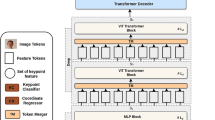
Abstract
Attention-only Transformers [34] have been applied to solve Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks and Computer Vision (CV) tasks. One particular Transformer architecture developed for CV is the Vision Transformer (ViT) [15]. ViT models have been used to solve numerous tasks in the CV area. One interesting task is the pose estimation of a human subject. We present our modified ViT model, Un-TraPEs (UNsupervised TRAnsformer for Pose Estimation), that can reconstruct a subject’s pose from its monocular image and estimated depth. We compare the results obtained with such a model against a ResNet [17] trained from scratch and a ViT finetuned to the task and show promising results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Images are augmented via random drops, random replace, color distortion, blurring, and grey-scaling.
- 2.
In the original paper, this value could be specified arbitrarily or even randomly per pixel. In our application, however, we want to simulate an occluded subject, so the user mask would reflect this as implemented.
- 3.
The number of patches is determined by the size of each patch and the dimension of the image; as we have set the size of a patch to \(16\times 16\) pixels, we end up with 300 patches.
- 4.
This has no repercussion on the estimation of the pose as the skeleton is normalized before any transformation and denormalized only when showing the prediction on image.
References
Andriluka, M., Pishchulin, L., Gehler, P., Schiele, B.: 2D human pose estimation: new benchmark and state of the art analysis. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014)
Anguelov, D., Srinivasan, P., Koller, D., Thrun, S., Rodgers, J., Davis, J.: Scape: shape completion and animation of people. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2005, pp. 408–416 (2005)
Atito, S., Awais, M., Kittler, J.: SIT: self-supervised vision transformer (2021)
Avanzato, R., Beritelli, F., Russo, M., Russo, S., Vaccaro, M.: Yolov3-based mask and face recognition algorithm for individual protection applications, vol. 2768, pp. 41–45 (2020)
Baldi, T.L., Farina, F., Garulli, A., Giannitrapani, A., Prattichizzo, D.: Upper body pose estimation using wearable inertial sensors and multiplicative Kalman filter. IEEE Sens. J. 20(1), 492–500 (2019)
Brandizzi, N., Bianco, V., Castro, G., Russo, S., Wajda, A.: Automatic RGB inference based on facial emotion recognition, vol. 3092, pp. 66–74 (2021)
Capizzi, G., Lo Sciuto, G., Napoli, C., Tramontana, E., Wozniak, M.: A novel neural networks-based texture image processing algorithm for orange defects classification. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Appl. 13(2), 45–60 (2016)
Chalearn: Montalbano v2 dataset, eCCV 2014 (2014)
Chen, M., et al.: Generative pretraining from pixels. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1691–1703. PMLR (2020)
Chen, W., et al.: A survey on hand pose estimation with wearable sensors and computer-vision-based methods. Sensors 20(4), 1074 (2020)
Chithrananda, S., Grand, G., Ramsundar, B.: Chemberta: large-scale self-supervised pretraining for molecular property prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.09885 (2020)
Choutas, V., Pavlakos, G., Bolkart, T., Tzionas, D., Black, M.J.: Monocular expressive body regression through body-driven attention. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12355, pp. 20–40. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58607-2_2
Das, S., Kishore, P.S.R., Bhattacharya, U.: An end-to-end framework for unsupervised pose estimation of occluded pedestrians. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) (2020)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale (2021)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition . In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2015)
Honari, S., Constantin, V., Rhodin, H., Salzmann, M., Fua, P.: Unsupervised learning on monocular videos for 3D human pose estimation (2021)
Jaiswal, A., Babu, A.R., Zadeh, M.Z., Banerjee, D., Makedon, F.: A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning (2021)
Lin, T.-Y., et al.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8693, pp. 740–755. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48
Liu, A.T., Li, S.W., Lee, H.Y.: Tera: self-supervised learning of transformer encoder representation for speech. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.06028 (2020)
Liu, J., Wang, G., Hu, P., Duan, L.Y., Kot, A.C.: Global context-aware attention LSTM networks for 3D action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1647–1656 (2017)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.14030 (2021)
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G., Black, M.J.: SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 34(6), 1–16 (2015)
Naseer, M., Ranasinghe, K., Khan, S., Hayat, M., Khan, F.S., Yang, M.H.: Intriguing properties of vision transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.10497 (2021)
Peng, X.B., Abbeel, P., Levine, S., van de Panne, M.: Deepmimic: example-guided deep reinforcement learning of physics-based character skills. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 37(4), 1–14 (2018)
Perla, S., Das, S., Mukherjee, P., Bhattacharya, U.: Cluenet: a deep framework for occluded pedestrian pose estimation. In: 30th British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–15 (2019)
Rhodin, H., Salzmann, M., Fua, P.: Unsupervised geometry-aware representation for 3D human pose estimation (2018)
Sigal, L., Black, M.J.: Humaneva: synchronized video and motion capture dataset for evaluation of articulated human motion. Brown Univertsity TR 120(2) (2006)
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15(1), 1929–1958 (2014)
Starczewski, J.T., Pabiasz, S., Vladymyrska, N., Marvuglia, A., Napoli, C., Woźniak, M.: Self organizing maps for 3D face understanding. In: Rutkowski, L., Korytkowski, M., Scherer, R., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zadeh, L.A., Zurada, J.M. (eds.) ICAISC 2016. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9693, pp. 210–217. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39384-1_19
Starke, S., Zhao, Y., Zinno, F., Komura, T.: Neural animation layering for synthesizing martial arts movements. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 40(4), 1–16 (2021)
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles, A., Jégou, H.: Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 10347–10357. PMLR (2021)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need (2017)
Wang, Y., Huang, M., Zhu, X., Zhao, L.: Attention-based LSTM for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 606–615 (2016)
Wozniak, M., Polap, D., Kosmider, L., Napoli, C., Tramontana, E.: A novel approach toward X-ray images classifier, pp. 1635–1641 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2015.230
Wozniak, M., Polap, D., Napoli, C., Tramontana, E.: Graphic object feature extraction system based on cuckoo search algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 66, 20–31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.08.068
Xie, Z., et al.: Self-supervised learning with swin transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.04553 (2021)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmentation (2017)
Zhou, Y., Habermann, M., Habibie, I., Tewari, A., Theobalt, C., Xu, F.: Monocular real-time full body capture with inter-part correlations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4811–4822 (2021)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the HERMES (WIRED) project within Sapienza University of Rome Big Research Projects Grant framework 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Brandizzi, N. et al. (2023). Unsupervised Pose Estimation by Means of an Innovative Vision Transformer. In: Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13589. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23480-4_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23480-4_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23479-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23480-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)