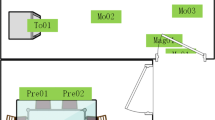
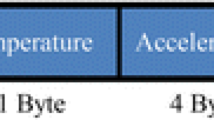
Abstract
As the population ages and health-care costs increase, smart environments can be an effective and economical way to provide care and support for the aged population. Human activity recognition (HAR), a key element of the smart environment research domain, has garnered a lot of attention lately. The present work is to provide a data-driven solution based on the extended belief rule base (EBRB) model for sensor-based HAR in the context of big data. More specifically, in order to increase the efficiency of the EBRB model, this research first offers a new rule generation method based on probability estimation, which forms the link between the extended belief rules and human activities. The number of extended belief rules used to extract knowledge from a sensor-based HAR dataset is exactly equal to the types of human activities, and each rule can be thought of as a collection of class conditional probability distributions. As a result, it is possible to create an EBRB-BD model, an EBRB model for HAR using big data that has a compact but representative rule base. The effectiveness of the EBRB-BD model is further supported by case studies. Experimental findings demonstrate that the modelling time of the EBRB-BD model is one in ten-thousand of the original EBRB model, and the EBRB-BD model also achieves the best area under the curve value (AUC) of 94.95\(\%\), surpassing the original EBRB model and some other benchmark classifiers.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72001043), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Nos. 2022J01178 and 2020J05122), and the Humanities and Social Science Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 20YJC630188).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venhatesh, V., Raj, P., Kannan, K., Balakrishnan, P.: Precision centric framework for activity recognition using Dempster Shaffer theory and information fusion algorithm in smart environment. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 36(3), 2117–2124 (2019)
Espinilla, M., Medina, J., Calzada, A., Liu, J., Martínez, L., Nugent, C.: Optimizing the configuration of an heterogeneous architecture of sensors for activity recognition, using the extended belief rule-based inference methodology. Microprocess. Microsyst. 52, 381–390 (2017)
Fahad, L.G., Rajarajan, M.: Integration of discriminative and generative models for activity recognition in smart homes. Appl. Soft Comput. 37, 992–1001 (2015)
Liu, J., Martínez, L., Calzada, A., Wang, H.: A novel belief rule base representation, generation and its inference methodology. Knowl. -Based Syst. 53, 129–141 (2013)
Ordonez, F.J., Toledo, P.D., Sanchis, A.: Activity recognition using hybrid generative discriminative models on home environments using binary sensors. Sensors 13, 5460–5477 (2017)
Gayathri, K.S., Easwarakumar, K.S., Elias, S.: Probabilistic ontology based activity recognition in smart homes using Markov logic network. Knowl. Based Syst. 121, 173–184 (2017)
Alshammari, N., Alshammari, T., Sedky, M., Champion, J., Bauer, C.: OpenSHS: open smart home simulator. Sensors 17(5), 1–22 (2017)
Calzada, A., Liu, J., Nugent, C., Wang, H., Martínez, L.: Sensor-based activity recognition using extended belief rule-based inference methodology. In: 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 2694-2697. IEEE, Chicago, IL, USA (2014)
Calzada, A., Liu, J., Wang, H., Kashyap, A.: A new dynamic rule activation method for extended belief rule-based systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(4), 880–894 (2014)
Yang, L.H., Liu, J., Wang, Y.M., Nugent, C., Martínez, L.: Online updating extended belief rule-based system for sensor-based activity recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 186, 115737 (2021)
Yang, L.H., Liu, J., Wang, Y.M., Martínez, L.: A micro-extended belief rule-based system for big data multiclass classification problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 51(1), 420–440 (2018)
Yang, L.H., Ren, T.Y., Ye, F.F., Nicholl, P., Wang, Y.M., Lu, H.T.: An ensemble extended belie rule base decision model for imbalanced classification problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 242, 108410 (2022)
Yang, J.B., Xu, D.L.: On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. -Part A: Syst. Humans 32(3), 289–304 (2002)
Choi, J.J., Yang, X.Y.: Asympototic properties of correlation-based principal component analysis. J. Econometrics 229(1), 1–18 (2022)
Hand, D.J., Till, R.J.: A simple generalisation of the area under the ROC curve for multiple class classification problems. Mach. Learn. 45, 171–186 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ren, TY., Yang, LH., Nugent, C., Ye, FF., Irvine, N., Liu, J. (2023). Extended Belief Rule Base Model with Novel Rule Generation for Sensor-Based Human Activity Recognition Under Big Data. In: Bravo, J., Ochoa, S., Favela, J. (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing & Ambient Intelligence (UCAmI 2022). UCAmI 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 594. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21333-5_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21333-5_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-21332-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-21333-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)