Abstract
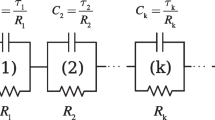
Physical and chemical phenomena of an electrochemical system can be described by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The spectral response of impedimetric biosensors is often modeled by the Randles circuit, whose parameters can be determined by regression techniques. As one of these parameters, the charge transfer resistance \(\mathrm {R_{ct}}\) is often used as the sensor response. Regression in the laboratory environment is usually performed using commercial software, which is typically computationally intensive. Therefore, applications of biosensors outside the laboratory require more efficient concepts, especially when miniaturized or portable instrumentations are used. In this work, an approach for geometric elliptical fitting of the graph in the Nyquist diagram is presented and compared with the complex nonlinear least squares (CNLS) regression. The evaluation is based, on the one hand, on artificial spectra and, on the other hand, on real data from a immunologically sensitive field-effect transistor (IMFET) for cortisol measurement in saliva. For simulated noisy data, the average error in computing \(\mathrm {R_{ct}}\) using the elliptical fit with \(\mathrm {-2.7\% }\) is worse than using the CNLS with \(0.024 \%\), but the former required only about
 of computation time compared to the latter. Applying the elliptic fitting to real data from an IMFET, the determination of \(R_{ct}\) showed deviations of only \(\mathrm 0.7\pm 2.7\%\) compared to CNLS. The impact of these variations on a standard addition method (SAM) was demonstrated for quantitative analysis of cortisol concentration. After application-oriented evaluations considering the possible accuracies, the elliptical fitting could prove to be a resource-saving option for the analysis of impedance spectra in mobile applications.
of computation time compared to the latter. Applying the elliptic fitting to real data from an IMFET, the determination of \(R_{ct}\) showed deviations of only \(\mathrm 0.7\pm 2.7\%\) compared to CNLS. The impact of these variations on a standard addition method (SAM) was demonstrated for quantitative analysis of cortisol concentration. After application-oriented evaluations considering the possible accuracies, the elliptical fitting could prove to be a resource-saving option for the analysis of impedance spectra in mobile applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayllon, D., Seoane, F., Gil-Pita, R.: Cole equation and parameter estimation from electrical bioimpedance spectroscopy measurements - a comparative study. In: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual International Conference 2009, pp. 3779–3782 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5334494
Bahadır, E.B., Sezgintürk, M.K.: A review on impedimetric biosensors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44(1), 248–262 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2014.942456
Barsoukov, E., Macdonald, J.R.: Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications. Wiley, Hoboken (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/0471716243
Barsukov, Y., Macdonald, J.R.: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, pp. 1–17. American Cancer Society (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/0471266965.com124
Bausells, J., et al.: On the impedance spectroscopy of field-effect biosensors. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/elsa.202100138
Ben Halima, H., et al.: Immuno field-effect transistor (immunoFET) for detection of salivary cortisol using potentiometric and impedance spectroscopy for monitoring heart failure. Talanta 123802 (2022). Manuscript submitted for publication
Bertsekas, D.P.: Nonlinear Programming, Second Edition (1999)
Bookstein, F.L.: Fitting conic sections to scattered data. Comput. Graphics Image Process. 9(1), 56–71 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-664X(79)90082-0
Chowdhury, A.D., Ganganboina, A.B., Park, E.Y., Doong, R.A.: Impedimetric biosensor for detection of cancer cells employing carbohydrate targeting ability of Concanavalin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 122, 95–103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.039
Dang, W., Manjakkal, L., Navaraj, W.T., Lorenzelli, L., Vinciguerra, V., Dahiya, R.: Stretchable wireless system for sweat pH monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 107, 192–202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.02.025
Fitzgibbon, A., Pilu, M., Fisher, R.B.: Direct least square fitting of ellipses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(5), 476–480 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.765658
Halima, H.B., et al.: A novel cortisol biosensor based on the capacitive structure of hafnium oxide: application for heart failure monitoring. In: 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems and Eurosensors, pp. 1067–1070 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TRANSDUCERS.2019.8808561
Hammer, F., et al.: High evening salivary cortisol is an independent predictor of increased mortality risk in patients with systolic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 203, 69–73 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.10.084
Kauffman, G.B.: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. By Mark E. Orazem and Bernard Tribollet. Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200805564
Kharitonov, A.B., Wasserman, J., Katz, E., Willner, I.: The use of impedance spectroscopy for the characterization of protein-modified ISFET devices: application of the method for the analysis of biorecognition processes. J. Phys. Chem. B 105(19), 4205–4213 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0045383
Leva-Bueno, J., Peyman, S.A., Millner, P.A.: A review on impedimetric immunosensors for pathogen and biomarker detection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 209, 343–362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-020-00668-0
Macdonald, D.D.: Some advantages and pitfalls of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Corrosion 46(3), 229–242 (1990). https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3585096
Orazem, M.E., Tribollet, B.: Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Wiley (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470381588
Papageorgiou, M., Leibold, M., Buss, M., Papageorgiou, M., Leibold, M., Buss, M.: Methode der kleinsten Quadrate. In: Optimierung (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46936-1_6
Pejcic, B., De Marco, R.: Impedance spectroscopy: over 35 years of electrochemical sensor optimization. Electrochim. Acta 51(28), 6217–6229 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2006.04.025
Pfeiffer, N., Jechow, M., Wachter, T., Hofmann, C., Errachid, A., Heuberger, A.: Impact of normalization, standardization and pre-fit on the success rate of fitting in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 7(2), 492–495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/cdbme-2021-2125
Pfeiffer, N., Wachter, T., Frickel, J., Hofmann, C., Errachid, A., Heuberger, A.: Elliptical fitting as an alternative approach to complex nonlinear least squares regression for modeling electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, pp. 42–49. SCITEPRESS - Science and Technology Publications (2021). https://doi.org/10.5220/0010231600420049
Prodromidis, M.I.: Impedimetric immunosensors—a review. Electrochim. Acta 55(14), 4227–4233 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.01.081
Randviir, E.P., Banks, C.E.: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: an overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal. Methods 5(5), 1098–1115 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay26476a
Rushworth, J.V., Ahmed, A., Griffiths, H.H., Pollock, N.M., Hooper, N.M., Millner, P.A.: A label-free electrical impedimetric biosensor for the specific detection of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta oligomers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 56, 83–90 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.12.036
Sgobbi, L.F., Razzino, C.A., Machado, S.A.: A disposable electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim antibiotics in urine based on multiwalled nanotubes decorated with Prussian blue nanocubes modified screen-printed electrode. Electrochim. Acta 191, 1010–1017 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.11.151
Shoar Abouzari, M.R., Berkemeier, F., Schmitz, G., Wilmer, D.: On the physical interpretation of constant phase elements. Solid State Ion. 180(14–16), 922–927 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2009.04.002
Sun, A., Venkatesh, A.G., Hall, D.A.: A multi-technique reconfigurable electrochemical biosensor: enabling personal health monitoring in mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 10(5), 945–954 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2586504
Sung, D., Koo, J.: A review of BioFET’s basic principles and materials for biomedical applications. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 11(2), 85–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-021-00187-8
Tu, J., Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M., Wang, M., Gao, W.: The era of digital health: a review of portable and wearable affinity biosensors. Adv. Func. Mater. 30(29), 1906713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201906713
Vozgirdaite, D., et al.: Development of an immunofet for analysis of tumour necrosis factor-\(\rm \alpha \) in artificial saliva: application for heart failure monitoring. Chemosensors 9(2), 26 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9020026
Yuan, X.Z., Song, C., Wang, H., Zhang, J.: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in PEM fuel cells. Springer, London (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84882-846-9
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by EU H2020 research and innovation program entitled KardiaTool with grant No 768686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pfeiffer, N. et al. (2022). Determination of Charge Transfer Resistance from Randles Circuit Spectra Using Elliptical Fitting. In: Gehin, C., et al. Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies. BIOSTEC 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1710. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20664-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20664-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20663-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20664-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)