Abstract
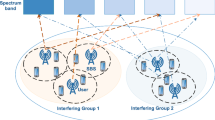
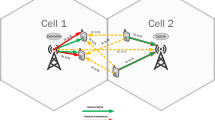
In this work, we consider a downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) network where multiple single-antenna users are served by multiple multi-antenna base stations (BSs). For practical considerations, we assume that only the imperfect channel state information (CSI) of each user is available at the BSs. Based on this model, the problem of joint user grouping and robust beamforming design is formulated to minimize the sum transmission power, and meanwhile, guarantee the quality of service requirements of users. Due to the integer variables of user grouping, coupling effects of beamformers, and infinitely many constraints caused by the imperfect CSI, the formulated problem is challenging to solve. For computational complexity reduction, the original problem is divided into a user grouping subproblem and a robust beamforming design subproblem. First, the user grouping problem is efficiently solved by a coalition formation game based algorithm. Then, for the robust beamforming design problem, a semidefinite relaxation (SDR) based method is proposed to produce a suboptimal solution efficiently. Moreover, we provide a sufficient condition under which the SDR based approach can guarantee to obtain an optimal rank-one solution, which is theoretically analyzed. Simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forecast, C.V.: Cisco visual networking index: global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2016–2017. White Paper, Cisco San Jose, CA, USA (2017)
Elbayoumi, M., Kamel, M., Hamouda, W., Youssef, A.: NOMA-assisted machine-type communications in UDN: state-of-the-art and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 22, 1 (2020)
Ding, Z., Lei, X., Karagiannidis, G.K., Schober, R., Yuan, J., Bhargava, V.K.: A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G networks: research challenges and future trends. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35(10), 2181–2195 (2017)
Fang, F., Zhang, H., Cheng, J., Leung, V.C.M.: Energy-efficient resource allocation for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access network. IEEE Trans. Commun. 64(9), 3722–3732 (2016)
Xu, Y., et al.: Joint beamforming and power-splitting control in downlink cooperative SWIPT NOMA systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 15(18), 4874–4886 (2017)
Wang, J., Kang, X., Sun, S., Liang, Y.: Throughput maximization for peer-assisted wireless powered IoT NOMA networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 19, 1 (2020)
Fang, F., Xu, Y., Pham, Q.-V., Ding, Z.: Energy-efficient design of IRS-NOMA networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Techn. 69(11), 14 088–14 092 (2020)
Fang, F., Xu, Y., Ding, Z., Shen, C., Peng, M., Karagiannidis, G.K.: Optimal resource allocation for delay minimization in NOMA-MEC networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(12), 7867–7881 (2020)
Ding, Z., Fan, P., Poor, H.V.: Impact of user pairing on 5G nonorthogonal multiple-access downlink transmissions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Techn. 65(8), 6010–6023 (2016)
Cui, J., Liu, Y., Ding, Z., Fan, P., Nallanathan, A.: Optimal user scheduling and power allocation for millimeter wave NOMA systems. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 17(3), 1502–1517 (2018)
Di, B., Song, L., Li, Y.: Sub-channel assignment, power allocation, and user scheduling for non-orthogonal multiple access networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 15(11), 7686–7698 (2016)
Xu, Y., Cai, D., Fang, F., Ding, Z., Shen, C., Zhu, G.: Outage constrained power efficient design for downlink NOMA systems with partial HARQ. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(8), 5188–5201 (2020)
Ni, W., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Tian, H., Chen, Y.: Resource allocation for Multi-Cell IRS-Aided NOMA networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 20(7), 4253–4268 (2021)
Chen, G., Qiu, L., Ren, C.: On the performance of cluster-based MIMO-NOMA in Multi-Cell dense networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(8), 4773–4787 (2020)
Ding, J., Cai, J.: Two-side coalitional matching approach for joint MIMO-NOMA clustering and BS selection in Multi-Cell MIMO-NOMA systems. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 19(3), 2006–2021 (2020)
Cai, D., Xu, Y., Fang, F., Ding, Z., Fan, P.: On the impact of time-correlated fading for downlink NOMA. IEEE Trans. Commun. 67(6), 4491–4504 (2019)
Wang, Z., Ng, D.W.K., Wong, V.W.S., Schober, R.: Robust beamforming design in C-RAN with sigmoidal utility and capacity-limited backhaul. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 16(9), 5583–5598 (2017)
Liang, W., Ding, Z., Li, Y., Song, L.: User pairing for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access networks using matching algorithm. IEEE Trans. Commun. 65(12), 5319–5332 (2017)
Saad, W., Han, Z., Debbah, M., Hjorungnes, A., Basar, T.: Coalitional game theory for communication networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 26(5), 77–97 (2009)
Bogomolnaia, A., Jackson, M.O.: The stability of hedonic coalition structures. Games Econ. Behav. 38(2), 201–230 (2002)
Luo, Z.Q., Ma, W.K., So, A.M.C., Ye, Y., Zhang, S.: Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 27(3), 20–34 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The work of Y. Xu was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grants No. 2021M693100 and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation under Grants No. 2021A1515110018. The work of D. Cai was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 62001190 and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grants No. 2021M691249. The work of Z. Dong was supported by National Science Foundation of China under Grant 61561046 and the Key Research & Development and Transformation Plan of Science and Technology Program for Tibet Autonomous Region (No. XZ201901-GB-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, Y., Cai, D., Wang, S., Dong, Z., Zhou, W. (2022). Energy-Efficient Multi-cell NOMA Design via Coalition Formation Game. In: Fang, F., Shu, F. (eds) Game Theory for Networks. GameNets 2022. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 457. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23141-4_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23141-4_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23140-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23141-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)