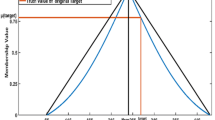
Abstract
This study considers a very important issue, which is the impact of preprocessing on model performance. On the example of data describing taxicab trips in New York City, a model predicting the average speed of a trip was built. The effectiveness of the obtained model was examined using relative error. The results were compared with the models obtained after prior data cleaning from the records containing missing data. Additionally, the effect of removing outliers on model quality was examined. An integral part of the paper is the description of a new method of anomaly detection. The author’s method involves fuzzy classification of the declared distance into three classes. As an indicator to allow for classification, the percentage of redundant distance with respect to Manhattan distance was selected. The results of a wide range of numerical experiments confirm the necessity of preprocessing. Comparison of a number of competing anomaly detection and prediction model building methods allows for reasonable generalization of the obtained conclusions. Additionally, the skillful use of fuzzy sets for anomaly detection allowed the development of a method that can be generalized to other transportation issues.
The work was co-financed by the Lublin University of Technology Scientific Fund: FD-20/IT-3/002.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitkin, M., Wilson, G.T.: Mixture models, outliers, and the EM algorithm. Technometrics 22(3), 325–331 (1980)
Alasadi, S.A., Bhaya, W.S.: Review of data preprocessing techniques in data mining. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 12(16), 4102–4107 (2017)
Arabameri, A., Pradhan, B., Rezaei, K., Sohrabi, M., Kalantari, Z.: Gis-based landslide susceptibility mapping using numerical risk factor bivariate model and its ensemble with linear multivariate regression and boosted regression tree algorithms. J. Mt. Sci. 16(3), 595–618 (2019)
Berthold, M.R.: Mixed fuzzy rule formation. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 32(2–3), 67–84 (2003)
Breunig, M.M., Kriegel, H.P., Ng, R.T., Sander, J.: LOF: identifying density-based local outliers. In: Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 93–104 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1145/342009.335388
Coppersmith, D., Hong, S.J., Hosking, J.R.: Partitioning nominal attributes in decision trees. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 3(2), 197–217 (1999)
Donovan, B., Work, D.: New York city taxi trip data (2010–2013) (2014). https://doi.org/10.13012/J8PN93H8
Friedman, J.H.: Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 38(4), 367–378 (2002)
Kamiran, F., Calders, T.: Data preprocessing techniques for classification without discrimination. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 33(1), 1–33 (2012)
Karczmarek, P., Kiersztyn, A., Pedrycz, W.: Fuzzy set-based isolation forest. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2020)
Karczmarek, P., Kiersztyn, A., Pedrycz, W., Al, E.: K-means-based isolation forest. Knowl.-Based Syst. 195, 105659 (2020)
Karczmarek, P., Kiersztyn, A., Pedrycz, W., Czerwiński, D.: Fuzzy c-means-based isolation forest. Appl. Soft Comput. 106, 107354 (2021)
Kiersztyn, A., Karczmarek, P., Kiersztyn, K., Pedrycz, W.: The concept of detecting and classifying anomalies in large data sets on a basis of information granules. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2020)
Kiersztyn, A., Karczmarek, P., Kiersztyn, K., Pedrycz, W.: Detection and classification of anomalies in large data sets on the basis of information granules. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(8), 2850–2860 (2021)
Kiersztyn, A., et al.: Data imputation in related time series using fuzzy set-based techniques. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Kiersztyn, A., et al.: A comprehensive analysis of the impact of selecting the training set elements on the correctness of classification for highly variable ecological data. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2021)
Kiersztyn, K.: Intuitively adaptable outlier detector. Stat. Anal. Data Min.: ASAData Sci. J. 15(4), 463–479 (2021)
Liu, F.T., Ting, K.M., Zhou, Z.H.: Isolation-based anomaly detection. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 6(1) (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2133360.2133363
Łopucki, R., Kiersztyn, A., Pitucha, G., Kitowski, I.: Handling missing data in ecological studies: ignoring gaps in the dataset can distort the inference. Ecol. Modell. 468, 109964 (2022)
Osman, M.S., Abu-Mahfouz, A.M., Page, P.R.: A survey on data imputation techniques: water distribution system as a use case. IEEE Access 6, 63279–63291 (2018)
Piironen, J., Vehtari, A.: Comparison of Bayesian predictive methods for model selection. Stat. Comput. 27(3), 711–735 (2017)
Priyanka, K.D.: Decision tree classifier: a detailed survey. Int. J. Inf. Decis. Sci. 12(3), 246–269 (2020)
Raval, K.M.: Data mining techniques. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 2(10) (2012)
Rousseeuw, P.J., Driessen, K.V.: A fast algorithm for the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Technometrics 41(3), 212–223 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1999.10485670
Vijayarani, S., Ilamathi, M.J., Nithya, M., et al.: Preprocessing techniques for text mining-an overview. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Commun. Netw. 5(1), 7–16 (2015)
Wang, H., Bah, M.J., Hammad, M.: Progress in outlier detection techniques: a survey. IEEE Access 7, 107964–108000 (2019)
Wu, C., Chau, K.W., Fan, C.: Prediction of rainfall time series using modular artificial neural networks coupled with data-preprocessing techniques. J. Hydrol. 389(1–2), 146–167 (2010)
Zhang, Z.: Missing data imputation: focusing on single imputation. Ann. Transl. Med. 4(1) (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kiersztyn, A., Kiersztyn, K. (2023). The Impact of Data Preprocessing on Prediction Effectiveness. In: Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J.M. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing. ICAISC 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13588. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23492-7_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23492-7_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23491-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23492-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)