Abstract
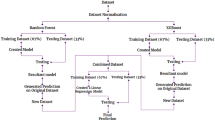
With Industry 4.0, companies must manage massive and generally imbalanced datasets. In an automotive company, the lots release decision process must cope with this problem by combining data from different sources to determine if a selected group of products can be released to the customers. This work focuses on this process and aims to classify the occurrence of customer complaints with a conception, tune and evaluation of five ML algorithms, namely XGBoost (XGB), LightGBM (LGBM), CatBoost (CatB), Random Forest(RF) and a Decision Tree (DT), based on an imbalanced dataset of automatic production tests. We used a non-sampling approach to deal with the problem of imbalanced datasets by analyzing two different methods, cost-sensitive learning and threshold-moving. Regarding the obtained results, both methods showed an effective impact on boosting algorithms, whereas RF only showed improvements with threshold-moving. Also, considering both approaches, the best overall results were achieved by the threshold-moving method, where RF obtained the best outcome with a F1-Score value of 76.2%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rojko, A.: Industry 4.0 concept: Background and overview. Int. J. Interact. Mobile Technol. 11(5) (2017). https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v11i5.7072
Fathy, Y., Jaber, M., Brintrup, A.: Learning with imbalanced data in smart manufacturing: a comparative analysis. IEEE Access 9, 2734–2757 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047838
Costa, C.F., Nascimento, M.A.: Ida 2016 industrial challenge: using machine learning for predicting failures. In: International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis, pp. 381–386. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46349-0_33
Altinger, H., Herbold, S., Schneemann, F., Grabowski, J., Wotawa, F.: Performance tuning for automotive software fault prediction. In: 2017 IEEE 24th International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER), pp. 526–530. IEEE (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/SANER.2017.7884667
Pereira, P.J., Pereira, A., Cortez, P., Pilastri, A.: A comparison of machine learning methods for extremely unbalanced industrial quality data. In: EPIA Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 561–572. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86230-5_44
Lobo, A., Moreira, G.: Tests and Complaints. Mendeley Data V1,(2022). https://doi.org/10.17632/5xnj2z5z48.1
Kanter, J.M., Veeramachaneni, K.: Deep feature synthesis: Towards automating data science endeavors. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/DSAA.2015.7344858
Jeni, L., Cohn, J., De La Torre, F.: Facing imbalanced data-recommendations for the use of performance metrics In: 2013 Humaine Association Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, pp. 245–251 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACII.2013.47
Sharma, H., Kumar, S.: A survey on decision tree algorithms of classification in data mining. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 5(4), 2094–2097 (2016). https://doi.org/10.21275/v5i4.NOV162954
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Al Daoud, E.: Comparison between XGBoost, LightGBM and CatBoost using a home credit dataset. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Eng. 13(1), 6–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3607805
Elkan, C.: The foundations of cost-sensitive learning. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 973–978. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Ltd (2001)
Sheng, V.S., Ling, C.X.: Thresholding for making classifiers cost-sensitive. In: AAAI, vol. 6, pp. 476–81 (2006)
Davis, J., Goadrich, M.: The relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC curves. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 233–240 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1143844.1143874
Putatunda, S., Rama, K.: A comparative analysis of hyperopt as against other approaches for hyper-parameter optimization of XGBoost. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning, pp. 6–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3297067.3297080
Brownlee, J.: Probability for machine learning: discover how to harness uncertainty with Python. Machine Learning Mastery (2019)
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia within the R &D Units Project Scope: UIDB/00319/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lobo, A., Oliveira, P., Sampaio, P., Novais, P. (2023). Cost-Sensitive Learning and Threshold-Moving Approach to Improve Industrial Lots Release Process on Imbalanced Datasets. In: Omatu, S., Mehmood, R., Sitek, P., Cicerone, S., Rodríguez, S. (eds) Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 19th International Conference. DCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 583. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20859-1_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20859-1_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-20858-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-20859-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)