Abstract
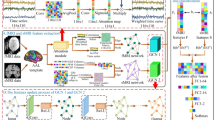
Machine learning and computer vision have opened new pathways to investigate imaging data captured from different sensors. Numerous application areas are getting benefit from these advancements and one of these areas is medical imaging. Despite rapid advancements in machine learning based medical condition diagnosis systems (CADs), some ailments and disorders are hard to diagnose/classify due to the absence or the lack of consensus on biomarkers for specific disorders, like the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). In this study, the challenging problem of classification of ASD using the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data is tackled. Hence, we propose an interpretable deep neural network based approach for ASD detection from MRI images. Our proposed explanation method is based on the selection of four regions of interest from the MRI images. The four significant CC400 functional brain parcellations are then concatenated and fed to a LeNet-5-based convolutional neural network to predict ASD. The performances of the proposed approach are evaluated on ABIDE dataset and promising results are achieved. Three augmented datasets are considered and an accuracy of \(95\%\) is achieved by using LeNet-5 which outperforms VGG16 and ResNet-50. The achieved accuracy outperforms also the existing deep neural networks based approaches on ABIDE dataset. The use of the four significant CC400 functional brain parcellations makes our approach more interpretable and more accurate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, H., Parikh, N.A., He, L.: A novel transfer learning approach to enhance deep neural network classification of brain functional connectomes. Front. Neurosci. 12, 491 (2018)
Dekhil, O., et al.: Using resting state functional MRI to build a personalized autism diagnosis system. PloS ONE 13(10), e020635 (2018)
Sherkatghanad, Z., et al.: Automated detection of autism spectrum disorder using a convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. Annalen der Physik 13, 1325 (2020)
Bullmore, E., Sporns, O.: Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 186 (2009)
Yang, X., Schrader, P.T., Zhang, N.: A deep neural network study of the ABIDE repository on autism spectrum classification. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. (IJACSA) 11(4) (2020). https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110401
Bellak, L.: The schizophrenic syndrome and attention deficit disorder: thesis, antithesis, and synthesis ? Am. Psychol. 49(1), 25 (1994)
Just, M.A., Cherkassky, V.L., Buchweitz, A., Keller, T.A., Mitchell, T.M.: Identifying autism from neural representations of social interactions: neurocognitive markers of autism. PloS ONE 9(12), e113879 (2014)
Sabuncu, M.R., Konukoglu, E.: Clinical prediction from structural brain MRI scans: a large-scale empirical study. Neuroinformatics 13(1), 31–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9238-1
Vapnik, V.: The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer, New York (2013)
Konukoglu, E., Glocker, B., Zikic, D., Criminisi, A.: Neighbourhood approximation forests. In: Ayache, N., Delingette, H., Golland, P., Mori, K. (eds.) MICCAI 2012. LNCS, vol. 7512, pp. 75–82. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33454-2_10
Tipping, M.E.: Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 1, 211–244 (2001)
Sherkatghanad, Z., et al.: Automated detection of autism spectrum disorder using a convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. 13, 1325 (2020)
Huang, Z.A., Zhu, Z., Yau, C.H., Tan, K.C.: Identifying autism spectrum disorder from resting-state fMRI using deep belief network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32, 847–2861 (2020)
Hinton, G.E.: Deep belief networks. Scholarpedia 4(5), 5947 (2009). Revision #91189
Thomas, R.M., Gallo, S., Cerliani, L., Zhutovsky, P., El-Gazzar, A., van Wingen, G.: Classifying autism spectrum disorder using the temporal statistics of resting-state functional MRI data with 3D convolutional neural networks. Front. Psychiatry 11, 440 (2020)
Dvornek, N.C., Ventola, P., Pelphrey, K.A., Duncan, J.S.: Identifying autism from resting-state fMRI using long short-term memory networks. In: Wang, Q., Shi, Y., Suk, H.-I., Suzuki, K. (eds.) MLMI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10541, pp. 362–370. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67389-9_42
Di Martino, A., et al.: The autism brain imaging data exchange: towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 19(6), 659–667 (2014)
Dvornek, N.C., Ventola, P., Duncan, J.S.: Combining phenotypic and resting-state fMRI data for autism classification with recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 725–728. IEEE (2018)
Eslami, T., Mirjalili, V., Fong, A., Laird, A.R., Saeed, F.: ASD-DiagNet: a hybrid learning approach for detection of autism spectrum disorder using fMRI data. Front. Neuroinform. 13, 70 (2019)
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Wu, F.X., Hayrat, R., Liu, J.: AIMAFE: autism spectrum disorder identification with multi-atlas deep feature representation and ensemble learning. J. Neurosci. Methods 343, 108840 (2020)
Craddock, C., et al.: The neuro bureau preprocessing initiative: open sharing of preprocessed neuroimaging data and derivatives. Front. Neuroinform. 7, 27 (2013)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Sarraf, S., Tofighi, G.: Classification of Alzheimer’s disease using fMRI data and deep learning convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.08631 (2016)
Wang, T., Lu, C., Shen, G., Hong, F.: Sleep apnea detection from a single-lead ECG signal with automatic feature-extraction through a modified LeNet-5 convolutional neural network. PeerJ 7, e7731 (2019)
Zhang, S., et al.: Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of pulmonary nodule of thoracic CT image using transfer learning. J. Digit. Imaging 32(6), 995–1007 (2019)
Walsh, J., Othmani, A., Jain, M., Dev, S.: Using U-net network for efficient brain tumor segmentation in MRI images. Healthc. Anal. 2, 100098 (2022). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772442522000429
Hu, W., Huang, Y., Wei, L., Zhang, F., Li, H.: Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. J. Sens. 2015, 12 p., 258619 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/258619
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Heinsfeld, A.S., Franco, A.R., Craddock, R.C., Buchweitz, A., Meneguzzi, F.: Identification of autism spectrum disorder using deep learning and the abide dataset. NeuroImage Clin. 17, 16–23 (2018)
Huang, Z.A., Zhu, Z., Yau, C.H., Tan, K.C.: Identifying autism spectrum disorder from resting-state fMRI using deep belief network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32, 2847–2861 (2020)
Ingalhalikar, M., Shinde, S., Karmarkar, A., Rajan, A., Rangaprakash, D., Deshpande, G.: Functional connectivity-based prediction of autism on site harmonized abide dataset. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68(12), 3628–3637 (2021)
Jha, R.R., Bhardwaj, A., Garg, D., Bhavsar, A., Nigam, A.: MHATC: autism spectrum disorder identification utilizing multi-head attention encoder along with temporal consolidation modules. In: 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 337–341. IEEE (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Othmani, A., Bizet, T., Pellerin, T., Hamdi, B., Bock, MA., Dev, S. (2023). Significant CC400 Functional Brain Parcellations Based LeNet5 Convolutional Neural Network for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection. In: Santosh, K., Goyal, A., Aouada, D., Makkar, A., Chiang, YY., Singh, S.K. (eds) Recent Trends in Image Processing and Pattern Recognition. RTIP2R 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1704. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23599-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23599-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23598-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23599-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)