Abstract
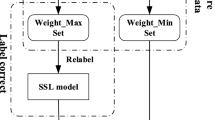
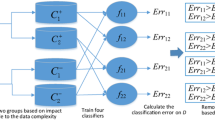
Recently, the robustness of machine learning against data poisoning attacks is widely concerned. As a subclass of poisoning attack, the label flipping attack can poison training data resulting in reducing the classification performance of training model. This attack poses a more serious threat in complex network or high-noise environments, such as in the environment of Internet of Things. In this paper, a new label flipping attack method and its defense strategy are proposed. First, a label flipping attack based on agglomerative hierarchical clustering is proposed. The attack uses agglomerative hierarchical clustering to identify vulnerable samples in training data and then carries out label flipping on them. To defend against this attack, a TrAdaBoost-based label correction defense method is proposed. This method uses the TrAdaBoost algorithm to update the weight of the contaminated data, and then uses the updated weight value to judge and remark the contaminated training samples. The contaminated samples are cleaned and used to retrain the classifier. Compared with the state-of-the-art methods, the proposed attack strategy can reduce the accuracy of the model more effectively and the proposed defense method can better protect the classification model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Springborg, A. A., Andersen, M. K., Hattel, K. H., et al.: Towards a secure API client generator for IoT devices (2022)
Naumov, M., Mudigere, D., Shi, H. J. M., Huang, J., Sundaraman, N., et al.: Deep learning recommendation model for personalization and recommendation systems. (2019)
Baracaldo, N., Chen, B., Ludwig, H., Safavi, A., Zhang, R.: Detecting poisoning attacks on machine learning in IoT environments. In: 2018 IEEE International Congress on Internet of Things (ICIOT), pp. 57–64 (2018)
Schwarzschild, A., Goldblum, M., Gupta, A., Dickerson, J. P., Goldstein, T.: Just how toxic is data poisoning? a unified benchmark for backdoor and data poisoning attacks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), pp. 9389–9398 (2021)
Chen, J.Y., Zou, J.F., Su, M.M., Zhang, L.Y.: A review of deep learning model for poison attack and defense. J. Cyber Sec. 5(04), 14–29 (2020)
Ren, Y., Zhou, Q., Wang, Z., Wu, T., Wu, G., Choo, K.K.R.: Query-efficient label-only attacks against black-box machine learning models. Comput. Sec. 90, 101698–101707 (2020)
Bootkrajang, J.: A generalised label noise model for classification in the presence of annotation errors. Neuro Comput. 192, 61–71 (2016)
Liu, H., Li, D., Li, Y.: Poisonous label attack: black-box data poisoning attack with enhanced conditional DCGAN. Neural Process. Lett. 53(6), 4117–4142 (2021)
Paudice, A., Munoz-Gonzalez, L., Lupu, EC.: Label sanitization against label flipping poisoning attacks. In: Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Springer, pp. 5–15 (2018)
Taheri, R., Javidan, R., Shojafar, M., Pooranian, Z., Miri, A., Conti, M.: On defending against label flipping attacks on malware detection systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(18), 14781–14800 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04831-9
Wu, R., Saxena, N., Jain, R.: Poisoning the search space in neural architecture search (2021)
Vasu, R. K., Seetharaman, S., Malaviya, S., Shukla, M., & Lodha, S.: Gradient-based data subversion attack against binary classifiers. (2021)
Ma, K., Xu, Q., Zeng, J., Cao, X., Huang, Q.: Poisoning attack against estimating from pairwise comparisons. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2021)
Tianyu, P., Xiao, Y., Yinpeng, D., Hang, S., Jun, Z.: Accumulative poisoning attacks on real-time data. Adv. Neu. Inf. Process. Syst. 34 (2021)
Chan, P.P.K., He, Z., Hu, X., Tsang, E.C.C., Yeung, D.S., Ng, W.W.Y.: Causative label flip attack detection with data complexity measures. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 12(1), 103–116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01159-7
Ishaq, N., Howard, T. J., Daniels, N. M.: Clustered hierarchical anomaly and outlier detection algorithms. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 5163–5174, IEEE (2021)
Ppkc, A., Fl, A., Zca, B., Ying, S.A., Dsy, C.: Transfer learning based countermeasure against label flipping poisoning attack. Inform. Sci. 548, 450–460 (2021)
Rosenfeld, E., Winston, E., Ravikumar, P., Kolter, Z.: Certified robustness to label-flipping attacks via randomized smoothing. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8230–8241. PMLR (2020)
Tavallali, P., Behzadan, V., Tavallali, P., Singhal, M.: Adversarial poisoning attacks and defense for general multi-class models based on synthetic reduced nearest neighbors (2021)
Cheng, N., Zhang, H., Li, Z.: Data sanitization against label flipping attacks using AdaBoost-based semi-supervised learning technology. Soft. Comput. 25(23), 14573–14581 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06384-y
Xie, Y., Shekhar, S., Li, Y.: Statistically-robust clustering techniques for mapping spatial hotspots: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 55(2), 1–38 (2022)
Rousseeuw, P.J.: Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987)
Antunes, J., Bernardino, A., Smailagic, A., et al.: Weighted multisource TrAdaBoost. In: Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, pp. 194–205. Springer, Cham (2019)
Arp, D., Spreitzenbarth, M., Hubner, M., Gascon, H., Rieck, K., Siemens, C. E. R. T.: Drebin: effective and explainable detection of android malware in your pocket. In: Proceedings of the 21st Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), Vol. 14, pp. 23–26 (2014)
Zhou, Y., Jiang, X.: Dissecting android malware: characterization and evolution. In: 2012 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 95–109. IEEE (2012)
Zhang, H., Cheng, N., Zhang, Y., Li, Z.: Label flipping attacks against naive Bayes on spam filtering systems. Appl. Intell. 2, 4503–4514 (2021)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by NSFC under Grants No. 61572170, Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province under Grant No. F2021205004, Science and Technology Foundation Project of Hebei Normal University under Grant No. L2021K06, Science Foundation of Hebei Province Under Grant No. C2020342, Science Foundation of Department of Human Resources and Social Security of Hebei Province under Grant No. ZD2021062, and Foundation of Hebei Normal University under Grant No. L072018Z10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, Q., Wang, X., Wang, F., Wang, C. (2023). A Label Flipping Attack on Machine Learning Model and Its Defense Mechanism. In: Meng, W., Lu, R., Min, G., Vaidya, J. (eds) Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13777. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22677-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22677-9_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22676-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22677-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)