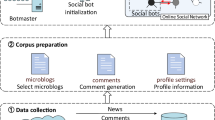
Abstract
Intersection attacks, which are popular traffic analysis attacks, have been extensively studied in anonymous point-to-point communication scenarios. These attacks are also known to be challenging threats to anonymous group communication, e.g., microblogging. However, it remains unclear how powerful these attacks can be, especially when considering realistic user communication behavior. In this paper, we study the effectiveness of intersection attacks on anonymous microblogging systems utilizing Twitter and Reddit datasets. Our findings show that the attacks are effective regardless of whether users post their messages under pseudonyms or publish them to topics without attaching identifiers. Additionally, we observed that attacks are feasible under certain settings despite increasing userbase size, communication rounds’ length, cover traffic, or traffic delays.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
It is noteworthy that a solution for this intersection attack direction has been addressed already by utilising broadcasting of published messages, i.e., sending every published message to all users, as seen in [1, 4, 5]. Nonetheless, broadcasting imposes a high communication overhead on users, which makes it an inefficient solution. Thus, more research in this area is clearly needed.
References
Abraham, I., Pinkas, B., Yanai, A.: Blinder-scalable, robust anonymous committed broadcast. In: Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 1233–1252 (2020)
Berthold, O., Langos, H.: Dummy traffic against long term intersection attacks. In: Dingledine, R., Syverson, P. (eds.) PET 2002. LNCS, vol. 2482, pp. 110–128. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36467-6_9
Cheng, R., et al.: Talek: private group messaging with hidden access patterns. In: Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, pp. 84–99 (2020)
Corrigan-Gibbs, H., et al.: Riposte: an anonymous messaging system handling millions of users. In: 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 321–338. IEEE (2015)
Corrigan-Gibbs, H., Ford, B.: Dissent: accountable anonymous group messaging. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 340–350 (2010)
Danezis, G., Serjantov, A.: Statistical disclosure or intersection attacks on anonymity systems. In: Fridrich, J. (ed.) IH 2004. LNCS, vol. 3200, pp. 293–308. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30114-1_21
Danezis, G., Diaz, C., Troncoso, C.: Two-sided statistical disclosure attack. In: Borisov, N., Golle, P. (eds.) PET 2007. LNCS, vol. 4776, pp. 30–44. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75551-7_3
Daubert, J., et al.: Anonpubsub: anonymous publish-subscribe overlays. Comput. Commun. 76, 42–53 (2016)
Dixon, S.: Number of twitter users worldwide from 2019 to 2024. https://www.statista.com/statistics/303681/twitter-users-worldwide/ (2022)
Gaballah, S.A., et al.: 2PPS-publish/subscribe with provable privacy. In: 2021 40th International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS), pp. 198–209. IEEE (2021)
Grube, T., Thummerer, M., Daubert, J., Mühlhäuser, M.: Cover traffic: a trade of anonymity and efficiency. In: Livraga, G., Mitchell, C. (eds.) STM 2017. LNCS, vol. 10547, pp. 213–223. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68063-7_15
Hayes, J., Troncoso, C., Danezis, G.: TASP: towards anonymity sets that persist. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society, pp. 177–180 (2016)
Karissa, M., et al.: Truthy: enabling the study of online social networks. In: Proceedings 16th ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing Companion (CSCW) (2013)
Kedogan, D., Agrawal, D., Penz, S.: Limits of anonymity in open environments. In: Petitcolas, F.A.P. (ed.) IH 2002. LNCS, vol. 2578, pp. 53–69. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36415-3_4
Kwon, A., et al.: Riffle: an efficient communication system with strong anonymity. Proc. Priv. Enhancing Technol. 2016(2), 115–134 (2016)
Kwon, A., et al.: Atom: horizontally scaling strong anonymity. In: Proceedings of the 26th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, pp. 406–422 (2017)
Madani, S.: Improving security and efficiency of mix-based anonymous communication systems. PhD thesis, RMIT University (2015)
Martiny, I., et al.: Improving signal’s sealed sender. In: The Internet Society, NDSS (2021)
McKelvey, K., et al.: Design and prototyping of a social media observatory. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, WWW 2013 Companion, pp. 1351–1358 (2013)
Newman, Z., et al.: Spectrum: high-bandwidth anonymous broadcast with malicious security. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. (2021)
Pfitzmann, A., Hansen, M.: A terminology for talking about privacy by data minimization: anonymity, unlinkability, undetectability, unobservability, pseudonymity, and identity management (2010)
Piotrowska, A.M.: Studying the anonymity trilemma with a discrete-event mix network simulator. In: Proceedings of the 20th Workshop on Workshop on Privacy in the Electronic Society, pp. 39–44 (2021)
Portela, J., et al.: Disclosing user relationships in email networks. J. Supercomput. 72(10), 3787–3800 (2016)
Thorbecke, C.: Facebook says government requests for user data have reached all-time high. https://abcnews.go.com/Business/facebook-government-requests-user-data-reached-time-high/story?id=66981424 (2019)
Troncoso, C., Gierlichs, B., Preneel, B., Verbauwhede, I.: Perfect matching disclosure attacks. In: Borisov, N., Goldberg, I. (eds.) PETS 2008. LNCS, vol. 5134, pp. 2–23. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70630-4_2
Trujillo, A.G.S., Orozco, A.L.S., Villalba, L.J.G., Kim, T.-H.: A traffic analysis attack to compute social network measures. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78(21), 29731–29745 (2019)
Wolinsky, D., et al.: Hang with your buddies to resist intersection attacks. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security, pp. 1153–1166 (2013)
Xu, T., Chen, Y., Fu, X., Hui, P.: Twittering by cuckoo: decentralized and socio-aware online microblogging services. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2010 Conference, pp. 473–474 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by funding from the German Research Foundation (DFG), research grant 317688284. We thank Tim Grube for his insightful comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript. We would also like to thank the anonymous NordSec reviewers for their feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gaballah, S.A., Abdullah, L., Tran, M.T., Zimmer, E., Mühlhäuser, M. (2022). On the Effectiveness of Intersection Attacks in Anonymous Microblogging. In: Reiser, H.P., Kyas, M. (eds) Secure IT Systems. NordSec 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13700. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22295-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22295-5_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22294-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22295-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)