Abstract
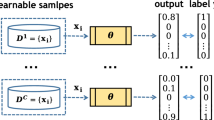
Federated Learning (FL) has recently attracted high attention since it allows clients to collaboratively train a model while the training data remains local. However, due to the inherent heterogeneity of local data distributions, the trained model usually fails to perform well on each client. Clustered FL has emerged to tackle this issue by clustering clients with similar data distributions. However, these model-dependent clustering methods tend to perform poorly and be costly. In this work, we propose a distribution similarity-based clustered federated learning framework FedDSMIC, which clusters clients by detecting the client-level underlying data distribution based on the model’s memory of training data. Furthermore, we extend the assumption about data distribution to a more realistic cluster structure. The center models are learned as good initial points to obtain common data properties in the cluster. Each client in a cluster gets a more personalized model by performing one step of gradient descent from the initial point. The empirical evaluation on real-world datasets shows that FedDSMIC outperforms popular state-of-the-art federated learning algorithms while keeping the lowest communication overhead.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-David, S., Blitzer, J., Crammer, K., Kulesza, A., Pereira, F., Vaughan, J.W.: A theory of learning from different domains. Mach. Learn. 79(1), 151–175 (2010)
Bezdek, J.C., Hathaway, R.J.: Some notes on alternating optimization. In: Pal, N.R., Sugeno, M. (eds.) AFSS 2002. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2275, pp. 288–300. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45631-7_39
Briggs, C., Fan, Z., Andras, P.: Federated learning with hierarchical clustering of local updates to improve training on non-IID data. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–9. IEEE (2020)
Caldarola, D., Mancini, M., Galasso, F., Ciccone, M., Rodolà, E., Caputo, B.: Cluster-driven graph federated learning over multiple domains. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2749–2758 (2021)
Caldas, S., et al.: Leaf: a benchmark for federated settings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.01097 (2018)
Chen, F., Luo, M., Dong, Z., Li, Z., He, X.: Federated meta-learning with fast convergence and efficient communication. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.07876 (2018)
Cohen, G., Afshar, S., Tapson, J., Van Schaik, A.: EMNIST: extending MNIST to handwritten letters. In: 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 2921–2926. IEEE (2017)
Corinzia, L., Beuret, A., Buhmann, J.M.: Variational federated multi-task learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.06268 (2019)
Cortes, C., Mohri, M.: Domain adaptation and sample bias correction theory and algorithm for regression. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 519, 103–126 (2014)
Fallah, A., Mokhtari, A., Ozdaglar, A.: On the convergence theory of gradient-based model-agnostic meta-learning algorithms. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 1082–1092. PMLR (2020)
Fallah, A., Mokhtari, A., Ozdaglar, A.: Personalized federated learning with theoretical guarantees: a model-agnostic meta-learning approach. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 3557–3568 (2020)
Finn, C., Abbeel, P., Levine, S.: Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1126–1135. PMLR (2017)
French, R.M.: Catastrophic forgetting in connectionist networks. Trends Cogn. Sci. 3(4), 128–135 (1999)
Ghosh, A., Chung, J., Yin, D., Ramchandran, K.: An efficient framework for clustered federated learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 19586–19597 (2020)
Hanzely, F., Richtárik, P.: Federated learning of a mixture of global and local models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05516 (2020)
Hsieh, K., Phanishayee, A., Mutlu, O., Gibbons, P.: The non-IID data quagmire of decentralized machine learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4387–4398. PMLR (2020)
Huang, Y., et al.: Personalized cross-silo federated learning on non-IID data. In: AAAI, pp. 7865–7873 (2021)
Jiang, Y., Konečnỳ, J., Rush, K., Kannan, S.: Improving federated learning personalization via model agnostic meta learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.12488 (2019)
Kairouz, P., et al.: Advances and open problems in federated learning. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 14(1–2), 1–210 (2021)
Karimireddy, S.P., Kale, S., Mohri, M., Reddi, S., Stich, S., Suresh, A.T.: Scaffold: stochastic controlled averaging for federated learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 5132–5143. PMLR (2020)
Khodak, M., Balcan, M.F.F., Talwalkar, A.S.: Adaptive gradient-based meta-learning methods. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32 (2019)
Konečnỳ, J., McMahan, H.B., Yu, F.X., Richtárik, P., Suresh, A.T., Bacon, D.: Federated learning: strategies for improving communication efficiency. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.05492 (2016)
Krizhevsky, A.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Master’s thesis, University of Tront (2009)
Kulkarni, V., Kulkarni, M., Pant, A.: Survey of personalization techniques for federated learning. In: 2020 Fourth World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems, Security and Sustainability (WorldS4), pp. 794–797. IEEE (2020)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Li, T., Hu, S., Beirami, A., Smith, V.: Ditto: fair and robust federated learning through personalization. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6357–6368. PMLR (2021)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated learning: challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 37(3), 50–60 (2020)
Li, T., Sahu, A.K., Zaheer, M., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A., Smith, V.: Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proc. Mach. Learn. Syst. 2, 429–450 (2020)
Mansour, Y., Mohri, M., Ro, J., Suresh, A.T.: Three approaches for personalization with applications to federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.10619 (2020)
Mansour, Y., Mohri, M., Rostamizadeh, A.: Domain adaptation: learning bounds and algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:0902.3430 (2009)
Marfoq, O., Neglia, G., Bellet, A., Kameni, L., Vidal, R.: Federated multi-task learning under a mixture of distributions. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34 (2021)
McCloskey, M., Cohen, N.J.: Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: the sequential learning problem. In: Psychology of Learning and Motivation, vol. 24, pp. 109–165. Elsevier (1989)
McMahan, B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., Arcas, B.A.: Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In: Artificial intelligence and statistics, pp. 1273–1282. PMLR (2017)
Mohri, M., Sivek, G., Suresh, A.T.: Agnostic federated learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4615–4625. PMLR (2019)
Nayak, G.K., Mopuri, K.R., Shaj, V., Radhakrishnan, V.B., Chakraborty, A.: Zero-shot knowledge distillation in deep networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4743–4751. PMLR (2019)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: Mobilenetv 2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Sarkar, S., Ghosh, A.K.: On perfect clustering of high dimension, low sample size data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(9), 2257–2272 (2019)
Sattler, F., Müller, K.R., Samek, W.: Clustered federated learning: model-agnostic distributed multitask optimization under privacy constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(8), 3710–3722 (2020)
Smith, V., Chiang, C.K., Sanjabi, M., Talwalkar, A.S.: Federated multi-task learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30 (2017)
Wang, H., Yurochkin, M., Sun, Y., Papailiopoulos, D., Khazaeni, Y.: Federated learning with matched averaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.06440 (2020)
Wang, K., Mathews, R., Kiddon, C., Eichner, H., Beaufays, F., Ramage, D.: Federated evaluation of on-device personalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.10252 (2019)
Xie, M., et al.: Multi-center federated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.08647 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Xiang, T., Hospedales, T.M., Lu, H.: Deep mutual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4320–4328 (2018)
Zhao, Y., Li, M., Lai, L., Suda, N., Civin, D., Chandra, V.: Federated learning with non-IID data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.00582 (2018)
Zhou, Z., Chu, L., Liu, C., Wang, L., Pei, J., Zhang, Y.: Towards fair federated learning. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 4100–4101 (2021)
Zhu, Z., Hong, J., Zhou, J.: Data-free knowledge distillation for heterogeneous federated learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 12878–12889. PMLR (2021)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China No. 2021YFB3101400 and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDC02040400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, X., Chen, X., Wang, S., Ding, Y., Li, K. (2023). Multi-initial-Center Federated Learning with Data Distribution Similarity-Aware Constraint. In: Meng, W., Lu, R., Min, G., Vaidya, J. (eds) Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing. ICA3PP 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13777. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22677-9_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22677-9_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22676-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22677-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)