Abstract
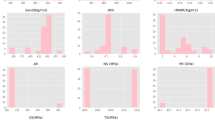
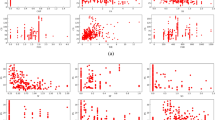
A novel proposed material for the potential replacement of cement in some of its applications was evaluated. This new material labeled Eco-Cement comprised of Biomass from the dairy and poultry industries, Urea, Cement Kiln Dust, Rice Husk Ash, Sand, and Water and was manufactured in a range of weight ratios. In this work, a comprehensive analysis of the ingredients in varying weight percentages of the novel material was manufactured and the corresponding strength and strains of the material were studied. A variety of concrete pastes using amounts of sought ratios were produced, molded into blocks, and allowed to cure under laboratory conditions. Unconfined compression tests were performed using a deformation control compressive strength machine. The strength and strains were evaluated from the initial zero load step incrementally, until the failure of each specimen. The resulting database was analyzed by utilizing Linear Regression, Random Forests, and the Gradient Boosting machine learning methods. Extensive sensitivity analysis with the machine learning algorithms, reveal certain patterns, which were established with three different methods. Furthermore, we present the analysis of the corresponding literature with Bibliometric techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi, N., et al.: Ecocement: A novel composite material for the construction industry. Identification of an Optimal Recipe Using Neural Networks (2016)
Bezanson, J., Edelman, A., Karpinski, S., Shah, V.B.: Julia: A fresh approach to numerical computing. SIAM Rev. 59, 65–98 (2017)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001)
Breit, W., Schnell, J.: Monolithic external architectural lightweight concrete components providing highly efficient thermal insulation-an experimental building. Betonwerk und Fertigteil-Technik 80(2), 128–130 (2014)
Chen, T., Guestrin, C.: XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. pp. 785–794. KDD ’16, ACM, New York, NY, USA (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Czapik, P., Zapała-Sławeta, J., Owsiak, Z., Stkepień, P.: Hydration of cement by- pass dust. Constr. Build. Mater. 231, 117139 (2020)
Elchalakani, M.: High strength rubberized concrete containing silica fume for the construction of sustainable road side barriers. Structures 1, 20–38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2014.06.001,citedBy43
Friedman, J.H.: Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 38, 367–378 (2002)
Gevrey, M., Dimopoulos, I., Lek, S.: Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00257-0
Huang, Y., Bird, R.N., Heidrich, O.: A review of the use of recycled solid waste materials in asphalt pavements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 52, 58–73 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2007.02.002,citedBy284
Irwan, J.M., et al.: The mechanical properties of pet fiber reinforced concrete from recycled bottle wastes. Adv. Mat. Res. 795, 347–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.795.347, cited By 14; Conference of 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Materials, ICoSM 2013; Conference Date: 26 March 2013 Through 27 March 2013; Conference Code:100411
Myhre, M., Mackillop, D.A.: Rubber recycling. Rubber Chem. Technol. 75, 429–474 (2002). https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547678,citedBy106
Neter, J., Kutner, M.H., Nachtsheim, C.J., Wasserman, W.: Applied linear statistical models (1996)
Olden, J.D., Jackson, D.A.: Illuminating the “black box”: a randomization approach for understanding variable contributions in artificial neural networks. Ecol. Model. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00064-9
Pelisser, F., Montedo, O.R.K., Gleize, P.J.P., Roman, H.R.: Mechanical properties of recycled pet fibers in concrete. Mater. Res. 15, 679–686 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392012005000088
Sadeghi, B.: Decisiontree.jl (2013)
Whiffin, V.S.: Microbial caco3 precipitation for the production of biocement (2004)
Xu, B., Chen, T.: Xgboost.jl (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was made under the frame of the ECOCE-MENT project (FP7 - Grant 282922).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Anastasi, N.R., Bakas, N.P. (2023). Significance of Eco-Cement Constituents to Its Mechanical Properties, by Machine Learning Algorithms. In: Papadaki, M., Rupino da Cunha, P., Themistocleous, M., Christodoulou, K. (eds) Information Systems. EMCIS 2022. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 464. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30694-5_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30694-5_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-30693-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-30694-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)