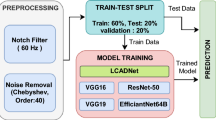
Abstract
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s diseases (AD) are two common neurodegenerative disorders which belong to the dementia family mostly found in elders. There is evidence that MCI may lead to Alzheimer’s disease. Since there is no treatment for AD after it has been diagnosed, it is a significant public health problem in the twenty-first century. Existing classical machine learning methods fail to detect AD and MCI more efficiently and accurately because of their shallow and limited architecture. Electroencephalography (EEG) is emerging as a portable, non-invasive, and cheap diagnostic tool to analyze MCI and AD, whereas other diagnostic tools like computed tomography, positron emission tomography, mini-mental state examination, and magnetic resonance imaging are expensive and time-consuming. To address these obstacles, a deep residual Alzheimer’s disease and MCI detection network (DRAM-Net) based framework has been introduced to detect MCI and AD using EEG data. This multi-class study contains EEG data collection, preprocessing (down-sampling, de-noising and temporal segmentation), DRAM-Net architecture to classify AD, MCI and normal subjects and experiment evaluation stages. Our proposed DRAM-Net framework has obtained 96.26% overall multiclass accuracy, outperforming existing multi-class studies, and also claimed accuracy of 96.66% for the normal class, 98.06% for the MCI class, and 97.79% for the AD class. This study will create a new pathway for future neuro-disease researchers and technology experts.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H., Wang, K., Whittaker, F.: A deep learning based framework for diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment. Knowl.-Based Syst. 248, 108815 (2022)
Pirrone, D., Weitschek, E., Di Paolo, P., De Salvo, S., De Cola, M.C.: EEG signal processing and supervised machine learning to early diagnose Alzheimer’s disease. Appl. Sci. 12(11), 5413 (2022)
Patterson, C.: World Alzheimer report 2018. The state of the art of dementia research: new frontiers. Alzheimer’s Disease International, London (2018)
Organization, W.H., et al.: Alzheimer’s disease international. Dementia: a public health priority. World Health Org. 1, 112 (2012)
Bracco, L., et al.: Factors affecting course and survival in Alzheimer’s disease: a 9-year longitudinal study. Arch. Neurol. 51(12), 1213–1219 (1994)
Alvi, A.M., Shaon, M.F.I., Das, P.R., Mustafa, M., Bari, M.R.: Automated course management system. In: 2017 12th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST), pp. 161–166. IEEE, December 2017
Morabito, F.C., Ieracitano, C., Mammone, N.: An explainable Artificial Intelligence approach to study MCI to AD conversion via HD-EEG processing. Clin. EEG Neurosci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/15500594211063662
Alvi, A., Tasneem, N., Hasan, A., Akther, S.: Impacts of blockades and strikes in Dhaka: a survey. Int. J. Innov. Bus. Strat. 6(1), 369–377 (2020)
Ieracitano, C., Mammone, N., Hussain, A., Morabito, F.C.: A novel multi-modal machine learning based approach for automatic classification of EEG recordings in dementia. Neural Netw. 123, 176–190 (2020)
Fiscon, G., et al.: Combining EEG signal processing with supervised methods for Alzheimer’s patients classification. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Making 18(1), 1–10 (2018)
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H.: A long short-term memory based framework for early detection of mild cognitive impairment from EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. (2022)
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H.: Neurological abnormality detection from electroencephalography data: a review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 55(3), 2275–2312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10062-8
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H., Sun, L., Cao, J.: An adaptive image smoothing technique based on localization. In: Developments of Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Computation and Robotics: Proceedings of the 14th International FLINS Conference (FLINS 2020), pp. 866–873 (2020)
Chatterjee, C.C., Krishna, G.: A novel method for IDC prediction in breast cancer histopathology images using deep residual neural networks. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Communication and Computational Techniques (ICCT), pp. 95–100. IEEE, September 2019
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H.: Developing a deep learning based approach for anomalies detection from EEG data. In: Zhang, W., Zou, L., Zakaria Maamar, Lu., Chen, (eds.) WISE 2021. LNCS, vol. 13080, pp. 591–602. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90888-1_45
Paul, S., Alvi, A.M., Nirjhor, M.A., Rahman, S., Orcho, A.K., Rahman, R.M.: Analyzing accident prone regions by clustering. In: Król, D., Nguyen, N.T., Shirai, K. (eds.) ACIIDS 2017. SCI, vol. 710, pp. 3–13. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56660-3_1
Alvi, A.M., Basher, S.F., Himel, A.H., Sikder, T., Islam, M., Rahman, R.M.: An adaptive grayscale image de-noising technique by fuzzy inference system. In: 2017 13th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), pp. 1301–1308. IEEE, July 2017
Paul, S., Alvi, A.M., Rahman, R.M.: An analysis of the most accident prone regions within the Dhaka Metropolitan Region using clustering. Int. J. Adv. Intell. Paradigms 18(3), 294–315 (2021)
Helzner, E.P., Scarmeas, N., Cosentino, S., Tang, M., Schupf, N., Stern, Y.: Survival in Alzheimer disease: a multiethnic, population-based study of incident cases. Neurology 71(19), 1489–1495 (2008)
Alvi, A.M., Tasneem, N., Hasan, M.A., Akther, S.B.: A study to find the impacts of strikes on students and local shopkeepers in Bangladesh. In: World Congress on Sustainable Technologies (WCST-2019) (2019)
Hasan, M.A., Tasneem, N., Akther, S.B., Das, K., Alvi, A.M.: An analysis on recent mobile application trend in Bangladesh. In: Barolli, L., Takizawa, M., Xhafa, F., Enokido, T. (eds.) WAINA 2019. AISC, vol. 927, pp. 195–204. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15035-8_18
Fouladi, S., Safaei, A.A., Mammone, N., Ghaderi, F., Ebadi, M.J.: Efficient deep neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from scalp EEG recordings. Cogn. Comput. 14, 1247–1268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-022-10033-3
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., Wang, H.: Challenges in electroencephalography data processing using machine learning approaches. In: Hua, W., Wang, H., Li, L. (eds.) Databases Theory and Applications: 33rd Australasian Database Conference, ADC 2022, Sydney, NSW, Australia, September 2–4, 2022, Proceedings, pp. 177–184. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15512-3_15
Vimalachandran, P., Liu, H., Lin, Y., Ji, K., Wang, H., Zhang, Y.: Improving accessibility of the Australian My Health Records while preserving privacy and security of the system. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 8(1), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00126-4
He, J., Rong, J., Sun, L., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Ma, J.: A framework for cardiac arrhythmia detection from IoT-based ECGs. World Wide Web 23(5), 2835–2850 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00776-9
Lee, J., Park, J.S., Wang, K.N., Feng, B., Tennant, M., Kruger, E.: The use of telehealth during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in oral and maxillofacial surgery–a qualitative analysis. EAI Endorsed Trans. Scalable Inf. Syst. 9(4), e10 (2022)
Pandey, D., Wang, H., Yin, X., Wang, K., Zhang, Y., Shen, J.: Automatic breast lesion segmentation in phase preserved DCE-MRIs. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 10(1), 1–19 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-022-00176-w
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alvi, A.M., Siuly, S., De Cola, M.C., Wang, H. (2022). DRAM-Net: A Deep Residual Alzheimer’s Diseases and Mild Cognitive Impairment Detection Network Using EEG Data. In: Traina, A., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Siuly, S., Zhou, R., Chen, L. (eds) Health Information Science. HIS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13705. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20627-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20627-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20626-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20627-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)