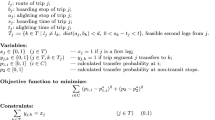Abstract
This paper tackles Origin-Destination (OD) matrix reconstruction at a station level, which consists in computing the volume of passengers traveling between two different stations on a public transportation network. This information is critical for the transport operator to compute various indicators concerning the network’s state and performance such as vehicle occupancy and travelers’ behavior. Trip reconstruction for smart card holders, whose history of validations is available, has been thoroughly investigated in prior work. Conversely, trip reconstruction for non smart card holders has received less attention, mainly due to the difficulty of obtaining ground truth data. Among recent work in this domain, very few contributions have tackled large networks in their entirety, with millions of validations over a month and the computational challenges that come with it.
In this work, we present a new Bayesian Markov Model for OD matrix reconstruction. The novelty of our model lies in its scalability and the fact that it uses all available data, including Automated Fare Collection (i.e. smart card holders) data and Automatic Passenger Counting data (i.e. data from counting sensors), to accurately infer the trips’ distribution. Moreover, the proposed approach produces proper OD matrices while taking into account sensor noise and fraud.
We empirically establish the relevance, robustness, and accuracy of the proposed method compared to the popular trip chaining algorithm and a previous Markov based approach on real-world, large-scale industrial datasets for two transportation networks in major cities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assemi, B., Alsger, A., Moghaddam, M., Hickman, M., Mesbah, M.: Improving alighting stop inference accuracy in the trip chaining method using neural networks. Public Transp. 12(1), 89–121 (2020)
Ben-Akiva, M., Macke, P.P., Hsu, P.S.: Alternative methods to estimate route-level trip tables and expand on-board surveys. No. 1037, Transportation Research Board (1985)
Carvalho, L.: A Bayesian statistical approach for inference on static origin-destination matrices in transportation studies. Technometrics 56(2), 225–237 (2014)
Egu, O., Bonnel, P.: Can we estimate accurately fare evasion without a survey? Results from a data comparison approach in Lyon using fare collection data, fare inspection data and counting data. Public Transp. 12(1), 1–26 (2020)
Faroqi, H., Mesbah, M., Kim, J.: Applications of transit smart cards beyond a fare collection tool: a literature review. Adv. Transp. Stud. 45 (2018)
Fog, A.: Sampling methods for Wallenius’ and Fisher’s noncentral hypergeometric distributions. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput.® 37(2), 241–257 (2008)
Gordon, J.B., Koutsopoulos, H.N., Wilson, N.H.: Estimation of population origin-interchange-destination flows on multimodal transit networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 90, 350–365 (2018)
Grgurević, I., Juršić, K., Rajič, V.: Review of automatic passenger counting systems in public urban transport. In: Knapčíková, L., Peraković, D., Behúnová, A., Periša, M. (eds.) 5th EAI International Conference on Management of Manufacturing Systems. EICC, pp. 1–15. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67241-6_1
Harrison, G., Grant-Muller, S.M., Hodgson, F.C.: New and emerging data forms in transportation planning and policy: opportunities and challenges for “track and trace’’ data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 117, 102672 (2020)
Hazelton, M.L.: Network tomography for integer-valued traffic. Ann. Appl. Stat. 9(1), 474–506 (2015)
He, L., Trépanier, M.: Estimating the destination of unlinked trips in transit smart card fare data. Transp. Res. Rec. 2535(1), 97–104 (2015)
Huang, D., Yu, J., Shen, S., Li, Z., Zhao, L., Gong, C.: A method for bus OD matrix estimation using multisource data. J. Adv. Transp. 2020 (2020)
Hussain, E., Bhaskar, A., Chung, E.: Transit OD matrix estimation using smartcard data: recent developments and future research challenges. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 125, 103044 (2021)
Ji, Y., You, Q., Jiang, S., Zhang, H.M.: Statistical inference on transit route-level origin-destination flows using automatic passenger counter data. J. Adv. Transp. 49(6), 724–737 (2015)
Jung, J., Sohn, K.: Deep-learning architecture to forecast destinations of bus passengers from entry-only smart-card data. IET Intel. Transp. Syst. 11(6), 334–339 (2017)
Kumar, P., Khani, A., Davis, G.A.: Transit route origin-destination matrix estimation using compressed sensing. Transp. Res. Rec. 2673(10), 164–174 (2019)
Kumar, P., Khani, A., He, Q.: A robust method for estimating transit passenger trajectories using automated data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 95, 731–747 (2018)
Lee, S., Lee, J., Bae, B., Nam, D., Cheon, S.: Estimating destination of bus trips considering trip type characteristics. Appl. Sci. 11(21), 10415 (2021)
Lei, D., Chen, X., Cheng, L., Zhang, L., Wang, P., Wang, K.: Minimum entropy rate-improved trip-chain method for origin-destination estimation using smart card data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 130, 103307 (2021)
Li, B.: Markov models for Bayesian analysis about transit route origin-destination matrices. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 43(3), 301–310 (2009)
Li, T., Sun, D., Jing, P., Yang, K.: Smart card data mining of public transport destination: a literature review. Information 9(1), 18 (2018)
Liu, X., Van Hentenryck, P., Zhao, X.: Optimization models for estimating transit network origin-destination flows with big transit data. J. Big Data Anal. Transp. 3(3), 247–262 (2021)
Liu, Z., Miranda, F., Xiong, W., Yang, J., Wang, Q., Silva, C.: Learning geo-contextual embeddings for commuting flow prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 808–816 (2020)
Luca, M., Barlacchi, G., Lepri, B., Pappalardo, L.: A survey on deep learning for human mobility. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 55(1), 1–44 (2021)
McNally, M.G.: The Four-Step Model. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, Bradford (2007)
Mishalani, R.G., Ji, Y., McCord, M.R.: Effect of onboard survey sample size on estimation of transit bus route passenger origin-destination flow matrix using automatic passenger counter data. Transp. Res. Rec. 2246(1), 64–73 (2011)
Munizaga, M., Devillaine, F., Navarrete, C., Silva, D.: Validating travel behavior estimated from smartcard data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 44, 70–79 (2014)
Simini, F., Barlacchi, G., Luca, M., Pappalardo, L.: A deep gravity model for mobility flows generation. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–13 (2021)
Trépanier, M., Tranchant, N., Chapleau, R.: Individual trip destination estimation in a transit smart card automated fare collection system. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 11(1), 1–14 (2007)
Vintsyuk, T.K.: Speech discrimination by dynamic programming. Cybernetics 4(1), 52–57 (1968)
Wilson, A.G.: The use of entropy maximising models, in the theory of trip distribution, mode split and route split. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 108–126 (1969)
Wilson, A.G.: A family of spatial interaction models, and associated developments. Environ. Plan. A 3(1), 1–32 (1971)
Wu, X., Guo, J., Xian, K., Zhou, X.: Hierarchical travel demand estimation using multiple data sources: a forward and backward propagation algorithmic framework on a layered computational graph. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 96, 321–346 (2018)
Yan, F., Yang, C., Ukkusuri, S.V.: Alighting stop determination using two-step algorithms in bus transit systems. Transportmetrica A Transp. Sci. 15(2), 1522–1542 (2019)
Yao, X., Gao, Y., Zhu, D., Manley, E., Wang, J., Liu, Y.: Spatial origin-destination flow imputation using graph convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(12), 7474–7484 (2020)
Zapata, L.P., Flores, M., Larios, V., Maciel, R., Antunez, E.A.: Estimation of people flow in public transportation network through the origin-destination problem for the South-Eastern corridor of Quito city in the smart cities context. In: 2019 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), pp. 181–186. IEEE (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Amblard, V., Dib, A., Cherrier, N., Barthe, G. (2023). A Bayesian Markov Model for Station-Level Origin-Destination Matrix Reconstruction. In: Amini, MR., Canu, S., Fischer, A., Guns, T., Kralj Novak, P., Tsoumakas, G. (eds) Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13718. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26422-1_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26422-1_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26421-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26422-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)