Abstract
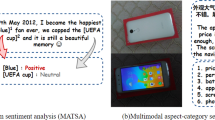
The goal of multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis is to comprehensively utilize data from different modalities (e.g.,, text and image) to identify aspect-specific sentiment polarity. Existing works have proposed many methods for fusing text and image information and achie-ved satisfactory results. However, they fail to filter noise in the image information and ignore the progressive learning process of sentiment features. To solve these problems, we propose an interactive fusion network with recurrent attention. Specifically, we first use two encoders to encode text and image data, respectively. Then we use the attention mechanism to obtain the semantic information of the image at the token level. Next, we employ GRU to filter out the noise in the image and fuse information from different modalities. Finally, we design a decoder with recurrent attention to progressively learn aspect-specific sentiment features for classification. The results on two Twitter datasets show that our method outperforms all baselines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The source code is publicly released at https://github.com/0wj0/IFNRA.
- 2.
We create an instance of GRU cell for each time step.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
References
Anderson, P., et al.: Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: Proceedings of CVPR, pp. 6077–6086 (2018). https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Anderson_Bottom-Up_and_Top-Down_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf
Cho, K., van Merriënboer, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 1724–1734 (2014). https://aclanthology.org/D14-1179.pdf
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of NAACL, pp. 4171–4186 (2019). https://aclanthology.org/N19-1423/
Dong, L., Wei, F., Tan, C., Tang, D., Zhou, M., Xu, K.: Adaptive recursive neural network for target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of ACL, pp. 49–54 (2014). https://aclanthology.org/P14-2009.pdf
Fan, F., Feng, Y., Zhao, D.: Multi-grained attention network for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 3433–3442 (2018). https://aclanthology.org/D18-1380/?ref=githubhelp.com
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016). https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2016/papers/He_Deep_Residual_Learning_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf
Jiang, L., Yu, M., Zhou, M., Liu, X., Zhao, T.: Target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of ACL, pp. 151–160 (2011). https://aclanthology.org/P11-1016.pdf
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of ICLR (Poster) (2015). https://openreview.net/forum?id=8gmWwjFyLj
Kiritchenko, S., Zhu, X., Cherry, C., Mohammad, S.: NRC-Canada-2014: detecting aspects and sentiment in customer reviews. In: Proceedings of SemEval, pp. 437–442 (2014). https://aclanthology.org/S14-2076.pdf
Mohammad, S., Kiritchenko, S., Zhu, X.: NRC-Canada: building the state-of-the-art in sentiment analysis of tweets. In: Proceedings of SemEval, pp. 321–327 (2013). https://aclanthology.org/S13-2053.pdf
Nguyen, D.Q., Vu, T., Nguyen, A.T.: BERTweet: a pre-trained language model for English Tweets. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 9–14 (2020). https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2.pdf
Phan, M.H., Ogunbona, P.O.: Modelling context and syntactical features for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of ACL, pp. 3211–3220 (2020). https://aclanthology.org/2020.acl-main.293/?ref=githubhelp.com
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: NIPS 28 (2015)
Tang, D., Qin, B., Feng, X., Liu, T.: Effective LSTMs for target-dependent sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of COLING, pp. 3298–3307 (2016). https://aclanthology.org/C16-1311/?ref=githubhelp.com
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NIPS 30 (2017). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf
Wagner, J., et al.: DCU: aspect-based polarity classification for Semeval task 4. In: Proceedings of COLING, pp. 223–229 (2014). https://aclanthology.org/S14-2.pdf#page=243
Wang, J., et al.: Aspect sentiment classification with both word-level and clause-level attention networks. In: Proceedings of IJCAI, vol. 2018, pp. 4439–4445 (2018). www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2018/0617.pdf
Xu, N., Mao, W., Chen, G.: Multi-interactive memory network for aspect based multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of AAAI, vol. 33, pp. 371–378 (2019). https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/3807/3685
Yu, J., Jiang, J.: Adapting BERT for target-oriented multimodal sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of IJCAI (2015). www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/2019/0751.pdf
Zadeh, A., Chen, M., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L.P.: Tensor fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 1103–1114 (2017)
Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., Li, X., Liu, N., Guo, B., Yu, Z.: ModalNet: an aspect-level sentiment classification model by exploring multimodal data with fusion discriminant attentional network. World Wide Web 24(6), 1957–1974 (2021). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11280-021-00955-7
Zhou, J., Zhao, J., Huang, J.X., Hu, Q.V., He, L.: MASAD: a large-scale dataset for multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing 455, 47–58 (2021). www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231221007931
Acknowledgments.
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61876053, 62006062, 62176076), Shenzhen Foundational Research Funding (JCYJ20200109113441941 and JCYJ2021032411 5614039), Joint Lab of HIT and KONKA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, J., Wang, Q., Wen, Z., Liang, X., Xu, R. (2022). Interactive Fusion Network with Recurrent Attention for Multimodal Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis. In: Fang, L., Povey, D., Zhai, G., Mei, T., Wang, R. (eds) Artificial Intelligence. CICAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13606. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20503-3_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20503-3_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20502-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20503-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)