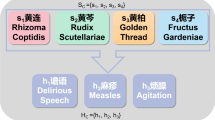
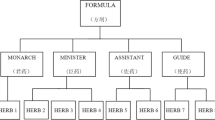
Abstract
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a highly empirical, subjective and practical discipline. Generating an appropriate prescription has been one of the most crucial components in building intelligent diagnosis systems that provide clinical decision support to physicians. While various machine learning models for prescription generation have been created, they suffer from specific limitations (e.g., data complexity and semantic ambiguity, lack of syndrome differentiation thinking, etc.). For handling these limitations, we propose a novel Heterogeneous Graph Contrastive Learning (HGCL) based model to conduct prescription generation with the idea of syndrome differentiation and treatment. Specifically, we first model the TCM clinical prescriptions as a Heterogeneous Information Network (THIN), and then explore node- and semantic-level contrastive learning on THIN, so as to enhance the quality of node representations for several downstream tasks such as node classification, prescription generation, etc. We conduct extensive experiments on three real TCM clinical datasets, demonstrating significant improvement over state-of-the-art methods, even though some of which are fully unsupervised.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
Chen, X., Ruan, C., Zhang, Y., Chen, H.: Heterogeneous information network based clustering for categorizations of traditional Chinese medicine formula. In: BIBM, pp. 839–846. IEEE (2018)
Guo, L., Wang, Y.Y.: Study thoughts on complex phenomena in syndrome of Chinese medicine. Chin. J. Basic Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 10(2), 3–12 (2004)
He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., Girshick, R.: Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: CVPR, pp. 9729–9738 (2020)
Hjelm, R.D., et al.: Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.06670 (2018)
Hu, Z., Dong, Y., Wang, K., Sun, Y.: Heterogeneous graph transformer. In: 2020 Proceedings of The Web Conference, pp. 2704–2710 (2020)
Jiang, M., et al.: Syndrome differentiation in modern research of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 140(3), 634–642 (2012)
Jin, Y., Zhang, W., He, X., Wang, X., Wang, X.: Syndrome-aware herb recommendation with multi-graph convolution network. In: ICDE, pp. 145–156. IEEE (2020)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: 5th ICLR (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907
Lee, D., Xu, H., Liu, H., Miao, Y.: Cognitive modelling of Chinese herbal medicine’s effect on breast cancer. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 7(1) (2019). Article number: 20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-019-0083-3
Li, C., et al.: Herb-know: knowledge enhanced prescription generation for traditional Chinese medicine. In: BIBM, pp. 1560–1567. IEEE (2020)
van den Oord, A., Li, Y., Vinyals, O.: Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748 (2018)
Park, C., Kim, D., Han, J., Yu, H.: Unsupervised attributed multiplex network embedding. In: AAAI, vol. 34, pp. 5371–5378 (2020)
Ruan, C., Ma, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Kraus, S.: Discovering regularities from traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions via bipartite embedding model. In: IJCAI, pp. 3346–3352 (2019)
Ruan, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y.: Exploring regularity in traditional Chinese medicine clinical data using heterogeneous weighted networks embedding. In: Li, G., Yang, J., Gama, J., Natwichai, J., Tong, Y. (eds.) DASFAA 2019. LNCS, vol. 11448, pp. 310–313. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18590-9_35
Shi, C., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Sun, Y., Philip, S.Y.: A survey of heterogeneous information network analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(1), 17–37 (2016)
Sun, F.Y., Hoffmann, J., Verma, V., Tang, J.: InfoGraph: unsupervised and semi-supervised graph-level representation learning via mutual information maximization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.01000 (2019)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10903 (2017)
Velickovic, P., Fedus, W., Hamilton, W.L., Liò, P., Bengio, Y., Hjelm, R.D.: Deep graph infomax. In: ICLR (Poster) (2019)
Wan, H., et al.: Extracting relations from traditional Chinese medicine literature via heterogeneous entity networks. JAMIA 23(2), 356–365 (2016)
Wang, T., Isola, P.: Understanding contrastive representation learning through alignment and uniformity on the hypersphere. In: ICML, pp. 9929–9939. PMLR (2020)
Wang, Z., Poon, J., Poon, S.: TCM translator: a sequence generation approach for prescribing herbal medicines. In: BIBM, pp. 2474–2480. IEEE (2019)
Wu, Y., et al.: A hybrid-scales graph contrastive learning framework for discovering regularities in traditional Chinese medicine formula. In: BIBM, pp. 1104–1111 (2021)
Wu, Z., et al.: Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3733–3742 (2018)
Yao, L., et al.: Discovering treatment pattern in traditional Chinese medicine clinical cases by exploiting supervised topic model and domain knowledge. J. Biomed. Inform. 58, 260–267 (2015)
Yao, L., Zhang, Y., Wei, B., Zhang, W., Jin, Z.: A topic modeling approach for traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 30(6), 1007–1021 (2018)
Zhu, Y., Xu, Y., Liu, Q., Wu, S.: An empirical study of graph contrastive learning (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2109.01116. arXiv:2109.01116
Zhu, Y., Xu, Y., Yu, F., Liu, Q., Wu, S., Wang, L.: Deep graph contrastive representation learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04131 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yin, Z., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y. (2022). HGCL: Heterogeneous Graph Contrastive Learning for Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription Generation. In: Traina, A., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Siuly, S., Zhou, R., Chen, L. (eds) Health Information Science. HIS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13705. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20627-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20627-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20626-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20627-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)