Abstract
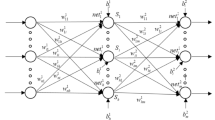
The learning process of feedforward neural networks, which determines suitable connection weights and biases, is a challenging machine learning problems and significantly impact how well neural networks work. Back-propagation, a gradient descent-based method, is one of the most popular learning algorithms, but tends to get stuck in local optima. Differential evolution (DE), a popular population-based metaheuristic algorithm, is an interesting alternative for tackling challenging optimisation problems. In this paper, we present Cen-CoDE, a centroid-based differential evolution algorithm with composite trial vector generation strategies and control parameters to train neural networks. Our algorithm encodes weights and biases into a candidate solution, employs a centroid-based strategy in three different ways to generate different trial vectors, while the objective function is based on classification error. In our experiments, we show Cen-CoDE to outperform other contemporary techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljarah, I., Faris, H., Mirjalili, S.: Optimizing connection weights in neural networks using the whale optimization algorithm. Soft. Comput. 22(1), 1–15 (2018)
Bairathi, D., Gopalani, D.: Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSA) for Training Feed-Forward Neural Networks. In: Bansal, J.C., Das, K.N., Nagar, A., Deep, K., Ojha, A.K. (eds.) Soft Computing for Problem Solving. AISC, vol. 816, pp. 521–534. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1592-3_41
Beale, H.D., Demuth, H.B., Hagan, M.: Neural Network Design. PWS, Boston (1996)
Choi, T.J., Ahn, C.W.: Adaptive Cauchy differential evolution with strategy adaptation and its application to training large-scale artificial neural networks. In: He, C., Mo, H., Pan, L., Zhao, Y. (eds.) BIC-TA 2017. CCIS, vol. 791, pp. 502–510. Springer, Singapore (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7179-9_39
Foresee, F.D., Hagan, M.T.: Gauss-Newton approximation to Bayesian learning. In: International Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 3, pp. 1930–1935 (1997)
Gudise, V.G., Venayagamoorthy, G.K.: Comparison of particle swarm optimization and backpropagation as training algorithms for neural networks. In: IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, pp. 110–117 (2003)
Heo, W., Lee, J.M., Park, N., Grable, J.E.: Using artificial neural network techniques to improve the description and prediction of household financial ratios. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 25, 100273 (2020)
Hiba, H., El-Abd, M., Rahnamayan, S.: Improving SHADE with center-based mutation for large-scale optimization. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 1533–1540 (2019)
Hiba, H., Mahdavi, S., Rahnamayan, S.: Differential evolution with center-based mutation for large-scale optimization. In: IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, pp. 1–8 (2017)
Jalaleddin, M.S., Shahryar, R., Gerald, S.: Many-level image thresholding using a center-based differential evolution algorithm. In: Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE (2020)
Karaboga, D., Akay, B., Ozturk, C.: Artificial bee colony (ABC) optimization algorithm for training feed-forward neural networks. In: International Conference on Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence, pp. 318–329 (2007)
Karaboga, D., Basturk, B.: A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Global Optim. 39(3), 459–471 (2007)
Khishe, M., Safari, A.: Classification of sonar targets using an MLP neural network trained by dragonfly algorithm. Wireless Pers. Commun. 108(4), 2241–2260 (2019)
Leema, N., Nehemiah, H.K., Kannan, A.: Neural network classifier optimization using differential evolution with global information and back propagation algorithm for clinical datasets. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 834–844 (2016)
Mahdavi, S., Rahnamayan, S., Deb, K.: Center-based initialization of cooperative co-evolutionary algorithm for large-scale optimization. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 3557–3565 (2016)
Minnema, J., van Eijnatten, M., Kouw, W., Diblen, F., Mendrik, A., Wolff, J.: Ct image segmentation of bone for medical additive manufacturing using a convolutional neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 103, 130–139 (2018)
Mirjalili, S.: How effective is the grey wolf optimizer in training multi-layer perceptrons. Appl. Intell. 43(1), 150–161 (2015)
Møller, M.F.: A scaled conjugate gradient algorithm for fast supervised learning. Aarhus University, Computer Science Department (1990)
Moravvej, S.V., Mousavirad, S.J., Moghadam, M.H., Saadatmand, M.: An LSTM-based plagiarism detection via attention mechanism and a population-based approach for pre-training parameters with imbalanced classes. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds.) ICONIP 2021. LNCS, vol. 13110, pp. 690–701. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92238-2_57
Moravvej, S.V., Mousavirad, S.J., Oliva, D., Schaefer, G., Sobhaninia, Z.: An improved de algorithm to optimise the learning process of a Bert-based plagiarism detection model. In: 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2022)
Mousavirad, S.J., Bidgoli, A.A., Ebrahimpour-Komleh, H., Schaefer, G., Korovin, I.: An effective hybrid approach for optimising the learning process of multi-layer neural networks. In: International Symposium on Neural Networks, pp. 309–317 (2019)
Mousavirad, S.J., Bidgoli, A.A., Komleh, H.E., Schaefer, G.: A memetic imperialist competitive algorithm with chaotic maps for multi-layer neural network training. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 14(4), 227–236 (2019)
Mousavirad, S.J., Bidgoli, A.A., Rahnamayan, S.: Tackling deceptive optimization problems using opposition-based de with center-based Latin hypercube initialization. In: 14th International Conference on Computer Science & Education, pp. 394–400 (2019)
Mousavirad, S.J., Gandomi, A.H., Homayoun, H.: A clustering-based differential evolution boosted by a regularisation-based objective function and a local refinement for neural network training. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 1–8 (2022)
Mousavirad, S.J., Oliva, D., Chakrabortty, R.K., Zabihzadeh, D., Hinojosa, S.: Population-based self-adaptive generalised masi entropy for image segmentation: A novel representation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 245, 108610 (2022)
Mousavirad, S.J., Oliva, D., Hinojosa, S., Schaefer, G.: Differential evolution-based neural network training incorporating a centroid-based strategy and dynamic opposition-based learning. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 1233–1240 (2021)
Mousavirad, S.J., Rahnamayan, S.: CenPSO: a novel center-based particle swarm optimization algorithm for large-scale optimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pp. 2066–2071 (2020)
Mousavirad, S.J., Rahnamayan, S.: Evolving feedforward neural networks using a quasi-opposition-based differential evolution for data classification. In: IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, pp. 2320–2326 (2020)
Mousavirad, S.J., Schaefer, G., Jalali, S.M.J., Korovin, I.: A benchmark of recent population-based metaheuristic algorithms for multi-layer neural network training. In: Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, pp. 1402–1408 (2020)
Mousavirad, S.J., Schaefer, G., Korovin, I., Oliva, D.: RDE-OP: A region-based differential evolution algorithm incorporation opposition-based learning for optimising the learning process of multi-layer neural networks. In: International Conference on the Applications of Evolutionary Computation, pp. 407–420 (2021)
Phansalkar, V., Sastry, P.: Analysis of the back-propagation algorithm with momentum. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 5(3), 505–506 (1994)
Rad, S.J.M., Tab, F.A., Mollazade, K.: Classification of rice varieties using optimal color and texture features and BP neural networks. In: 7th Iranian Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing, pp. 1–5 (2011)
Rahnamayan, S., Wang, G.G.: Center-based sampling for population-based algorithms. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 933–938 (2009)
Riedmiller, M., Braun, H.: A direct adaptive method for faster backpropagation learning: the RPROP algorithm. In: IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 586–591 (1993)
Scales, L.: Introduction to Non-linear Optimization. Macmillan International Higher Education (1985)
Shi, Y., Eberhart, R.: A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 69–73 (1998)
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Global Optim. 11(4), 341–359 (1997)
Tsai, C.F., Wu, J.W.: Using neural network ensembles for bankruptcy prediction and credit scoring. Expert Syst. Appl. 34(4), 2639–2649 (2008)
Wang, Y., Cai, Z., Zhang, Q.: Differential evolution with composite trial vector generation strategies and control parameters. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 15(1), 55–66 (2011)
Whitley, D.: A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat. Comput. 4(2), 65–85 (1994)
Yi, J.H., Xu, W.H., Chen, Y.T.: Novel back propagation optimization by cuckoo search algorithm. Scientific World J. 2014 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rahmani, S., Mousavirad, S.J., El-Abd, M., Schaefer, G., Oliva, D. (2023). Centroid-Based Differential Evolution with Composite Trial Vector Generation Strategies for Neural Network Training. In: Correia, J., Smith, S., Qaddoura, R. (eds) Applications of Evolutionary Computation. EvoApplications 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13989. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30229-9_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30229-9_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-30228-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-30229-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)