(7), 2070072 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202070072
Polygerinos, P., et al.: Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation. In: 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1512–1517. IEEE, Tokyo, Japan (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696549
Herianto, W.I., Ritonga, A.S., Prastowo, A.: Design and fabrication in the loop of soft pneumatic actuators using fused deposition modelling. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 298, 111556 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.111556
Hu, W., Alici, G.: Bioinspired three-dimensional-printed helical soft pneumatic actuators and their characterization. Soft Rob. 7(3), 267–282 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2019.0015
Moseley, P., Florez, J.M., Sonar, H.A., Agarwal, G., Curtin, W., Paik, J.: Modeling, design, and development of soft pneumatic actuators with finite element method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 18(6), 978–988 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201500503
Sun, Y., Song, Y.S., Paik, J.: Characterization of silicone rubber based soft pneumatic actuators. In: 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4446–4453. IEEE (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696995
Sun, Y., et al.: Stiffness customization and patterning for property modulation of silicone-based soft pneumatic actuators. Soft Rob. 4(3), 251–260 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2016.0047
Rus, D., Tolley, M.T.: Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 521(7553), 467–475 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14543
Wallin, T.J., Pikul, J., Shepherd, R.F.: 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3(6), 84–100 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-018-0002-2
Keneth, E.S., Kamyshny, A., Totaro, M., Beccai, L., Magdassi, S.: 3D Printing materials for soft robotics. Adv. Mater. Spec. Issue: Soft Robot. 33(19), 2003387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202003387
Tebyani, M., et al.: 3D Printing an assembled biomimetic robotic finger. In: 2020 17th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), pp. 526–532. IEEE (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/UR49135.2020.9144774
Shih, B., et al.: Design considerations for 3D printed, soft, multimaterial resistive sensors for soft robotics. Front. Robot. AI 6, 30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2019.00030
Conrad, S., Speck, T., Tauber, F.J.: Multi-material 3D-printer for rapid prototyping of bio-inspired soft robotic elements. In: Vouloutsi, V., Mura, A., Tauber, F.J., Speck, T., Prescott, T.J., Verschure, P.F.M.J. (eds.) Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems: Living Machines 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol. 12413, pp. 46–54. Springer, Cham. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64313-3_6
Conrad, S., Speck, T., Tauber, F.J.: Tool changing 3D printer for rapid prototyping of advanced soft robotic elements. Bioinspir. Biomim. 16(5), 055010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-3190/ac095a
Low, Z.-X., Chua, Y.T., Ray, B.M., Mattia, D., Metcalfe, I.S., Patterson, D.A.: Perspective on 3D printing of separation membranes and comparison to related unconventional fabrication techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 523, 596–613 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.10.006
Kluska, E., Gruda, P., Majca-Nowak, N.: The Accuracy and the printing resolution comparison of different 3D printing technologies. Trans. Aerosp. Res. 3(252), 69–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2478/tar-2018-0023
Maurya, N.K., Rastogi, V., Singh, P.: Comparative study and measurement of form errors for the component printed by FDM and PolyJet process. Instrum. Mesure Métrologie 18(4), 353–359 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18280/i2m.180404
Lee, K.-Y., et al.: Accuracy of three-dimensional printing for manufacturing replica teeth. Korean J. Orthod. 45(5), 217–225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2015.45.5.217
Dorweiler, B., Baqué, P.E., Chaban, R., Ghazy, A., Salem, O.: Quality control in 3D printing: accuracy analysis of 3D-printed models of patient-specific anatomy. Materials 14(4), 1021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041021
Yap, Y.L., Sing, S.L., Yeong, W.Y.: A review of 3D printing processes and materials for soft robotics. RPJ 26(8), 1345–1361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-11-2019-0302
Bass, L., Meisel, N.A., Williams, C.B.: Exploring variability of orientation and aging effects in material properties of multi-material jetting parts. Rapid Prototyping J. 22, 826–834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-11-2015-0169
Zatopa, A., Walker, S., Menguc, Y.: Fully soft 3D-printed electroactive fluidic valve for soft hydraulic robots. Soft Rob. 5(3), 258–271 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2017.0019
Bartlett, N.W., et al.: A 3D-printed, functionally graded soft robot powered by combustion. Science 349(6244), 161–165 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab0129
Zhang, Y.-F., et al.: Fast-response, stiffness-tunable soft actuator by hybrid multimaterial 3D printing. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(15), 1806698 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201806698
Funding
Funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) under Germany’s Excellence Strategy – EXC-2193/1-390951807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kappel, P., Kramp, C., Speck, T., Tauber, F.J. (2022). Application-Oriented Comparison of Two 3D Printing Processes for the Manufacture of Pneumatic Bending Actuators for Bioinspired Macroscopic Soft Gripper Systems. In: Hunt, A., et al. Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems. Living Machines 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13548. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20470-8_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20470-8_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20469-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20470-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)