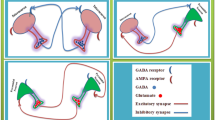
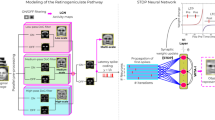
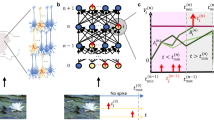
Abstract
Brain-inspired computation and information processing alongside compatibility with neuromorphic hardware have made spiking neural networks (SNN) a promising method for solving learning tasks in machine learning (ML). Spiking neurons are only one of the requirements for building a bio-plausible learning model. Network architecture and learning rules are other important factors to consider when developing such artificial agents. In this work, inspired by the human visual pathway and the role of dopamine in learning, we propose a reward-modulated locally connected spiking neural network, BioLCNet, for visual learning tasks. To extract visual features from Poisson-distributed spike trains, we used local filters that are more analogous to the biological visual system compared to convolutional filters with weight sharing. In the decoding layer, we applied a spike population-based voting scheme to determine the decision of the network. We employed Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) for learning the visual features, and its reward-modulated variant (R-STDP) for training the decoder based on the reward or punishment feedback signal. For evaluation, we first assessed the robustness of our rewarding mechanism to varying target responses in a classical conditioning experiment. Afterwards, we evaluated the performance of our network on image classification tasks of MNIST and XOR MNIST datasets.
H. Ghaemi, E. Mirzaei, M. Nouri—Equal contribution
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allred, J.M., Roy, K.: Unsupervised incremental stdp learning using forced firing of dormant or idle neurons. In: 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 2492–2499. IEEE (2016)
Bartunov, S., Santoro, A., Richards, B., Marris, L., Hinton, G.E., Lillicrap, T.: Assessing the scalability of biologically-motivated deep learning algorithms and architectures. In: Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Grauman, K., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31. Curran Associates, Inc. (2018)
Bellec, G., et al.: A solution to the learning dilemma for recurrent networks of spiking neurons. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 1–15 (2020)
Bing, Z., Jiang, Z., Cheng, L., Cai, C., Huang, K., Knoll, A.: End to end learning of a multi-layered snn based on r-stdp for a target tracking snake-like robot. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 9645–9651. IEEE (2019)
Cao, Y., Chen, Y., Khosla, D.: Spiking deep convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 113(1), 54–66 (2015)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12346, pp. 213–229. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13
Connors, B.W., Gutnick, M.J.: Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons. Trends Neurosci. 13(3), 99–104 (1990)
Diehl, P.U., Cook, M.: Unsupervised learning of digit recognition using spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 9, 99 (2015)
Florian, R.V.: Reinforcement learning through modulation of spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Neural Comput. 19(6), 1468–1502 (2007)
Frémaux, N., Gerstner, W.: Neuromodulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity, and theory of three-factor learning rules. Front. Neural Circ. 9, 85 (2016)
Gerstner, W., Kistler, W.M., Naud, R., Paninski, L.: Neuronal Dynamics: From Single Neurons to Networks and Models of Cognition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2014)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press (2016). https://www.deeplearningbook.org
Gregor, K., LeCun, Y.: Emergence of complex-like cells in a temporal product network with local receptive fields (2010)
Hazan, H.: Bindsnet: a machine learning-oriented spiking neural networks library in python. Front. Neuroinform. 12, 89 (2018)
Hebb, D.O.: The Organisation of Behaviour: A Neuropsychological Theory. Science Editions New York, New York (1949)
Illing, B., Gerstner, W., Brea, J.: Biologically plausible deep learning-but how far can we go with shallow networks? Neural Netw. 118, 90–101 (2019)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling. Cereb. Cortex 17(10), 2443–2452 (2007)
Kheradpisheh, S.R., Ganjtabesh, M., Masquelier, T.: Bio-inspired unsupervised learning of visual features leads to robust invariant object recognition. Neurocomputing 205, 382–392 (2016)
Kheradpisheh, S.R., Ganjtabesh, M., Thorpe, S.J., Masquelier, T.: Stdp-based spiking deep convolutional neural networks for object recognition. Neural Netw. 99, 56–67 (2018)
Kheradpisheh, S.R., Masquelier, T.: Temporal backpropagation for spiking neural networks with one spike per neuron. Int. J. Neural Syst. 30(06), 2050027 (2020)
LeCun, Y., Cortes, C., Burges, C.: The mnist dataset of handwritten digits (images). NYU: New York, NY, USA (1999)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Lee, C., Srinivasan, G., Panda, P., Roy, K.: Deep spiking convolutional neural network trained with unsupervised spike-timing-dependent plasticity. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 11(3), 384–394 (2018)
Liao, Q., Leibo, J., Poggio, T.: How important is weight symmetry in backpropagation? In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 30 (2016)
Lillicrap, T.P., Santoro, A., Marris, L., Akerman, C.J., Hinton, G.: Backpropagation and the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 21(6), 335–346 (2020)
Lowel, S., Singer, W.: Selection of intrinsic horizontal connections in the visual cortex by correlated neuronal activity. Science 255(5041), 209–212 (1992)
Mozafari, M., Ganjtabesh, M., Nowzari-Dalini, A., Thorpe, S.J., Masquelier, T.: Bio-inspired digit recognition using reward-modulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity in deep convolutional networks. Pattern Recogn. 94, 87–95 (2019)
Mozafari, M., Kheradpisheh, S.R., Masquelier, T., Nowzari-Dalini, A., Ganjtabesh, M.: First-spike-based visual categorization using reward-modulated stdp. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(12), 6178–6190 (2018)
Paszke, A., et al.: Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alché-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 32, pp. 8024–8035. Curran Associates, Inc. (2019). https://papers.neurips.cc/paper/9015-pytorch-an-imperative-style-high-performance-deep-learning-library.pdf
Poggio, T., Mhaskar, H., Rosasco, L., Miranda, B., Liao, Q.: Why and when can deep-but not shallow-networks avoid the curse of dimensionality: a review. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 14(5), 503–519 (2017)
Pogodin, R., Mehta, Y., Lillicrap, T., Latham, P.E.: Towards biologically plausible convolutional networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 13924–13936 (2021)
Saunders, D.J., Patel, D., Hazan, H., Siegelmann, H.T., Kozma, R.: Locally connected spiking neural networks for unsupervised feature learning. Neural Netw. 119, 332–340 (2019)
Saunders, D.J., Siegelmann, H.T., Kozma, R., et al.: Stdp learning of image patches with convolutional spiking neural networks. In: 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2018)
Saunders, D.J., Sigrist, C., Chaney, K., Kozma, R., Siegelmann, H.T.: Minibatch processing for speed-up and scalability of spiking neural network simulation. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Schemmel, J., Brüderle, D., Grübl, A., Hock, M., Meier, K., Millner, S.: A wafer-scale neuromorphic hardware system for large-scale neural modeling. In: 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1947–1950. IEEE (2010)
Schrimpf, M., et al.: Brain-score: which artificial neural network for object recognition is most brain-like? BioRxiv, p. 407007 (2020)
Schultz, W., Dayan, P., Montague, P.R.: A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275(5306), 1593–1599 (1997)
Sun, S.H.: Multi-digit mnist for few-shot learning (2019). https://github.com/shaohua0116/MultiDigitMNIST
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge (2018)
Tavanaei, A., Ghodrati, M., Kheradpisheh, S.R., Masquelier, T., Maida, A.: Deep learning in spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 111, 47–63 (2019)
Weidel, P., Duarte, R., Morrison, A.: Unsupervised learning and clustered connectivity enhance reinforcement learning in spiking neural networks. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 15, 18 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ghaemi, H., Mirzaei, E., Nouri, M., Kheradpisheh, S.R. (2023). BioLCNet: Reward-Modulated Locally Connected Spiking Neural Networks. In: Nicosia, G., et al. Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science. LOD 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13811. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25891-6_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25891-6_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25890-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25891-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)