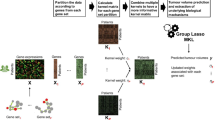
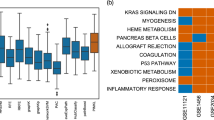
Abstract
Standard machine learning algorithms have limited knowledge extraction capability in discriminating cancer stages based on genomic characterizations, due to the strongly correlated nature of high-dimensional genomic data. Moreover, activation of pathways plays a crucial role in the growth and progression of cancer from early-stage to late-stage. That is why we implemented a kernel-based neural network framework that integrates pathways and gene expression data using multiple kernels and discriminates early- and late-stages of cancers. Our goal is to identify the relevant molecular mechanisms of the biological processes which might be driving cancer progression. As the input of developed multilayer perceptron (MLP), we constructed kernel matrices on multiple views of expression profiles of primary tumors extracted from pathways. We used Hallmark and Pathway Interaction Database (PID) datasets to restrict the search area to interpretable solutions. We applied our algorithm to 12 cancer cohorts from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), including more than 5100 primary tumors. The results showed that our algorithm could extract meaningful and disease-specific mechanisms of cancers. We tested the predictive performance of our MLP algorithm and compared it against three existing classification algorithms, namely, random forests, support vector machines, and multiple kernel learning. Our MLP method obtained better or comparable predictive performance against these algorithms.
Our implementation of proposed algorithm in R is available at https://github.com/MSoleimanpoor/Neural-Network.git.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaur, H., Bhalla, S., Raghava, G.P.: Classification of early and late stage liver hepatocellular carcinoma patients from their genomics and epigenomics profiles. PLoS ONE 14(9), e0221476 (2019)
Mokhtaridoost, M., Gönen, M.: Identifying key miRNA–mRNA regulatory modules in cancer using sparse multivariate factor regression. In: Nicosia, G., et al. (eds.) LOD 2020. LNCS, vol. 12565, pp. 422–433. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64583-0_38
Broët, P., et al.: Identifying gene expression changes in breast cancer that distinguish early and late relapse among uncured patients. Bioinformatics 22(12), 1477–1485 (2006)
Bhalla, S., et al.: Expression based biomarkers and models to classify early and late-stage samples of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 15(4), e0231629 (2020)
Bhalla, S., et al.: Gene expression-based biomarkers for discriminating early and late stage of clear cell renal cancer. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–13 (2017)
Ein-Dor, L., Zuk, O., Domany, E.: Thousands of samples are needed to generate a robust gene list for predicting outcome in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103(15), 5923–5928 (2006)
Rahimi, A., Gönen, M.: Discriminating early-and late-stage cancers using multiple kernel learning on gene sets. Bioinformatics 34(13), i412–i421 (2018)
Rahimi, A., Gönen, M.: A multitask multiple kernel learning formulation for discriminating early-and late-stage cancers. Bioinformatics (2020)
Kumar, R., et al.: Gene expression-based supervised classification models for discriminating early-and late-stage prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci., 1–2 (2019)
Ma, B., et al.: Diagnostic classification of cancers using extreme gradient boosting algorithm and multi-omics data. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103761 (2020)
Saabith, A.L.S., Sundararajan, E., Bakar, A.A.: Comparative study on different classification techniques for breast cancer dataset. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 3(10), 185–191 (2014)
Seo, H., Cho, D.-H.: Cancer-related gene signature selection based on boosted regression for multilayer perceptron. IEEE Access 8, 64 992–65 004 (2020)
Pati, J.: Gene expression analysis for early lung cancer prediction using machine learning techniques: an eco-genomics approach. IEEE Access 7, 4232–4238 (2018)
Chaubey, V., Nair, M.S., Pillai, G.: Gene expression prediction using a deep 1D convolution neural network. In: 2019 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), pp. 1383–1389. IEEE (2019)
Xie, R., et al.: A predictive model of gene expression using a deep learning framework. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 676–681. IEEE (2016)
Mojarad, S.A., et al.: Breast cancer prediction and cross validation using multilayer perceptron neural networks. In: Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), pp. 760–764. IEEE (2010)
Schaefer, C.F., et al.: PID: the pathway interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(suppl_1), D674–D679 (2009)
Liberzon, A., et al.: The molecular signatures database hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 1(6), 417–425 (2015)
Abadi, M., et al.: TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems (2015). http://tensorflow.org/
Chollet, F., et al.: Keras (2015). https://keras.io
Bergers, G., Benjamin, L.E.: Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3(6), 401–410 (2003)
Chiang, J.Y.L.: Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 3(3), 1191–1212 (2013)
Kotha, P.L., et al.: Adenovirus entry from the apical surface of polarized epithelia is facilitated by the host innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 11(3), e1004696 (2015)
Zeitouni, N.E., Chotikatum, S., von Köckritz-Blickwede, M., Naim, H.Y.: The impact of hypoxia on intestinal epithelial cell functions: consequences for invasion by bacterial pathogens. Mol. Cellular Pediatr. 3(1), 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40348-016-0041-y
Branzei, D., Foiani, M.: Regulation of DNA repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9(4), 297–308 (2008)
Blais, A., Dynlacht, B.D.: E2F-associated chromatin modifiers and cell cycle control. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19(6), 658–662 (2007)
Zhao, L., et al.: Identification of a novel cell cycle-related gene signature predicting survival in patients with gastric cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 234(5), 6350–6360 (2019)
Palaniappan, M., Menon, B., Menon, K.: Stimulatory effect of insulin on theca-interstitial cell proliferation and cell cycle regulatory proteins through MTORC1 dependent pathway. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 366(1), 81–89 (2013)
Melo, S.A., et al.: Glypican1 identifies cancer exosomes and facilitates early detection of cancer. Nature 523(7559), 177 (2015)
Kandikattu, H.K., Venkateshaiah, S.U., Mishra, A.: Synergy of interleukin (IL)-5 and IL-18 in eosinophil mediated pathogenesis of allergic diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 47, 83–98 (2019)
Xia, L., et al.: Role of the NF\(\kappa \)B-signaling pathway in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 11, 2063 (2018)
Gupta, S.K., et al.: Integrin \(\alpha \)9\(\beta \)1 promotes malignant tumor growth and metastasis by potentiating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 32(2), 141–150 (2013)
Dard, L., et al.: RAS signalling in energy metabolism and rare human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg. 1859(9), 845–867 (2018)
Chung, J.H.: The role of DNA-PK in aging and energy metabolism. FEBS J. 285(11), 1959–1972 (2018)
Mo, Y., et al.: The role of WNT signaling pathway in tumor metabolic reprogramming. J. Cancer 10(16), 3789 (2019)
Xia, Y., Jiang, L., Zhong, T.: The role of HIF-1\(\alpha \) in chemo-/radioresistant tumors. OncoTargets Ther. 11, 3003 (2018)
Wild, J.R., et al.: Neuropilins: expression and roles in the epithelium. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 93(2), 81–103 (2012)
Joly, D., et al.: \(\beta \)4 integrin and laminin 5 are aberrantly expressed in polycystic kidney disease: role in increased cell adhesion and migration. Am. J. Pathol. 163(5), 1791–1800 (2003)
Bai, H., et al.: Integrated genomic characterization of idh1-mutant glioma malignant progression. NAT 48(1), 59–66 (2016)
Chen, C., et al.: Analysis of the expression of cell division cycle-associated genes and its prognostic significance in human lung carcinoma: a review of the literature databases. Biomed Res. Int. 2020 (2020)
Ishwaran, H., Kogalur, U.: Random forests for survival, regression, and classification (RF-SRC), R package version 2.5. 1 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Soleimanpoor, M., Mokhtaridoost, M., Gönen, M. (2023). A Kernel-Based Multilayer Perceptron Framework to Identify Pathways Related to Cancer Stages. In: Nicosia, G., et al. Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science. LOD 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13810. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25599-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25599-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25598-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25599-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)