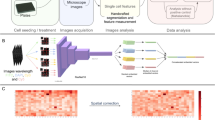
Abstract
Progress in automated microscopy and quantitative image analysis has promoted high-content screening (HCS) as an efficient drug discovery and research tool. While HCS offers to quantify complex cellular phenotypes from images at high throughput, this process can be obstructed by image aberrations such as out-of-focus image blur, fluorophore saturation, debris, a high level of noise, unexpected auto-fluorescence or empty images. While this issue has received moderate attention in the literature, overlooking these artefacts can seriously hamper downstream image processing tasks and hinder detection of subtle phenotypes. It is therefore of primary concern, and a prerequisite, to use quality control in HCS. In this work, we evaluate deep learning options that do not require extensive image annotations to provide a straightforward and easy to use semi-supervised learning solution to this issue. Concretely, we compared the efficacy of recent self-supervised and transfer learning approaches to provide a base encoder to a high throughput artefact image detector. The results of this study suggest that transfer learning methods should be preferred for this task as they not only performed best here but present the advantage of not requiring sensitive hyperparameter settings nor extensive additional training.
U. Masud and E. Cohen—Equal co-contribution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardes, A., Ponce, J., Lecun, Y.: Vicreg: variance-invariance-covariance regularization for self-supervised learning. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2022)
Bray, M.A., Carpenter, A.E.: Quality control for high-throughput imaging experiments using machine learning in cell profiler. Method. Mol. Biol. 1683, 89–112 (2018)
Caie, P.D., et al.: High-content phenotypic profiling of drug response signatures across distinct cancer cells phenotypic profiling across cancer cell types. Mol. Cancer Ther. 9(6), 1913–1926 (2010)
Caron, M., Bojanowski, P., Joulin, A., Douze, M.: Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 132–149 (2018)
Caron, M., Misra, I., Mairal, J., Goyal, P., Bojanowski, P., Joulin, A.: Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 9912–9924 (2020)
Carpenter, A.E., et al.: Cell profiler: image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 7, R100–R100 (2006)
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., Hinton, G.: A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1597–1607. PMLR (2020)
da Costa, V.G.T., Fini, E., Nabi, M., Sebe, N., Ricci, E.: solo-learn: a library of self-supervised methods for visual representation learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 23, 56:1-56:6 (2022)
Grill, J.B., et al.: Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 33, 21271–21284 (2020)
Gustafsdottir, S.M., et al.: Multiplex cytological profiling assay to measure diverse cellular states. PLoS ONE 8(12), e80999 (2013)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Jaiswal, A., Babu, A.R., Zadeh, M.Z., Banerjee, D., Makedon, F.: A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning. Technologies 9(1), 2 (2020)
Kensert, A., Harrison, P.J., Spjuth, O.: Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural networks for classifying cellular morphological changes. SLAS Discov. 24(4), 466–475 (2019)
Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wu, C.Y., Feichtenhofer, C., Darrell, T., Xie, S.: A convnet for the 2020s. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11976–11986 (2022)
Ljosa, V., et al.: Comparison of methods for image-based profiling of cellular morphological responses to small-molecule treatment. J. Biomol. Screen. 18, 1321–1329 (2013)
Ljosa, V., Sokolnicki, K.L., Carpenter, A.E.: Annotated high-throughput microscopy image sets for validation. Nat. Methods 9, 637–637 (2012)
Perakis, A., Gorji, A., Jain, S., Chaitanya, K., Rizza, S., Konukoglu, E.: Contrastive learning of single-cell phenotypic representations for treatment classification. International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging (2021)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv (2014)
Singh, S., Carpenter, A.E., Genovesio, A.: Increasing the content of high-content screening. J. Biomol. Screen. 19, 640–650 (2014)
Van Gansbeke, W., Vandenhende, S., Georgoulis, S., Proesmans, M., Van Gool, L.: SCAN: learning to classify images without labels. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12355, pp. 268–285. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58607-2_16
Yang, S.J., et al.: Assessing microscope image focus quality with deep learning. BMC Bioinformatics 19 (2018)
Yang, X., He, X., Liang, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, S., Xie, P.: Transfer learning or self-supervised learning? a tale of two pretraining paradigms. ArXiv (2020)
Yao, K., Rochman, N.D., Sun, S.X.: Cell type classification and unsupervised morphological phenotyping from low-resolution images using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 13467 (2019)
Zbontar, J., Jing, L., Misra, I., LeCun, Y., Deny, S.: Barlow twins: Self-supervised learning via redundancy reduction. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 12310–12320. PMLR (2021)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by ANR-10-LABX-54 MEMOLIFE and ANR-10 IDEX 0001 -02 PSL* Université Paris and was granted access to the HPC resources of IDRIS under the allocation 2020-AD011011495 made by GENCI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Masud, U., Cohen, E., Bendidi, I., Bollot, G., Genovesio, A. (2023). Comparison of Semi-supervised Learning Methods for High Content Screening Quality Control. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13804. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25069-9_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25069-9_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25068-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25069-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)