Abstract
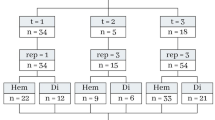
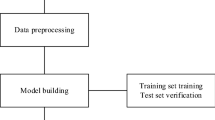
The sport-related concussion (SRC) battery relies heavily upon subjective symptom reporting in order to determine the diagnosis of a concussion. Unfortunately, athletes with SRC may return-to-play (RTP) too soon if they are untruthful of their symptoms. It is critical to provide accurate assessments that can overcome underreporting to prevent further injury. To lower the risk of injury, a more robust and precise method for detecting concussion is needed to produce reliable and objective results. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to detect SRC using long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network (RNN) architectures from oculomotor data. In particular, we propose a new error metric that incorporates mean squared error in different proportions. The experimental results on the smooth pursuit test of the VR-VOMS dataset suggest that the proposed approach can predict concussion symptoms with higher accuracy compared to symptom provocation on the vestibular ocular motor screening (VOMS).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneshvar, D.H., Nowinski, C.J., McKee, A.C., Cantu, R.C.: The epidemiology of sport-related concussion. Clin. Sports Med. 30(1), 1–17 (2011)
Kontos, A.P., et al.: Discriminative validity of vestibular ocular motor screening in identifying concussion among collegiate athletes: a national collegiate athletic association-department of defense concussion assessment, research, and education consortium study. Am J. Sports Med. 49, 03635465211012359 (2021)
Echemendia, R.J., et al.: The sport concussion assessment tool 5th edition (scat5): background and rationale. Brit. J. Sports Med. 51(11), 848–850 (2017)
McCrea, M., et al.: Acute effects and recovery time following concussion in collegiate football players: the ncaa concussion study. Jama 290(19), 2556–2563 (2003)
Galetta, K.M., Liu, M., Leong, D.F., Ventura, R.E, Galetta, S.L., Balcer, L.J.: The king-devick test of rapid number naming for concussion detection: meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature. Concussion 1(2), (2016)
Bell, D.R., Guskiewicz, K.M., Clark, M.A., Padua, D.A.: Systematic review of the balance error scoring system. Sports Health 3(3), 287–295 (2011)
Mucha, A., et al.: A brief vestibular/ocular motor screening (VOMS) assessment to evaluate concussions: preliminary findings. Am. J. Sports Med. 42(10), 2479–2486 (2014)
Shahim, P., et al.: Blood biomarkers for brain injury in concussed professional ice hockey players. JAMA Neurol. 71(6), 684–692 (2014)
Yorke, A.M., Smith, L., Babcock, M., Alsalaheen, B.: Validity and reliability of the vestibular/ocular motor screening and associations with common concussion screening tools. Sports Health 9(2), 174–180 (2017)
McKeithan, L., Hibshman, N., Yengo-Kahn, A.M., Solomon, G.S., Zuckerman, S.L.: Sport-related concussion: evaluation, treatment, and future directions. Med. Sci. 7(3), 44 (2019)
Howell, D.R., Osternig, L.R., Chou, L.-S.: Return to activity after concussion affects dual-task gait balance control recovery. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 47(4), 673–680 (2015)
Baker, C.S., Cinelli, M.E.: Visuomotor deficits during locomotion in previously concussed athletes 30 or more days following return to play. Physiol. Rep. 2(12), e12252 (2014)
Wright, W., Tierney, R., McDevitt, J.: Visual-vestibular processing deficits in mild traumatic brain injury. J. Vestib. Res. 27(1), 27–37 (2017)
Moran, R.N., Covassin, T., Elbin, R., Gould, D., Nogle, S.: Reliability and normative reference values for the vestibular/ocular motor screening (VOMS) tool in youth athletes. Am. J. Sports Med. 46(6), 1475–1480 (2018)
Sussman, E.S., Ho, A.L., Pendharkar, A.V., Ghajar, J.: Clinical evaluation of concussion: the evolving role of oculomotor assessments. Neurosurg. Focus 40(4), E7 (2016)
Kontos, A.P., Sufrinko, A., Elbin, R., Puskar, A., Collins, M.W.: Reliability and associated risk factors for performance on the vestibular/ocular motor screening (VOMS) tool in healthy collegiate athletes. Am. J. Sports Med. 44(6), 1400–1406 (2016)
Greff, K., Srivastava, R.K., Koutník, J., Steunebrink, B.R., Schmidhuber, J.: LSTM: a search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(10), 2222–2232 (2016)
Schuster, M., Paliwal, K.K.: Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(11), 2673–2681 (1997)
Wang, Y., Tian, F.: Recurrent residual learning for sequence classification, In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 938–943 (2016)
Wang, J., Yu, L.C., Lai, K.R., Zhang, X.: Dimensional sentiment analysis using a regional CNN-LSTM model. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp. 225–230 (2016)
Acknowledgments
Portions of this material is based upon work supported by the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering under award number FA9550-21–1-0207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sarker, P., Hossain, K.F., Adhanom, I.B., Pavilionis, P.K., Murray, N.G., Tavakkoli, A. (2022). Analysis of Smooth Pursuit Assessment in Virtual Reality and Concussion Detection Using BiLSTM. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13599. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20716-7_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20715-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20716-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)