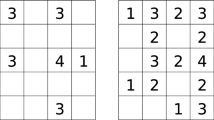
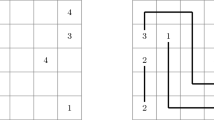
Abstract
This paper shows a zero-knowledge proof protocol of a solution to ABC end view puzzle using physical cards. Card-based cryptographic protocols are proposed to execute a secure multi-party calculation using physical cards instead of computers. This paper shows a card-based zero-knowledge proof of the ABC end view puzzle. The puzzle needs a new technique to prove the nearest neighbor from an end. We show a new zero-knowledge proof protocol to securely calculate the nearest neighbor using physical cards.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
It is unnecessary to divide the piles as z(1) and \(z[2-]\). We set \(y_j(1), y_j(2), z, y_j\) in this order, swap the second and the third, execute a random bisection cut, swap the second and the third, open the left two cards, and obtain the result as the AND protocol. The result is the same as the protocol shown in this paper.
References
Abe, Y., et al.: Efficient card-based majority voting protocols. New Gener. Comput. 40(1), 173–198 (2022)
den Boer, B.: More efficient match-making and satisfiability The Five Card Trick. In: Quisquater, J.-J., Vandewalle, J. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 1989. LNCS, vol. 434, pp. 208–217. Springer, Heidelberg (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46885-4_23
Bultel, X., Dreier, J., Dumas, J.G., Lafourcade, P.: Physical zero-knowledge proofs for Akari, Takuzu, Kakuro and Kenken. In: Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Fun with Algorithms, vol. 49, pp. 1–8. Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik (2016)
Bultel, X., et al.: Physical zero-knowledge proof for Makaro. In: Izumi, T., Kuznetsov, P. (eds.) SSS 2018. LNCS, vol. 11201, pp. 111–125. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03232-6_8
Chien, Y.-F., Hon, W.-K.: Cryptographic and physical zero-knowledge proof: from Sudoku to Nonogram. In: Boldi, P., Gargano, L. (eds.) FUN 2010. LNCS, vol. 6099, pp. 102–112. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13122-6_12
crossa@list.ru: Puzzles: Abc end view. http://www.cross-plus-a.com/puzzles.htm#EasyAsABC. Accessed 31 Aug 2022
Dumas, J.-G., Lafourcade, P., Miyahara, D., Mizuki, T., Sasaki, T., Sone, H.: Interactive Physical Zero-Knowledge Proof for Norinori. In: Du, D.-Z., Duan, Z., Tian, C. (eds.) COCOON 2019. LNCS, vol. 11653, pp. 166–177. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26176-4_14
Gradwohl, R., Naor, M., Pinkas, B., Rothblum, G.N.: Cryptographic and physical zero-knowledge proof systems for solutions of Sudoku puzzles. Theor. Comput. Syst. 44(2), 245–268 (2009)
Hart, E., McGinnis, J.A.: Physical zero-knowledge proofs for flow free, Hamiltonian cycles, and many-to-many k-disjoint covering paths (2022) arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.04113
Kastner, J., et al.: The minimum number of cards in practical card-based protocols. In: Takagi, T., Peyrin, T. (eds.) ASIACRYPT 2017. LNCS, vol. 10626, pp. 126–155. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70700-6_5
Komano, Y., Mizuki, T.: Physical zero-knowledge proof protocol for topswops. In: Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Information Security Practice and Experience (ISPEC 2022), LNCS. Springer (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21280-2_30
Lafourcade, P., Miyahara, D., Mizuki, T., Robert, L., Sasaki, T., Sone, H.: How to construct physical zero-knowledge proofs for puzzles with a “single loop” condition. Theor. Comput. Sci. 888, 41–55 (2021)
Manabe, Y.: Survey: card-based cryptographic protocols to calculate primitives of boolean functions. Int. J. Comput. Softw. Eng. 27(1), 178 (2022)
Miyahara, D., Hayashi, Y.I., Mizuki, T., Sone, H.: Practical card-based implementations of Yao’s millionaire protocol. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 803, 207–221 (2020)
Miyahara, D., et al.: Card-based ZKP protocols for Takuzu and Juosan. In: Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Fun with Algorithms (FUN 2020). Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik (2020)
Miyahara, D., Sasaki, T., Mizuki, T., Sone, H.: Card-based physical zero-knowledge proof for kakuro. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 102(9), 1072–1078 (2019)
Mizuki, T., Asiedu, I.K., Sone, H.: Voting with a logarithmic number of cards. In: Mauri, G., Dennunzio, A., Manzoni, L., Porreca, A.E. (eds.) UCNC 2013. LNCS, vol. 7956, pp. 162–173. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39074-6_16
Mizuki, T., Shizuya, H.: A formalization of card-based cryptographic protocols via abstract machine. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 13(1), 15–23 (2014)
Mizuki, T., Sone, H.: Six-card secure AND and four-card secure XOR. In: Deng, X., Hopcroft, J.E., Xue, J. (eds.) FAW 2009. LNCS, vol. 5598, pp. 358–369. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02270-8_36
Nakai, Takeshi, Misawa, Yuto, Tokushige, Yuuki, Iwamoto, Mitsugu, Ohta, Kazuo: How to Solve Millionaires’ Problem with Two Kinds of Cards. New Gener. Comput. 39(1), 73–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00354-020-00118-8
Ono, H., Manabe, Y.: Efficient card-based cryptographic protocols for the millionaires problem using private input operations. In: Proceedings of 13th Asia Joint Conference on Information Security(AsiaJCIS 2018), pp. 23–28 (2018)
Robert, L., Miyahara, D., Lafourcade, P., Libralesso, L., Mizuki, T.: Physical zero-knowledge proof and np-completeness proof of Suguru puzzle. Inf. Comput. 285, 104858 (2022)
Robert, L., Miyahara, D., Lafourcade, P., Mizuki, T.: Card-based ZKP for connectivity: applications to nurikabe, Hitori and Heyawake. New Gener. Comput. 40(1), 149–171 (2022)
Robert, L., Miyahara, D., Lafourcade, P., Mizuki, T.: Card-based ZKP protocol for Nurimisaki. In: Proceedings of 24th International Symposium on Stabilization, Safety, and Security of Distributed Systems (SSS 2022), LNCS. Springer (2022)
Ruangwises, S.: An improved physical ZKP for nonogram. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.14020 (2021)
Ruangwises, S.: Two standard decks of playing cards are sufficient for a ZKP for sudoku. New Gener. Comput. 40(1), 49–65 (2022)
Ruangwises, Suthee, Itoh, Toshiya: Physical Zero-Knowledge Proof for Number link Puzzle and k Vertex-Disjoint Paths Problem. New Generation Computing 39(1), 3–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00354-020-00114-y
Ruangwises, Suthee, Itoh, Toshiya: Physical zero-knowledge proof for Ripple Effect. Theor. Comput. Sci. 895, 115–123 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2021.09.034
Ruangwises, S., Itoh, T.: Physical ZKP for Makaro using a standard deck of cards. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.12042 (2021)
Ruangwises, S., Itoh, T.: How to physically verify a rectangle in a grid: a physical ZKP for shikaku (2022). arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.09788
Sasaki, T., Miyahara, D., Mizuki, T., Sone, H.: Efficient card-based zero-knowledge proof for Sudoku. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 839, 135–142 (2020)
Shinagawa, Kazumasa, Nuida, Koji: A single shuffle is enough for secure card-based computation of any Boolean circuit. Discrete Applied Mathematics 289, 248–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dam.2020.10.013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fukasawa, T., Manabe, Y. (2022). Card-Based Zero-Knowledge Proof for the Nearest Neighbor Property: Zero-Knowledge Proof of ABC End View. In: Batina, L., Picek, S., Mondal, M. (eds) Security, Privacy, and Applied Cryptography Engineering. SPACE 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13783. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22829-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22829-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22828-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22829-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)