Abstract
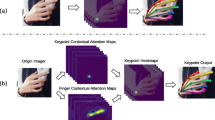
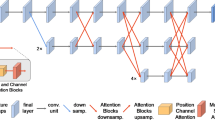
This paper presents a real-time lightweight network, LiteHandNet, for 2D hand pose estimation from monocular color images. In recent years, keypoint heatmap representation is dominant in pose estimation due to its high accuracy. Nevertheless, keypoint heatmaps require high-resolution representation to extract accurate spatial features, which commonly means high computational costs, e.g., high delay and tremendous model parameters. Therefore, the existing heatmap-based methods are not suitable for the scenes with computation-limited resources and high real-time requirements. We find that high-resolution representation can obtain more clear structural features of a hand, e.g., contours and key regions, which can provide high-quality spatial features to the keypoint heatmap, thus improving the robustness and accuracy of a model. To fully extract the structural features without introducing unnecessary computational costs, we propose a lightweight module, which consists of two parts: a multi-scale feature block (MSFB) and a spatial channel attention block (SCAB). MSFB can extract structural features from hands using multi-scale information, while SCAB can further screen out high-quality structural features and suppress low-quality features. Comprehensive experimental results verify that our model is state-of-the-art in terms of the tradeoff between accuracy, speed, and parameters.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., et al.: Nonparametric structure regularization machine for 2D hand pose estimation. In: WACV, pp. 370–379 (2020)
Cheng, B., Xiao, B., Wang, J., Shi, H., Huang, T.S., Zhang, L.: Higherhrnet: scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 5385–5394 (2020)
Gu, K., Yang, L., Yao, A.: Removing the bias of integral pose regression. In: ICCV, pp. 11047–11056 (2021)
Han, K., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Guo, J., Xu, C., Xu, C.: Ghostnet: more features from cheap operations. In: CVPR, pp. 1577–1586 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Howard, A.G., et al.: Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Ioannou, Y., Robertson, D.P., Cipolla, R., Criminisi, A.: Deep roots: improving CNN efficiency with hierarchical filter groups. In: CVPR, pp. 5977–5986 (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR (2015)
Kong, D., Ma, H., Chen, Y., Xie, X.: Rotation-invariant mixed graphical model network for 2d hand pose estimation. In: WACV, pp. 1535–1544 (2020)
Kong, D., Ma, H., Xie, X.: SIA-GCN: a spatial information aware graph neural network with 2D convolutions for hand pose estimation. In: BMVC (2020)
Li, J., et al.: Human pose regression with residual log-likelihood estimation. In: ICCV, pp. 11005–11014 (2021)
Li, J., Fang, F., Mei, K., Zhang, G.: Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11212, pp. 527–542. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_32
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. In: CVPR, pp. 510–519 (2019)
Li, Y., et al.: Is 2D heatmap representation even necessary for human pose estimation? arXiv (2021)
Ma, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, H.-T., Sun, J.: ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11218, pp. 122–138. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_8
Newell, A., Yang, K., Deng, J.: Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 483–499. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_29
Nibali, A., He, Z., Morgan, S., Prendergast, L.A.: Numerical coordinate regression with convolutional neural networks. arXiv (2018)
Sandler, M., Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.: Mobilenetv 2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: CVPR, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Santavas, N., Kansizoglou, I., Bampis, L., Karakasis, E.G., Gasteratos, A.: Attention! A lightweight 2D hand pose estimation approach. arXiv (2020)
Simon, T., Joo, H., Matthews, I.A., Sheikh, Y.: Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping. In: CVPR, pp. 4645–4653 (2017)
Sun, K., Xiao, B., Liu, D., Wang, J.: Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 5693–5703 (2019)
Toshev, A., Szegedy, C.: Deeppose: human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In: CVPR, pp. 1653–1660 (2014)
Wang, R.J., Li, X., Ao, S., Ling, C.X.: PELEE: a real-time object detection system on mobile devices. In: ICLR (2018)
Wang, Y., Peng, C., Liu, Y.: Mask-pose cascaded CNN for 2D hand pose estimation from single color image. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 29, 3258–3268 (2019)
Wang, Y., Zhang, B., Peng, C.: SrhandNet: real-time 2D hand pose estimation with simultaneous region localization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 2977–2986 (2020)
Wang, Z., Nie, X., Qu, X., Chen, Y., Liu, S.: Distribution-aware single-stage models for multi-person 3d pose estimation. arXiv (2022)
Wei, S., Ramakrishna, V., Kanade, T., Sheikh, Y.: Convolutional pose machines. In: CVPR, pp. 4724–4732 (2016)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
Yu, C., et al.: Lite-hrNet: a lightweight high-resolution network. In: CVPR, pp. 10440–10450 (2021)
Zhang, F., Zhu, X., Dai, H., Ye, M., Zhu, C.: Distribution-aware coordinate representation for human pose estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 7091–7100 (2020)
Zhang, Z., Tang, J., Wu, G.: Simple and lightweight human pose estimation. arXiv (2019)
Zhao, H., et al.: PSANet: point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11213, pp. 270–286. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_17
Zimmermann, C., Brox, T.: Learning to estimate 3D hand pose from single RGB images. In: ICCV, pp. 4913–4921 (2017)
Zimmermann, C., Ceylan, D., Yang, J., Russell, B.C., Argus, M.J., Brox, T.: Freihand: a dataset for markerless capture of hand pose and shape from single RGB images. In: ICCV, pp. 813–822 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020AAA0109701), National Natural Science Foundation of China (62076024, 62006018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, ZY., Chen, SL., Liu, Q., Zhang, CJ., Chen, F., Yin, XC. (2023). LiteHandNet: A Lightweight Hand Pose Estimation Network via Structural Feature Enhancement. In: Dang-Nguyen, DT., et al. MultiMedia Modeling. MMM 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13833. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27077-2_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27077-2_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-27076-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-27077-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)