Abstract
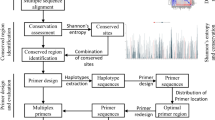
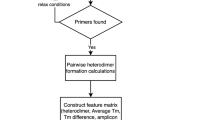
Objective: To design and implement a simple and highly integrated primer design software for detection of highly variable bacteria. Methods: Firstly, gene named entity recognition technology was applied to annotate the genes in the literature, thus the conservative gene knowledge base of highly variable bacteria could be established. Then, new primer design workflow was created by integrating Clustal Omega, Gblocks, Primer3, MFEprimer3.0, which achieves high-performance specificity detection with improved index algorithms and parallel computing. Finally, multiple primers could be obtained by combining primers designed by different conservative genes based on the greedy algorithm. Results: A web-based primer design software was implemented. Primers were designed for five highly variable bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Shigella, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella. By comparison, the single primers designed by our software were more specific and sensitive than primers in the literature for detecting the same conservative gene. The multiple primers designed for each bacterium have strong specificity, and the coverage rate of Escherichia coli primers is 93. 14% in terms of sensitivity, and the coverage rate of other bacterial primers is more than 99%. Conclusion: The software can be applied to the design of PCR primers for the detection of highly variable bacteria.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ling, T.K., Xiong, J., Yu, Y., Lee, C.C., Ye, H., Hawkey, P.M.: Multicenter antimicrobial susceptibility survey of gram-negative bacteria isolated from patients with community-acquired infections in the People’s Republic of China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(1), 374–378 (2006)
Conter, C.C., et al.: PCR primers designed for new world Leishmania: a systematic review. Exp. Parasitol. 207, 107773 (2019)
Bui, T.H., et al.: Multiplex PCR method for differentiating highly pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica and low pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 83(12), 1982–1987 (2021)
Bouju-Albert, A., Saltaji, S., Dousset, X., Prévost, H., Jaffrès, E.: Quantification of Viable Brochothrix thermosphacta in Cold-Smoked Salmon Using PMA/PMAxx-qPCR. Front Microbiol 12, 654178 (2021)
Wang, K., et al.: MFEprimer-3.0: quality control for PCR primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(1),W610–W613 (2019)
Sievers, F., et al.: Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 539 (2011)
Talavera, G., Castresana, J., Kjer, K., Page, R., Sullivan, J.: Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 56(4), 564–577 (2007)
Untergasser, A., et al.: Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(15), e115 (2012)
Qu, W., Li, J., Cai, H., Zhao, D.: PCR primer design for the rapidly evolving SARS-CoV-2 genome. Methods Mol. Biol. 2392, 185–197 (2021)
Tong, F., Luo, Z., Zhao, D.S.: A deep network based integrated model for dis-ease named entity recognition. IEEE 2017, 618 (2017)
Velhner, M., Suvajdžić, L., Todorović, D., Milanov, D., Kozoderović, G.: Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli: diagnosis, virulence and prevention. Arch. Vet. Med. 11(2), 21–31 (2019)
Hernández-Chiñas, U., et al.: Characterization of auto-agglutinating and non-typeable uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 13(6), 465–472 (2019)
Soltan Dallal, M.M., Yaghoubi, S., Dezhkam, A., Yavari, S., Jamee, A., Yaghoubi, S.: Rapid identification of mutations in quinolone-resistant Shigella isolates by scanning of gyrA and parC genes using high-resolution melting curve analysis. Online J. Health Allied Sci. 19(1), 1–3 (2020)
Waterman, S.R., Small, P.L.C.: Identification of the promoter regions and σs-dependent regulation of the gadA and gadBC genes associated with glutamate-dependent acid resistance in Shigella flexneri. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 225(1), 155–160 (2003)
Jung, Y.S., Frank, J.F., Brackett, R.E., Chen, J.: Polymerase chain reaction detection of Listeria monocytogenes on frankfurters using oligonucleotide primers targeting the genes encoding internalin AB. J. Food Prot. 66(2), 237–241 (2003)
Du, J., Wu, S., Niu, L., Li, J., Zhao, D., Bai, Y.: A gold nanoparticles-assisted multiplex PCR assay for simultane-ous detection of Salmonella typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal. Methods 12(2), 212–217 (2020)
Amin, B., Nasir, N.: Evaluation of femA gene and different primers for mecA gene for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Zanco J. Pure Appl. Sci. 31(3), 16–22 (2019)
Al-Talib, H., et al.: A pentaplex PCR assay for the rapid detection of methicil-lin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Panton-Valentine Leucocidin. BMC Micro-biol 9, 113 (2009)
Ben-Darif, E., et al.: Development of a multiplex primer extension assay for rapid detection of Salmonella isolates of diverse serotypes. J. Clin. Microbiol 48(4), 1055–1060 (2010)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank other people working in the same group for their help and guidance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hu, D., Qu, W., Tong, F., Zheng, X., Li, J., Zhao, D. (2022). An Efficient and User-Friendly Software for PCR Primer Design for Detection of Highly Variable Bacteria. In: Bansal, M.S., Cai, Z., Mangul, S. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13760. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23198-8_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23198-8_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23197-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23198-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)