Abstract
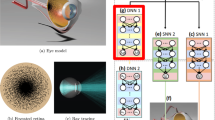
Spiking neural networks (SNNs) are comprised of artificial neurons that, like their biological counterparts, communicate via electrical spikes. We develop and train a biomimetic, SNN-driven, neuromuscular oculomotor controller for a realistic biomechanical model of the human eye. Event-based data flow in the SNN directs the necessary extraocular-muscle-actuated eye movements. We train our SNN models from scratch using modified deep learning techniques. We use surrogate gradients and introduce a linear layer to convert membrane voltages from the final spiking layer into the desired outputs. Our SNN foveation network enhances the biomimetic properties of the virtual eye model and enables it to perform reliable visual tracking.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekolay, T., et al.: Nengo: a Python tool for building large-scale functional brain models. Front. Neuroinformat. 7(48), 1–13 (2014)
Bouvier, M., et al.: Spiking neural networks hardware implementations and challenges: a survey. ACM J. on Emerging Technol. Comput. Syst. 15(2) (2019)
Diehl, P., Cook, M.: Unsupervised learning of digit recognition using spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 9 (2015)
Diehl, P.U., Neil, D., Binas, J., Cook, M., Liu, S.C., Pfeiffer, M.: Fast-classifying, high-accuracy spiking deep networks through weight and threshold balancing. In: 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8 (2015)
Eshraghian, J.K., et al.: Training spiking neural networks using lessons from deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.12894 (2021)
Gehrig, M., Shrestha, S.B., Mouritzen, D., Scaramuzza, D.: Event-based angular velocity regression with spiking networks. CoRR abs/2003.02790 (2020)
Jose, J.T., Amudha, J., Sanjay, G.: A survey on spiking neural networks in image processing. In: El-Alfy, E.-S.M., Thampi, S.M., Takagi, H., Piramuthu, S., Hanne, T. (eds.) Advances in Intelligent Informatics. AISC, vol. 320, pp. 107–115. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11218-3_11
Kim, S., Park, S., Na, B., Yoon, S.: Spiking-YOLO: spiking neural network for energy-efficient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 34(07), pp. 11270–11277 (2020)
Lakshmipathi, A.S.: Biomimetic modeling of the eye and deep NeuroMuscular oculomotor control. Master’s thesis, University of California, Los Angeles (2018)
Maqueda, A.I., Loquercio, A., Gallego, G., Garcia, N., Scaramuzza, D.: Event-based vision meets deep learning on steering prediction for self-driving cars. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Nakada, M., Chen, H., Lakshmipathy, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Locally-connected, irregular deep neural networks for biomimetic active vision in a simulated human. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 4465–4472 (2021)
Nakada, M., Lakshmipathy, A., Chen, H., Ling, N., Zhou, T., Terzopoulos, D.: Biomimetic eye modeling & deep neuromuscular oculomotor control. ACM Trans. Graph. 38(6) (2019)
Nakada, M., Zhou, T., Chen, H., Weiss, T., Terzopoulos, D.: Deep learning of biomimetic sensorimotor control for biomechanical human animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37(4) (2018)
Neftci, E.O., Mostafa, H., Zenke, F.: Surrogate gradient learning in spiking neural networks: bringing the power of gradient-based optimization to spiking neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 36(6), 51–63 (2019)
Purves, D., Augustine, G., Fitzpatrick, D., et al.: Anatomical distribution of rods and cones. Sinauer Associates (2001)
Rueckauer, B., Lungu, I.A., Hu, Y., Pfeiffer, M., Liu, S.C.: Conversion of continuous-valued deep networks to efficient event-driven networks for image classification. Front. Neurosci. 11 (2017)
Rullen, R., Thorpe, S.: Rate coding versus temporal order coding: what the retinal ganglion cells tell the visual cortex. Neural Comput. 13, 1255–1283 (2001)
Schraa-Tam, C., Lugt, A., Frens, M., Smits, M., Broekhoven, P., Geest, J.: An fMRI study on smooth pursuit and fixation suppression of the optokinetic reflex using similar visual stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 185, 535–44 (2008)
Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., Liu, C., Roy, K.: Going deeper in spiking neural networks: VGG and residual architectures. Front. Neurosci. 13 (2019)
Shirley, P., Morley, R.K.: Realistic Ray Tracing, 2nd edn. A. K. Peters Ltd, Natick, MA, USA (2003)
Tayarani-Najaran, M.H., Schmuker, M.: Event-based sensing and signal processing in the visual, auditory, and olfactory domain: a review. Front. Neural Circuits 15 (2021)
Thomas, J.G.: The dynamics of small saccadic eye movements. J. Physiol. 200(1), 109–127 (1969)
Acknowledgements
We thank Arjun Lakshmipathy and Masaki Nakada for providing their software and otherwise assisting with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Saquib, T., Terzopoulos, D. (2022). Biomimetic Oculomotor Control with Spiking Neural Networks. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13599. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20715-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20716-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)