Abstract
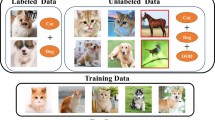
Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has been a powerful strategy to incorporate few labels in learning better representations. In this paper, we focus on a practical scenario that one aims to apply SSL when unlabeled data may contain out-of-class samples - those that cannot have one-hot encoded labels from a closed-set of classes in label data, i.e., the unlabeled data is an open-set. Specifically, we introduce OpenCoS, a simple framework for handling this realistic semi-supervised learning scenario based upon a recent framework of self-supervised visual representation learning. We first observe that the out-of-class samples in the open-set unlabeled dataset can be identified effectively via self-supervised contrastive learning. Then, OpenCoS utilizes this information to overcome the failure modes in the existing state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods, by utilizing one-hot pseudo-labels and soft-labels for the identified in- and out-of-class unlabeled data, respectively. Our extensive experimental results show the effectiveness of OpenCoS under the presence of out-of-class samples, fixing up the state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods to be suitable for diverse scenarios involving open-set unlabeled data.
J. Park and S. Yun—Equal contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
The detection performances with various choices of t are provided in Section D.2 of the supplementary material.
- 3.
If \(\mathcal {D}_{l}\cup \mathcal {D}_{l}^{\text {pseudo}}\) is class-imbalanced, we apply oversampling method [22] for balancing class distributions.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
Nevertheless, we observe that OpenCoS also improves the opposite choices, i.e., FixMatch for CIFAR and ReMixMatch for ImageNet as presented in the supplementary materials..
References
Bendale, A., Boult, T.E.: Towards open set deep networks. In: CVPR (2016)
Bergman, L., Hoshen, Y.: Classification-based anomaly detection for general data. In: ICLR (2020)
Berthelot, D., et al.: Remixmatch: semi-supervised learning with distribution matching and augmentation anchoring. In: ICLR (2020)
Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Goodfellow, I., Papernot, N., Oliver, A., Raffel, C.A.: Mixmatch: a holistic approach to semi-supervised learning. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Caron, M., Touvron, H., Misra, I., Jégou, H., Mairal, J., Bojanowski, P., Joulin, A.: Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers. In: ICCV (2021)
Chapelle, O., Scholkopf, B., Zien, A.: Semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 20(3), 542–542 (2009)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: ICML (2020)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Swersky, K., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: Big self-supervised models are strong semi-supervised learners. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Chen, X., Fan, H., Girshick, R., He, K.: Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04297 (2020)
Chen, Y., Zhu, X., Li, W., Gong, S.: Semi-supervised learning under class distribution mismatch. In: AAAI (2020)
Cubuk, E.D., Zoph, B., Shlens, J., Le, Q.V.: Randaugment: practical data augmentation with no separate search. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.13719 (2019)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Grandvalet, Y., Bengio, Y.: Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization. In: NeurIPS (2004)
Guo, L.Z., Zhang, Z.Y., Jiang, Y., Li, Y.F., Zhou, Z.H.: Safe deep semi-supervised learning for unseen-class unlabeled data. In: ICML (2020)
He, K., Fan, H., Wu, Y., Xie, S., Girshick, R.: Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: CVPR (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Hénaff, O.J., et al.: Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.09272 (2019)
Hendrycks, D., Gimpel, K.: A baseline for detecting misclassified and out-of-distribution examples in neural networks. In: ICLR (2017)
Hendrycks, D., Mazeika, M., Dietterich, T.: Deep anomaly detection with outlier exposure. In: ICLR (2019)
Hendrycks, D., Mazeika, M., Kadavath, S., Song, D.: Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty. In: NeurIPS (2019)
Japkowicz, N.: The class imbalance problem: significance and strategies. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2000)
Krizhevsky, A., Hinton, G., et al.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Tech. rep, Citeseer (2009)
Lee, D.H.: Pseudo-label: The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: ICML Workshop (2013)
Lee, K., Lee, H., Lee, K., Shin, J.: Training confidence-calibrated classifiers for detecting out-of-distribution samples. In: ICLR (2018)
Lee, K., Lee, K., Lee, H., Shin, J.: A simple unified framework for detecting out-of-distribution samples and adversarial attacks. In: NeurIPS (2018)
Lee, K., Yun, S., Lee, K., Lee, H., Li, B., Shin, J.: Robust inference via generative classifiers for handling noisy labels. In: ICML (2019)
Li, Z., Hoiem, D.: Learning without forgetting. In: ECCV (2016)
Liang, S., Li, Y., Srikant, R.: Enhancing the reliability of out-of-distribution image detection in neural networks. In: ICLR (2018)
Liu, Y., Gao, T., Yang, H.: Selectnet: learning to sample from the wild for imbalanced data training. In: MSML (2020)
Miyato, T., Maeda, S.i., Koyama, M., Ishii, S.: Virtual adversarial training: a regularization method for supervised and semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 41(8), 1979–1993 (2018)
Nair, V., Alonso, J.F., Beltramelli, T.: Realmix: towards realistic semi-supervised deep learning algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.08766 (2019)
Netzer, Y., Wang, T., Coates, A., Bissacco, A., Wu, B., Ng, A.Y.: Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning. In: NeurIPS Workshop (2011)
Oliver, A., Odena, A., Raffel, C.A., Cubuk, E.D., Goodfellow, I.: Realistic evaluation of deep semi-supervised learning algorithms. In: NeurIPS (2018)
Oord, A.v.d., Li, Y., Vinyals, O.: Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.03748 (2018)
Raina, R., Battle, A., Lee, H., Packer, B., Ng, A.Y.: Self-taught learning: transfer learning from unlabeled data. In: ICML (2007)
Saito, K., Kim, D., Saenko, K.: Openmatch: open-set consistency regularization for semi-supervised learning with outliers. In: NeurIPS (2021)
Sajjadi, M., Javanmardi, M., Tasdizen, T.: Regularization with stochastic transformations and perturbations for deep semi-supervised learning. In: NeurIPS (2016)
Sergey Ioffe, C.S.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: ICML (2015)
Sohn, K., et al.: Fixmatch: simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Tack, J., Mo, S., Jeong, J., Shin, J.: Csi: novelty detection via contrastive learning on distributionally shifted instances. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Tsipras, D., Santurkar, S., Engstrom, L., Turner, A., Madry, A.: Robustness may be at odds with accuracy. In: ICLR (2019)
Wang, Y., et al.: Iterative learning with open-set noisy labels. In: CVPR (2018)
Wu, Z., Xiong, Y., Yu, S., Lin, D.: Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance-level discrimination. In: CVPR (2018)
Xie, C., Tan, M., Gong, B., Wang, J., Yuille, A., Le, Q.V.: Adversarial examples improve image recognition. In: CVPR (2020)
Xie, Q., Dai, Z., Hovy, E., Luong, M.T., Le, Q.V.: Unsupervised data augmentation for consistency training. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.12848 (2019)
Zagoruyko, S., Komodakis, N.: Wide residual networks. In: BMVC (2016)
Zhai, X., Oliver, A., Kolesnikov, A., Beyer, L.: S4l: Self-supervised semi-supervised learning. In: ICCV (2019)
Zhang, H., Cisse, M., Dauphin, Y.N., Lopez-Paz, D.: mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. In: ICLR (2018)
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Colorful image colorization. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9907, pp. 649–666. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, J., Yun, S., Jeong, J., Shin, J. (2023). OpenCoS: Contrastive Semi-supervised Learning for Handling Open-Set Unlabeled Data. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13802. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25063-7_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25063-7_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25062-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25063-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)