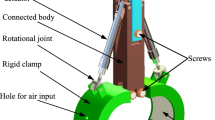
Abstract
This paper describes the design of a gripper in which fingers have a resting position maintained by springs. Fingers can be displaced if the proper forces are applied during the grasping procedure, and the correct path is followed for the releasing. This mechanism solves the constraint of using conventional actuators, which is a common limitation in hazardous environments with a high level of radiation. However, it implies redesigning the objects that will be manipulated. This paper shows in detail the mechanical gripper design, from the study of the already existing solution and modelling, including the kinematic and dynamic models, to the gripper simulation performance and experimental tests with their corresponding conclusions. The origin of this study is related to the maintenance tasks to be performed in the future International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility – Demo Oriented Neutron Source (IFMIF-DONES) facility, where a high level of ionizing radiation is expected even after the shutdown of the accelerator.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoist & Winch. https://www.hoistandwinch.co.uk/camlok-dc500-steel-drum-lifting-clamp-500-kg-swl.html. Accessed 12 July 2022
Fantoni, G., et al.: Grasping devices and methods in automated production processes. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 63(2), 679–701 (2014)
Królas, W., Ibarra, A., et al.: The IFMIF-DONES fusion oriented neutron source: evolution of the design. Nucl. Fusion 61, 125002 (2021)
Miccichè, G., et al.: The remote handling system of IFMIF-DONES. Fusion Eng. Des. 146, 2786–2790 (2019)
Heemskerk, C.J.M., et al.: Introducing artificial depth cues to improve task performance in ITER maintenance actions. Fusion Eng. Des. 88, 1969–1972 (2013)
Decr, M.: Position sensing in nuclear remote operation. Measurement 15, 43–51 (1995)
Reinhart, G., Eursch, A.: A camera-based support system with augmented reality functions for manual tasks in radioactive production environments. Prod. Eng. Res. 2(2), 139–147 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-008-0096-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Redondo Gallego, V. et al. (2023). Design and Evaluation of a Passive Gripper for Remote Manipulation Tasks. In: Tardioli, D., Matellán, V., Heredia, G., Silva, M.F., Marques, L. (eds) ROBOT2022: Fifth Iberian Robotics Conference. ROBOT 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 589. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21065-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21065-5_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21064-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21065-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)