Abstract
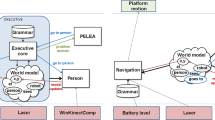
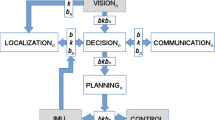
In this paper, we present some conceptual and experimental results obtained from the integration of a Robotics Cognitive Architecture (RCA) with an embedded Physics simulator. The RCA used, CORTEX, is based on a highly efficient, distributed working memory (WM) called Deep State Representation (DSR). This WM already provides a basic ontology, state persistency, geometric and logical relationships among elements and tools to read, update and reason about its contents. The hypothesis that we want to explore here is that integrating a physics simulator into the architecture facilitates the enacting of a series of additional functionalities that, otherwise, would require extensive coding and debugging. Also, we characterize these functionalities in broad types according to the kind of problem they tackle, including occlusion, model-based perception, self-calibration, scene’s structural stability and human activity interpretation. To show the results of these experiments, we use CoppeliaSim as the embedded simulator, and a Kinova Gen3 robotic arm as the real scenario. The simulator is kept synchronized with the stream of real events and, depending on the current task, several queries are computed, and the results projected to the working memory, where the participating agents can take advantage of them to improve the overall performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Bullet, ODE, Newton or Vortex.
References
Ullman, T.D., Spelke, E., Battaglia, P., Tenenbaum, J.B.: Mind games: game engines as an architecture for intuitive physics. Trends Cogn. Sci. 21(9), 649–665 (2017)
Kubricht, J.R., Holyoak, K.J., Lu, H.: Intuitive physics: current research and controversies. Trends Cogn. Sci. 21(10), 749–759 (2017), ISSN 1364-6613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2017.06.002
Davis, E., Marcus, G.: The scope and limits of simulation in automated reasoning. Artif. Intell. 233, 60–72 (2016)
Patrick, M., et al.: Imagination-enabled robot perception. In: 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE (2020)
Battaglia, P.W., Hamrick, J.B., Tenenbaum, J.B.: Simulation as an engine of physical scene understanding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110(45), 18327–18332 (2013)
Garcia, J.C.: G: a low-latency, shared-graph for robotics cognitive architectures. Master Thesis, University of Extremadura (2021)
Núñez, P., García, J.C., Bustos, P., Bsahciller, P.: Towards the design of efficient and versatile cognitive robotic architecture based on distributed, low-latency working memory. International Conference in Advanced Robotics and Competitions, Santa Maria da Feira, Portugal (2022)
Fan, Z., et al.: Mediapipe hands: On-device real-time hand tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.10214 (2020)
Bustos, P., Luis, M.-A., Bandera, A., Bandera, J.P., García-Varea, I., Martínez-Gómez J.: EUCognition Meeting - Cognitive Robot Architectures, CORTEX: a new Cognitive Architecture for Social Robots, Viena (2016)
Bustos, P., Manso, L., Bandera, A., Bandera, J., García-Varea, Martín-Gomez, J.: The cortex cognitive robotics architecture: use cases. Cogn. Syst. Res. 55, 107–123 (2019)
Bustos, P., et al.: DSRD: a proposal for a low-latency, distributed working memory for CORTEX. In: Bergasa, L.M., Ocaña, M., Barea, R., López-Guillén, E., Revenga, P. (eds.) Advances in Physical Agents II. AISC, vol. 1285, pp. 109-122. Springer, Cham (2021). ISBN 978-3-030-62579-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62579-5_8
Sallami, Y., Lemaignan, S., Clodic, A., Alami, R.: Simulation-based physics reasoning for consistent scene estimation in an HRI context. In: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 7834–7841 (2019)
Mosenlechner, L., Beetz, M.: Fast temporal projection using accurate physics-based geometric reasoning. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1821–1827 (2013)
Rohmer, E., Singh, S.P.N., Freese, M.: CoppeliaSim (formerly V-REP): a Versatile and Scalable Robot Simulation Framework. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (2013). www.coppeliarobotics.com
Olson, E.: AprilTag: a robust and flexible visual fiducial system. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2011.5979561
Hesslow, G.: Conscious thought as simulation of behaviour and perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 6, 242–247 (2002)
Michael, B., et al.: Know rob 2.0-a 2nd generation knowledge processing framework for cognition-enabled robotic agents. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE (2018)
Wintermute, S.: Integrating action and reasoning through simulation. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Artificial General Intelligence, pp. 102–107 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2991/agi.2009.24. (Atlantis Press)
Ziemke, T., Jirenhed, D.A., Hesslow, G.: Internal simulation of perception: a minimal neuro-robotic model. Neurocomputing 68, 85–104 (2005)
Jirenhed, D.-A., Hesslow, G., Ziemke, T.: Exploring internal simulation of perception in mobile robots. In: Arras, K., Baerveldt, A.-J., Balkenius, C., Burgard, W., Siegwart, R. (eds.) 2001 Fourth European Workshop on Advanced Mobile Robotics-Proceedings, Lund University Cognitive Studies, vol. 86, pp. 107–113. Lund, Sweden (2001)
Bass, I., Smith, K.A., Bonawitz, E., Ullman, T.D.: Partial mental simulation explains fallacies in physical reasoning. Cogn. Neuropsychol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2022.2083950
Ellis, K., et al.: Tenenbaum, DreamCoder: growing generalizable, interpretable knowledge with wake-sleep Bayesian program learning (2020). arXiv:2006.08381, https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2006.08381
Laird, J.E., Lebiere, C., Rosenbloom, P.S.: A standard model of the mind: toward a common computational framework across artificial intelligence, cognitive science, neuroscience, and robotics. Ai Magazine 38(4), 13–26 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the Feder funds and by the Extremaduran Goverment (projects GR21018 and IB18056), the MICINN RTI2018-099522-B-C42, by the Feder project 0770\(\_\)EuroAGE2\(\_\)4\(\_\)E (Interreg V-A Portugal-Spain - POCTEP), and CSIC and CAP from Universidad de la República.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Trinidad Barnech, G., Tejera, G., Valle-Lisboa, J., Núñez, P., Bachiller, P., Bustos, P. (2023). Initial Results with a Simulation Capable Robotics Cognitive Architecture. In: Tardioli, D., Matellán, V., Heredia, G., Silva, M.F., Marques, L. (eds) ROBOT2022: Fifth Iberian Robotics Conference. ROBOT 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 590. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21062-4_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21062-4_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21061-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21062-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)