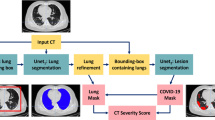
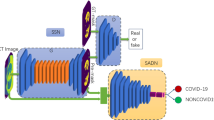
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate the transferability limitations when using deep learning models, for semantic segmentation of pneumonia-infected areas in CT images. The proposed approach adopts a 4 channel input; 3 channels based on Hounsfield scale, plus one channel (binary) denoting the lung area. We used 3 different, publicly available, CT datasets. If the lung area mask was not available, a deep learning model generates a proxy image. Experimental results suggest that transferability should be used carefully, when creating Covid segmentation models; retraining the model more than one times in large sets of data results in a decrease in segmentation accuracy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
COVID-19 Map (2022). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
Statement on the tenth meeting of the International Health Regulations: emergency Committee regarding the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic (2022), https://www.who.int/news/item/19-01-2022-statement-on-the-tenth-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-pandemic
Hundreds of AI tools have been built to catch Covid. None of them helped. (2022), https://www.technologyreview.com/2021/07/30/1030329/machine-learning-ai-failed-covid-hospital-diagnosis-pandemic/
Ardakani, A.A., Kanafi, A.R., Acharya, U.R., Khadem, N., Mohammadi, A.: Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103795 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103795, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010482520301645
Chakraborty, S., Mali, K.: SuFMoFPA: A superpixel and meta-heuristic based fuzzy image segmentation approach to explicate COVID-19 radiological images. Expert Syst. Appl. 167, 114142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114142, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417420308897
Chen, J., et al.: Deep learning-based model for detecting 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia on high-resolution computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 19196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76282-0, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-76282-0, number: 1 Publisher: Nature Publishing Group
Cifci, M.: Deep learning model for diagnosis of corona virus disease from CT images. Int.J. Sci. Res. Manag. 11, 273 (2020). Apr
Cozzi, D., et al.: Ground-glass opacity (GGO): a review of the differential diagnosis in the era of COVID-19. Jpn. J. Radiol. 39(8), 721–732 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-021-01120-w, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8071755/
DenOtter, T.D., Schubert, J.: Hounsfield Unit. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) (2021). http://europepmc.org/books/NBK547721
Fan, D.P., et al.: Inf-Net: automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 39(8), 2626–2637 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2996645, conference Name: IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. Aug
Islam, M.Z., Islam, M.M., Asraf, A.: A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inform. Med. Unlock. 20, 100412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100412, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352914820305621
Jun, M., et al.: COVID-19 CT lung and infection segmentation dataset, April 2020. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3757476, https://zenodo.org/record/3757476, type: dataset
Katsamenis, I., Protopapadakis, E., Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, A., Doulamis, N.: Transfer learning for COVID-19 pneumonia detection and classification in chest X-ray images. Tech. rep., medRxiv, December 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.14.20248158, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.14.20248158v1, type: article
Kazerooni, E.A., Gross, B.H.: The Core Curriculum, p. 379. (September Core Curriculum Series). Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia (2003)
Le, N.Q.K.: Fertility-GRU: identifying fertility-related proteins by incorporating deep-gated recurrent units and original position-specific scoring matrix profiles. J. Proteome Res. 18(9), 3503–3511 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00411, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00411, publisher: American Chemical Society
Li, L., et al.: Using artificial intelligence to detect COVID-19 and community-acquired pneumonia based on pulmonary CT: evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy. Radiology 296(2), E65–E71 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200905, https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2020200905, publisher: Radiological Society of North America
Li, Y., Xia, L.: Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): role of chest CT in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 214(6), 1280–1286 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.22954, https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.20.22954, publisher: American Roentgen Ray Society
Maganaris, C., Protopapadakis, E., Bakalos, N., Doulamis, N., Kalogeras, D., Angeli, A.: Evaluating transferability for Covid 3D localization using CT SARS-COV-2 segmentation models. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, PETRA 2022, pp. 615–621., Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3529190.3534736, https://doi.org/10.1145/3529190.3534736
COVID-19 (2022). http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/
Morozov, S., et al.: Mosmeddata: Chest CT scans with Covid-19 related findings dataset. medRxiv (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.20.20100362, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2020/05/22/2020.05.20.20100362
Singh, D., Kumar, V., Vaishali, Kaur, M.: Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution-based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 39(7), 1379–1389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03901-z, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03901-z
Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, N., Doulamis, A., Protopapadakis, E.: Deep learning for computer vision: a brief review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, e7068349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7068349, https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2018/7068349/, publisher: Hindawi
ParaView (2022). https://www.paraview.org/
Acknowledgements
This research has been co-financed by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 883441 for the STAMINA Innovation action.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Maganaris, C., Protopapadakis, E., Bakalos, N., Doulamis, N., Kalogeras, D., Angeli, A. (2022). Transferability Limitations for Covid 3D Localization Using SARS-CoV-2 Segmentation Models in 4D CT Images. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13599. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20715-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20716-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)