Abstract
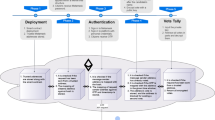
We propose an pseudo-anonymous e-voting platform based on the blockchain of Ethereum and a coin-mixer, that is Tornado Cash. After an online authentication and authorization phase, the user receives a fungible (i.e., pseudo-anonymous) voting token that can be deposited to a coin pool belonging to Tornado Cash (TC), together with an amount of Ether (ETH) A that will be used to pay successive fees. TC uses a smart contract that accepts token deposits that can be later withdrawn by a different address. In order to preserve privacy, a relayer contract can then be used to withdraw to a fresh ETH address (thus pseudo-anonymous) using A to pay fees. Relayers solve “fee payment dilemma”, that is paying withdrawal fees by maintaining pseudo-anonymity. Finally, a further smart contract collects preferences and, after the closure of the elections, it automatically performs the counting of votes. All the front-end has been developed in a Web browser, by using Javascript and avoiding the voter to perform any command-line operation to prepare transactions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Non-custodial wallet services are platforms that allow users to possess their private keys.
- 5.
Web-connection of Tornado Cash to Metamask or a private wallet: https://tornadocash.eth.limo/.
- 6.
With || that stands for concatenation.
- 7.
- 8.
zk-SNARK: https://z.cash/technology/zksnarks/.
- 9.
Goerli Testnet Network: https://goerli.etherscan.io/address/0x454d870a72e29d5e5697f635128d18077bd04c60.
- 10.
DevToken.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
The PoA is a consensus method that gives a small and designated number of blockchain actors the power to validate transactions or interactions with the network and to update its registry. Goerli is said to switch to proof-of-stake soon.
- 14.
Using gas price to compute fees on 23rd of July 2022.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
Web-site of the Bitcongress.org project: http://www.bitcongress.org.
- 18.
FollowMyVote.com: https://followmyvote.com.
- 19.
TIVI: https://tivi.io.
- 20.
MultiChain is a bridging platform for cryptocurrencies and NFTs across blockchains.
- 21.
References
Ahn, B.: Implementation and early adoption of an ethereum-based electronic voting system for the prevention of fraudulent voting. Sustainability 14(5) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052917. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/5/2917
Alvarez, R.M., Hall, T.E., Trechsel, A.H.: Internet voting in comparative perspective: the case of Estonia. PS: Polit. Sci. Polit. 42(03), 497–505 (2009)
Ayed, A.B.: A conceptual secure blockchain-based electronic voting system. Int. J. Netw. Secur. Appl. 9(3), 1–9 (2017)
Bistarelli, S., Mercanti, I., Santancini, P., Santini, F.: End-to-end voting with non-permissioned and permissioned ledgers. J. Grid Comput. 17(1), 97–118 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-019-09478-y
Buterin, V.: Ethereum white paper: a next generation smart contract & decentralized application platform (2013). https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/White-Paper
Fouard, L., Duclos, M., Lafourcade, P.: Survey on electronic voting schemes (2007). http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.295.7959 &rep=rep1 &type=pdf. Verimag technical report. Accessed 28 Jan 2018
Hardwick, F., Akram, R.N., Markantonakis, K.: E-voting with blockchain: an e-voting protocol with decentralisation and voter privacy. CoRR abs/1805.10258 (2018). http://arxiv.org/abs/1805.10258
Loeber, L.: E-voting in the Netherlands; from general acceptance to general doubt in two years. In: Electronic Voting, vol. 131, pp. 21–30 (2008)
McCorry, P., Shahandashti, S.F., Hao, F.: A smart contract for boardroom voting with maximum voter privacy. In: Kiayias, A. (ed.) FC 2017. LNCS, vol. 10322, pp. 357–375. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70972-7_20
Mote, C.D.: Report of the national workshop on internet voting: issues and research agenda. In: Proceedings of the 2000 Annual National Conference on Digital Government Research, pp. 1–59. Digital Government Society of North America (2000)
Omohundro, S.: Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and artificial intelligence. AI Matters 1(2), 19–21 (2014)
Pilkington, M.: Blockchain technology: principles and applications. In: Research Handbook on Digital Transformations, p. 225 (2016)
Pramulia, D., Anggorojati, B.: Implementation and evaluation of blockchain based e-voting system with Ethereum and Metamask. In: 2020 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS), pp. 18–23 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIMCIS51567.2020.9354310
Schneider, A., Meter, C., Hagemeister, P.: Survey on remote electronic voting. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.02798 (2017)
Suegami, S.: Smart contracts obfuscation from blockchain-based one-time program. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, p. 549 (2022). https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/549
Swan, M.: Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy. O’Reilly Media, Inc. (2015)
Acknowledgement
The authors are a member of the INdAM Research group GNCS and Consorzio CINI. This work has been partially supported by:
– GNCS-INdAM, CUP E55F22000270001;
– Project RACRA - funded by Ricerca di Base 2018–2019, University of Perugia;
– Project BLOCKCHAIN4FOODCHAIN: funded by Ricerca di Base 2020, University of Perugia;
– Project DopUP - REGIONE UMBRIA PSR 2014–2020;
– Project GIUSTIZIA AGILE, CUP: J89J22000900005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bistarelli, S., La Torre Montalvo, B.L., Mercanti, I., Santini, F. (2023). An E-Voting System Based on Tornado Cash. In: Saracino, A., Mori, P. (eds) Emerging Technologies for Authorization and Authentication. ETAA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13782. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25467-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25467-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25466-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25467-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)