Abstract
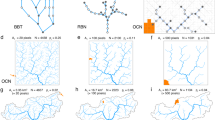
The between-community beta diversity of fish species—characterized using similarity of species between river basins, shows a non-linear drop with topological distance on river networks. In this work, we investigate the pattern of this drop with network distances and the role of underlying topology. Using the framework of optimal channel networks, the species abundances are evolved under the neutral biodiversity model. We observe that the steady-state species-similarity shows a transition at a critical network distance. At this critical distance, the average degree over the nodes crosses the global average degree of the network. This study sheds light on the role of branching in dendritic networks in ecological community assembly rules.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed-Elmdoust, A., Singh, A., Yang, Z.L.: Emergent spectral properties of river network topology: an optimal channel network approach. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–9 (2017)
Balister, P., Balogh, J., Bertuzzo, E., Bollobás, B., Caldarelli, G., Maritan, A., Mastrandrea, R., Morris, R., Rinaldo, A.: River landscapes and optimal channel networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 115(26), 6548–6553 (2018)
Borthagaray, A.I., Teixeira-de Mello, F., Tesitore, G., Ortiz, E., Illarze, M., Pinelli, V., Urtado, L., Raftopulos, P., González-Bergonzoni, I., Abades, S., et al.: Community isolation drives lower fish biomass and species richness, but higher functional evenness, in a river metacommunity. Freshwater Biol. 65(12), 2081–2095 (2020)
Brown, B., Swan, C.: Dendritic network structure constrains metacommunity properties in riverine ecosystems. J. Animal Ecol. 79(3), 571–580 (2010)
Carraro, L., Altermatt, F., Fronhofer, E.A., Furrer, R., Gounand, I., Rinaldo, A., Bertuzzo, E., Carraro, M.L.: Package ‘ocnet’ (2021)
Colaiori, F., Flammini, A., Maritan, A., Banavar, J.R.: C. Phys. Rev. E 55(2), 1298 (1997)
Condit, R., Pitman, N., Leigh, E.G., Jr., Chave, J., Terborgh, J., Foster, R.B., Núnez, P., Aguilar, S., Valencia, R., Villa, G., et al.: Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees. Science 295(5555), 666–669 (2002)
Economo, E.P., Keitt, T.H.: Network isolation and local diversity in neutral metacommunities. Oikos 119(8), 1355–1363 (2010)
Etienne, R.S., Rosindell, J.: The spatial limitations of current neutral models of biodiversity. PloS One 6(3), e14717 (2011)
Fang, Y., Ceola, S., Paik, K., McGrath, G., Rao, P.S.C., Montanari, A., Jawitz, J.W.: Globally universal fractal pattern of human settlements in river networks. Earth’s Future 6(8), 1134–1145 (2018)
Gilarranz, L.J., Bascompte, J.: Spatial network structure and metapopulation persistence. J. Theor. Biol. 297, 11–16 (2012)
Hubbell, S.P.: The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography (mpb-32). In: The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press (2011)
Krioukov, D., Papadopoulos, F., Kitsak, M., Vahdat, A., Boguná, M.: Hyperbolic geometry of complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 82(3), 036106 (2010)
Kuemmerlen, M., Reichert, P., Siber, R., Schuwirth, N.: Ecological assessment of river networks: from reach to catchment scale. Sci. Total Environ. 650, 1613–1627 (2019)
Muneepeerakul, R., Bertuzzo, E., Lynch, H.J., Fagan, W.F., Rinaldo, A., Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.: Neutral metacommunity models predict fish diversity patterns in Mississippi-Missouri Basin. Nature 453(7192), 220–222 (2008)
Muneepeerakul, R., Bertuzzo, E., Rinaldo, A., Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.: Evolving biodiversity patterns in changing river networks. J. Theor. Biol. 462, 418–424 (2019)
Rinaldo, A., Gatto, M., Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.: River networks as ecological corridors: a coherent ecohydrological perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 112, 27–58 (2018)
Terui, A., Ishiyama, N., Urabe, H., Ono, S., Finlay, J.C., Nakamura, F.: Metapopulation stability in branching river networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 115(26), E5963–E5969 (2018)
Terui, A., Kim, S., Dolph, C.L., Kadoya, T., Miyazaki, Y.: Emergent dual scaling of riverine biodiversity. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 118(47) (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially funded by the Center of Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS), which is financed by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and by the Saxon Ministry for Science, Culture, and Tourism (SMWK) with tax funds on the basis of the budget approved by the Saxon State Parliament. A.R is supported by the research program of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tripathi, R., Reza, A., Calabrese, J.M. (2023). Role of Network Topology in Between-Community Beta Diversity on River Networks. In: Cherifi, H., Mantegna, R.N., Rocha, L.M., Cherifi, C., Micciche, S. (eds) Complex Networks and Their Applications XI. COMPLEX NETWORKS 2016 2022. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1078. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21131-7_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21131-7_49
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21130-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21131-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)