Abstract
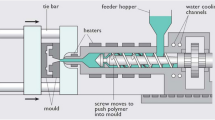
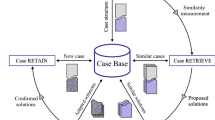
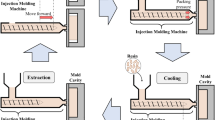
Nowadays, injection molds are manually designed by humans using computer-aided design (CAD) systems. The placement of ejector pins is a critical step in the injection mold design to enable demolding complex parts in the production. Since each injection mold is unique, designers are limited in using standard ejector layouts or previous mold designs, which results in high design time so that an automation of the design process is needed. For such a system, human knowledge is essential. Therefore, we propose a human-centric machine learning (HCML) approach for the automatic placement of ejector pins for injection molds. In this work, we extract mental models of injection mold designers to obtain machine-readable fundamental design rules and train a machine learning model using an ongoing human-machine learning approach.
The work of RWTH Aachen University within the AutoEnSys joint research project is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the grant number 01IS20081C.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrlenspiel, K., Kiewert, A., Mörtl, M., Lindemann, U.: Kostengünstig Entwickeln und Konstruieren. Kostenmanagement bei der integrierten Produktentwicklung, 8th edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2020)
Kwak, S., Kim, T., Park, S., Lee, K.: Layout and sizing of ejector pins for injection mould desian using the wavelet transform. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 217(4), 463–473 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1243/095440503321628143
Chin, K.-S., Wong, T.N.: An expert system for injection mold cost estimation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 14(4), 303–314 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1002/ADV.1995.060140404
Sterman, J.D.: Business Dynamics. Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. Irwin/McGraw-Hill, Boston (2000)
Wang, Z., et al.: Optimum ejector system design for plastic injection moulds. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 9(4), 211–218. (1996). ScholarBank@NUS Repository. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMPT.1996.036339
Ferreira, I., Cabral, J.A., Saraiva, P., Oliveira, M.C.: A multidisciplinary framework to support the design of injection mold tools. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 49(3), 501–521 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0990-x
Alvarado-Iniesta, A., Cuate, O., Schütze, O.: Multi-objective and many objective design of plastic injection molding process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102(9–12), 3165–3180 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03432-8
Li, K., Yan, S., Zhong, Y., Pan, W., Zhao, G.: Multi-objective optimization of the fiber-reinforced composite injection molding process using Taguchi method, RSM, and NSGA-II. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 91, 69–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2018.09.003
Chin, K.-S., Wong, T.N.: An expert system for injection mold cost estimation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 9(4), 303–314 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1002/ADV.1995.060140404
Kaluarachchi, T., Reis, A., Nanayakkara, S.: A review of recent deep learning approaches in human-centered machine learning. 21(7) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072514
Sperrle, F., et al.: A survey of human-centered evaluations in human-centered machine learning. Comput. Graph. Forum 40(3), 543–568 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.14329
Gary, M.S., Wood, R.E.: Unpacking mental models through laboratory experiments. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 32(2), 101–129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/sdr.1560
Bubeck, S.: Convex Optimization. Algorithms and Complexity. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning Ser, 26th. Now Publishers, Norwell (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jungnickel, R., Lauwigi, J., Samsonov, V., Lütticke, D. (2023). Human-Centric Machine Learning Approach for Injection Mold Design: Towards Automated Ejector Pin Placement. In: Nicosia, G., et al. Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science. LOD 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13811. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25891-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25891-6_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25890-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25891-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)