Abstract
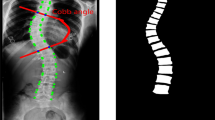
Spinal diseases are common and difficult to cure, which causes much suffering. Accurate diagnosis and assessment of these diseases can considerably improve cure rates and the quality of life for patients. The spinal disease assessment relies primarily on accurate vertebra landmark detection, such as scoliosis assessment. However, existing approaches do not adequately exploit the relationships between vertebrae and analyze the global spine structure, meaning scarcity annotations are underutilized. In addition, the practical design of ground-truth is also deficient in model learning due to the suboptimal coordinate system. Therefore, we propose a unified end-to-end vertebra landmark detection network called Dcor-VLDet, contributing to the scoliosis assessment task. This network takes the positional information from within and between vertebrae into account. At the same time, through fusing the advantages of both Cartesian and polar coordinate systems, the symmetric mean absolute percentage error (SMAPE) value can be reduced significantly in scoliosis assessment. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method is superior in measuring Cobb angle and detecting landmarks on low-contrast X-ray images.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo, Y., Li, Y., Zhou, X., He, W.: A keypoint transformer to discover spine structure for cobb angle estimation. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2021)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 25, 1097–1105 (2012)
Law, H., Deng, J.: CornerNet: detecting objects as paired keypoints. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11218, pp. 765–781. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_45
Li, S., Wang: Accurate automated spinal curvature estimation MICCAI 2019 (2019). https://aasce19.github.io/
O’Brien, M., Group, S.D.S.: Radiographic Measurement Manual. Medtronic Sofamor Danek USA (2008). https://www.oref.org/docs/default-source/default-document-library/sdsg-radiographic-measuremnt-manual.pdf?sfvrsn=2 &sfvrsn=2
Ruder, S.: An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05098 (2017)
Scholten, P., Veldhuizen, A.: Analysis of cobb angle measurements in scoliosis. Clin. Biomech. 2(1), 7–13 (1987)
Weinstein, S.L., Dolan, L.A., Cheng, J.C., Danielsson, A., Morcuende, J.A.: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. The Lancet 371(9623), 1527–1537 (2008)
Wu, H., Bailey, C., Rasoulinejad, P., Li, S.: Automatic landmark estimation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis assessment Using BoostNet. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10433, pp. 127–135. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66182-7_15
Yi, J., Wu, P., Huang, Q., Qu, H., Metaxas, D.N.: Vertebra-focused landmark detection for scoliosis assessment. In: 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 736–740. IEEE (2020)
Zhang, K., Xu, N., Guo, C., Wu, J.: MPF-Net: an effective framework for automated cobb angle estimation. Med. Image Anal. 75, 102277 (2022)
Zhou, L., Wei, H., Li, H., Zhao, W., Zhang, Y.: Objects detection for remote sensing images based on polar coordinates. arxiv 2020. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.02988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, H., Mok, T.C.W., Chung, A.C.S. (2022). Dcor-VLDet: A Vertebra Landmark Detection Network for Scoliosis Assessment with Dual Coordinate System. In: Lian, C., Cao, X., Rekik, I., Xu, X., Cui, Z. (eds) Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13583. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21014-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21014-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21013-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21014-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)