Abstract
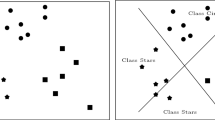
Given M vectors in N-dimensional attribute space, it is much easier to find M hyperplanes that separate each of the vectors from all the others than to solve M arbitrary linear dichotomies with approximately equal class memberships. An explanation of the rapid growth with M and N of the number of separable one-against-all linear halfplane dichotomies is proposed in terms of convex polyhedra in a hyperspherical shell. The counterintuitive surge is illustrated by averaged results on pseudo-random integer arrays obtained by Linear Programming and Neural Networks. Although the initial motivation arose from seemingly arbitrary rankings of scientists and universities, this project is not directed at any application.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagy, G., Krishnamoorthy, M.: MeFirst ranking and multiple dichotomies via linear programming and neural networks. In: ICPR 2022 (2022). Accepted
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern Classification. Wiley, New York (2001)
Fukunaga, K.: Statistical Pattern Recognition, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge (1990)
Theodoridis, S., Koutroumbas, K.: Pattern Recognition. Academic Press, Cambridge (2009)
Bishop, C.M.: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer, New York (2006). ISBN 978-0387-31073-2
Li, F.-F., Fergus, R., Perona, P.: One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(4), 594–611 (2006)
Nilsson, N.J.: Learning Machines: The Foundations of Trainable Pattern-Classifying Systems. McGraw-Hill, New York (1965)
Hughes, G.F.: On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory IT 4(1), 55–63 (1968)
Hilbert, D., Cohn-Vossen, S.: Geometry and the Imagination, Chap. III. Chelsea Publishing, Hartford (1952)
Coxeter, H.S.M.: Introduction to Geometry, Chap. 22. Wiley, Hoboken (1989)
Woldfram MathWorld, Hypersphere. https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Hypersphere.html
Shawe-Taylor, J., Cristianini, N.: Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Dantzig, G.B.: Maximization of a linear function of variables subject to linear inequalities. In: Koopmans, T.C. (ed.) Activity Analysis of Production and Allocation. Wiley & Chapman-Hall (1951)
Gass, S.L.: Linear Programming, 5th edn. Dover, Downers Grove (2003)
Karmarkar, N.: A new polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC 1984, p. 302 (1984)
Nabli, H.: An overview on the simplex algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 210(2), 479–489 (2009)
Rosenblatt, F.: The perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 65, 386 (1958)
Rosenblatt, F.: Principles of Neurodynamics. Spartan Books, New York (1962)
Barker, T.: A Computer Program for Simulation of Perceptrons and Similar Neural Networks: User’s Manual. CSRP Report #8. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY (1966)
MATLAB: Deep Learning Toolbox. https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html. Accessed 12 Jan 2021
Muller, J.Z.: The Tyranny of Metrics. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2018)
Biangioli, M., Lippman, A.: Gaming the Metrics. MIT Press, Cambridge (2020)
Johnson, S.: The Writing on the Wall, The New York Times Magazine, 17 April 2022 (2022)
Ioannidis, J.P.A., Boyack, K.W., Baas, J.: Updated science-wide author databases of standardized citation indicators. PLoS Biol. 18(10), e3000918 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000918
Mendelay: Data for “Updated science-wide author databases of standardized citation indicators”. https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/btchxktzyw/2. Accessed 10 Apr 2021
QS World University Ratings. https://group.intesasanpaolo.com/content/dam/portalgroup/nuove-immagini/sociale/2022_QS_World_University_Rankings_1.pdf. Accessed 30 Nov 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nagy, G., Krishnamoorthy, M. (2022). One-Against-All Halfplane Dichotomies. In: Krzyzak, A., Suen, C.Y., Torsello, A., Nobile, N. (eds) Structural, Syntactic, and Statistical Pattern Recognition. S+SSPR 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13813. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23028-8_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23028-8_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23027-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23028-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)