Abstract
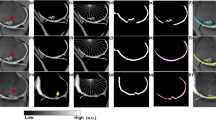
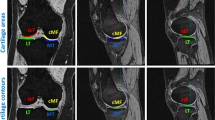
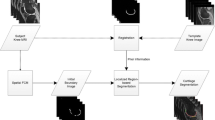
Patellofemoral instability is a knee disorder in which the patella, slips out of its usual placement leading to knee pain. The patella may displace from its position due to abnormality in the shape of patellar surface on femur bone. The orthopaedic experts manually measure certain parameters from the available axial knee scans for the patellar instability diagnosis, which is labor-intensive and susceptible to inter- and intra-observer variations. The automated segmentation of femur region in knee magnetic resonance (MR) image can help in easily identifying the abnormality in the patellar surface. Therefore, in this paper, the femur bone in the axial knee MR scans has been segmented using two variants of U-Net: basic U-Net and U-Net++ and the results have been compared and visualized. The validation dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and accuracy of 89.62% and 94.05% were obtained, respectively, for U-Net. For U-Net++, the validation DSC of 95.04% and validation accuracy of 94.91% were obtained. Further, in this paper, the sulcus depth measurement has been automated using basic image processing techniques. A mean error of 0.565 mm was obtained when tested on 20 axial knee MR images. The T2-weighted knee MRI dataset of 55 patients has been acquired from Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh for training and testing of the proposed approach.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fithian, D.C., Paxton, E.W., Stone, M.L., et al.: Epidemiology and natural history of acute patellar dislocation. Am. J. Sports Med. 32(5), 1114–21 (2004)
Diederichs, G., Issever, A.S., Scheffler, S.: MR imaging of patellar instability: injury patterns and assessment of risk factors. Radiographics 30(4), 961–981 (2010)
Horng, M.H., Kuok, C.P., Fu, M.J., et al.: Cobb angle measurement of spine from X-ray images using convolutional neural network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019 (2019)
Masad, I.S., Fahoum, A.A., Qasmieh, I.A.: Automated measurements of lumbar lordosis in T2-MR images using decision tree classifier and morphological image processing. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 22(4), 1027–1034 (2019)
Caesarendra, W., Rahmaniar, W., Mathew, J., et al.: Automated cobb angle measurement for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using convolutional neural network. Diagnostics 12(2), 396 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020396
Zhang, K., Xu, N., Guo, C., et al.: MPF-net: an effective framework for automated cobb angle estimation. Med. Image Anal. 75, 102277 (2022)
Prieto, J.C., Shah, H., Rosenbaum, A.J., et al.: An automated framework for image classification and segmentation of fetal ultrasound images for gestational age estimation. In: Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering 2021, Bellingham, Washington, PMC (2016). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2582243
Sun, L., Kong, Q., Huang, Y., et al.: Automatic segmentation and measurement on knee computerized tomography images for patellar dislocation diagnosis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020 (2020)
Pfirrmann, C.W., Zanetti, M., Romero, J., Hodler, J.: Femoral trochlear dysplasia: MR findings. Radiology 216(3), 858–64 (2000)
Osman, N.M., Ebrahim, S.M.B.: Patellofemoral instability: quantitative evaluation of predisposing factors by MRI. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nuclear Med. 47(4), 1529–1538 (2016)
Ridhma, Kaur, M., Sofat, S., et al.: Review of automated segmentation approaches for knee images. IET Image Process. 15(2), 302–324 (2021)
Kang, Y., Engelke, K., Kalender, W.A.: A new accurate and precise 3-D segmentation method for skeletal structures in volumetric CT data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 22(5), 586–598 (2003)
Wu, D., Sofka, M., Birkbeck, N., Zhou, S.K.: Segmentation of multiple knee bones from CT for orthopedic knee surgery planning. In: Golland, P., Hata, N., Barillot, C., Hornegger, J., Howe, R. (eds.) MICCAI 2014. LNCS, vol. 8673, pp. 372–380. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10404-1_47
Dam, E.B., Lillholm, M., Marques, J., et al.: Automatic segmentation of high- and low-field knee MRIs using knee image quantification with data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J. Med. Imaging 2(2), 024001 (2015)
Gandhamal, A., Talbar, S., Gajre, S., et al.: Fully automated subchondral bone segmentation from knee MR images: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Comput. Biol. Med. 88(1), 110–125 (2017)
Chen, H., Sprengers, André M.J., Kang, Y., et al.: Automated segmentation of trabecular and cortical bone from proton density weighted MRI of the knee. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 57(5), 1015–1027 (2019)
Driban, J., Fripp, J., Tamez-Pena, J., et al.: On the use of coupled shape priors for segmentation of magnetic resonance images of the knee. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 19(3), 1153–1167 (2015)
Fripp, J., Crozier, S., Warfield, S.K., et al.: Automatic segmentation of the bone and extraction of the bone-cartilage interface from magnetic resonance images of the knee. Phys. Med. Biol. 52(6), 1617–1631 (2007)
Yin, Y., Zhang, X., Williams, R., et al.: LOGISMOS-layered optimal graph image segmentation of multiple objects and surfaces: cartilage segmentation in the knee joint. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29(12), 2023–2037 (2010)
Prasoon, A., Igel, C., Loog, M., et al.: Femoral cartilage segmentation in Knee MRI scans using two stage voxel classification. In: Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Osaka, Japan, pp. 5469–5472 (2013)
Pang, J., Li, P.Y., Qiu, M., Chen, W., Qiao, L.: Automatic articular cartilage segmentation based on pattern recognition from Knee MRI images. J. Digit. Imaging 28(6), 695–703 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9780-x
Ambellan, F., Tack, A., Ehlke, M., et al.: Automated segmentation of knee bone and cartilage combining statistical shape knowledge and convolutional neural networks: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Med. Image Anal. 52, 109–118 (2019)
Burton, W., Myers, C., Rullkoetter, P.: Semi-supervised learning for automatic segmentation of the knee from MRI with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 189, 105328 (2020)
Gaj, S., Yang, M., Nakamura, K., et al.: Automated cartilage and meniscus segmentation of knee MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks. Magn. Reson. Med. 84(1), 437–449 (2020)
Deng, Y., You, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, X.: A coarse-to-fine framework for automated knee bone and cartilage segmentation data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J. Digit. Imaging 34(4), 833–840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00464-z
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Shelhamer, E., Long, J., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 640–651 (2017)
Goodfellow, Ian J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27. Curran Associates, Inc. (2014)
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Stoyanov, D., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2018. LNCS, vol. 11045, pp. 3–11. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2017, pp. 2261–2269 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ridhma, Kaur, M., Sofat, S., Chouhan, D.K., Prakash, M. (2023). Automated Sulcus Depth Measurement on Axial Knee MR Images. In: Gupta, D., Bhurchandi, K., Murala, S., Raman, B., Kumar, S. (eds) Computer Vision and Image Processing. CVIP 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1776. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31407-0_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31407-0_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-31406-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-31407-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)