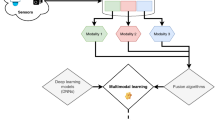
Abstract
In this work, we explore various approaches for automated visual classification of multimodal inputs such as EEG and Image data for the same item, focusing on finding an optimal solution. Our new technique examines the fusion of EEG and Image data using a concatenation of deep learning models for classification, where the EEG feature space is encoded with 8-bit-grayscale images. This concatenated-based model achieves a 95% accuracy for the 39 class EEG-ImageNet dataset, setting a new benchmark and surpassing all prior work. Furthermore, we show that it is computationally effective in multimodal classification when human subjects are presented with visual stimuli of objects in three-dimensional real-world space rather than images of the same. These findings will improve machine visual perception and bring it closer to human-learned vision.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin, M., Kiymik, M.K.: Application of periodogram and AR spectral analysis to EEG signals. J. Med. Syst. 24(4), 247–256 (2000)
Arandjelovic, R., Zisserman, A.: Look, listen and learn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 609–617 (2017)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), vol. 1, pp. 886–893. IEEE (2005)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Fares, A., Zhong, S., Jiang, J.: Region level bi-directional deep learning framework for EEG-based image classification. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 368–373. IEEE (2018)
Funke, C.M., et al.: Five points to check when comparing visual perception in humans and machines. J. Vis. 21(3), 16–16 (2021)
Guillaumin, M., Verbeek, J., Schmid, C.: Multimodal semi-supervised learning for image classification. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 902–909. IEEE (2010)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. CoRR abs/1512.03385 (2015)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Howard, A.G., et al.: MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. CoRR abs/1704.04861 (2017)
Ilievski, I., Feng, J.: Multimodal learning and reasoning for visual question answering. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Kaneshiro, B., Guimaraes, P., et al.: A representational similarity analysis of the dynamics of object processing using single-trial EEG classification. PLoS ONE 10(8), e0135697 (2015)
Kavasidis, I., Palazzo, S., Spampinato, C., Giordano, D., Shah, M.: Brain2Image: converting brain signals into images. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1809–1817 (2017)
Koelstra, S., Mühl, C., Patras, I.: EEG analysis for implicit tagging of video data. In: 2009 3rd International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction and Workshops, pp. 1–6 (2009)
Lawhern, V.J., et al.: EEGNet: a compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 15(5), 056013 (2018)
Li, Y., Dzirasa, K., Carin, L., Carlson, D.E., et al.: Targeting EEG/LFP synchrony with neural nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
MacInnes, J., Santosa, S., Wright, W.: Visual classification: expert knowledge guides machine learning. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 30(1), 8–14 (2010)
Marini, F., Breeding, K.A., Snow, J.C.: Dataset of 24-subject EEG recordings during viewing of real-world objects and planar images of the same items. Data Brief 24, 103857 (2019)
Marini, F., Breeding, K.A., Snow, J.C.: Distinct visuo-motor brain dynamics for real-world objects versus planar images. Neuroimage 195, 232–242 (2019)
Mishra, A., Raj, N., Bajwa, G.: EEG-based image feature extraction for visual classification using deep learning. In: 2022 Third International Conference on Intelligent Data Science Technologies and Applications (IDSTA) In Press. IEEE (2022). https://intelligenttech.org/IDSTA2022/IDSTApackingList/26_DTL2022_RC_8931.pdf
Owens, A., Wu, J., McDermott, J.H., Freeman, W.T., Torralba, A.: Ambient sound provides supervision for visual learning. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 801–816. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_48
Palazzo, S., Spampinato, C., et al.: Correct block-design experiments mitigate temporal correlation bias in EEG classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.03849 (2020)
Palazzo, S., Spampinato, C., et al.: Decoding brain representations by multimodal learning of neural activity and visual features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(11), 3833–3849 (2020)
Pedregosa, F., et al.: Scikit-Learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Phoha, S.: Machine perception and learning grand challenge: situational intelligence using cross-sensory fusion. Front. Robot. AI 1, 7 (2014)
Raghu, S., Sriraam, N., Temel, Y., Rao, S.V., Kubben, P.L.: EEG based multi-class seizure type classification using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Neural Netw. 124, 202–212 (2020)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint:1409.1556 (2014)
Spampinato, C., Palazzo, S., et al.: Deep learning human mind for automated visual classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6809–6817 (2017)
Tan, M., Le, Q.V.: EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. CoRR abs/1905.11946 (2019)
Tao, Y., et al.: Gated transformer for decoding human brain EEG signals. In: 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 125–130. IEEE (2021)
Zhang, H., Silva, F.H.S., Ohata, E.F., Medeiros, A.G., Rebouças Filho, P.P.: Bi-dimensional approach based on transfer learning for alcoholism pre-disposition classification via EEG signals. Front. Human Neurosci. 14 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mishra, A., Bajwa, G. (2022). A New Approach to Visual Classification Using Concatenated Deep Learning for Multimode Fusion of EEG and Image Data. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13598. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20713-6_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20713-6_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20712-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20713-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)