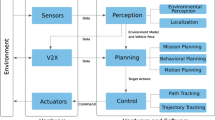
Abstract
Recently there has been an increase in the number of available autonomous vehicle (AV) models. To evaluate and compare the safety of the various models the AVs need to be tested in several diverse safety-critical scenarios. We propose the Adversarial Test Case Generator (ATCG) that differently from previous test case generators allows for the generation of realistic collision scenarios with varied AV and pedestrian behaviour models, on varied scenes and with varied traffic density. Given a top-view image and the semantic segmentation of a traffic scene, the ATCG learns to place multiple AVs and goal-reaching pedestrians in the scene such that collisions occur. Pedestrians in previous multi-agent traffic scenario generation works are confined to unrealistic behaviours such as seeking collisions with the AV or ignoring the AV. Although such scenarios with multiple suicidal pedestrians are collision prone it is unlikely in reality that all pedestrians act abnormally. In realistic collision scenarios the generated pedestrians’ behaviours must resemble real pedestrians. The ATCG is a team of Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents and can be easily extended with additional RL agents to produce more complex scenes allowing for advanced AVs to be tested.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, Z., Zhao, H.: A survey of deep RL and IL for autonomous driving policy learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 14043–14065 (2021)
Ye, F., Zhang, S., Wang, P., Chan, C.-Y.: A survey of deep reinforcement learning algorithms for motion planning and control of autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 1073–1080 (2021)
Paden, B., Čáp, M., Yong, S.Z., Yershov, D., Frazzoli, E.: A survey of motion planning and control techniques for self-driving urban vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 1, 33–55 (2016)
Kang, Y., Yin, H., Berger, C.: Test your self-driving algorithm: an overview of publicly available driving datasets and virtual testing environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 4, 171–185 (2019)
Suzuki, T., Aoki, Y., Kataoka, H.: Pedestrian near-miss analysis on vehicle-mounted driving recorders. In: Proceedings of Fifteenth International Conference on Machine Vision Applications, pp. 416–419. IEEE (2017)
Yao, Y., Xu, M., Wang, Y., Crandall, D.J., Atkins, E.M.: Unsupervised traffic accident detection in first-person videos. In: Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 273–280. IEEE (2019)
Aliakbarian, M.S., Saleh, F.S., Salzmann, M., Fernando, B., Petersson, L., Andersson, L.: VIENA\(^2\): a driving anticipation dataset. In: Jawahar, C.V., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K. (eds.) ACCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11361, pp. 449–466. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20887-5_28
Chandra, R., et al.: METEOR: a massive dense & heterogeneous behavior dataset for autonomous driving. CoRR abs/2109.07648. arXiv: 2109.07648 (2021)
Ding, W., et al.: A survey on safety-critical driving scenario generation - a methodological perspective. CoRR abs/2202.02215. arXiv: 2202.02215 (2022)
Abdessalem, R.B., Panichella, A., Nejati, S., Briand, L.C., Stifter, T.: Testing autonomous cars for feature interaction failures using many-objective search. In: Huchard, M., Kästner, C., Fraser, G. (eds.) Proceedings of the 33rd IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 143–154. ACM (2018)
Li, Y., Tao, J., Wotawa, F.: Ontology-based test generation for automated and autonomous driving functions. Inf. Softw. Technol. 117, 106200 (2020)
Abdessalem, R.B., Nejati, S., Briand, L.C., Stifter, T.: Testing advanced driver assistance systems using multi-objective search and neural networks. In: Lo, D., Apel, S., Khurshid, S. (eds.) Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 63–74. ACM (2016)
Zhong, Z., Kaiser, G., Ray, B.: Neural network guided evolutionary fuzzing for finding traffic violations of autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. (2022)
Bussler, A., Hartjen, L., Philipp, R., Schuldt, F.: Application of evolutionary algorithms and criticality metrics for the verification and validation of automated driving systems at urban intersections. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 128–135 (2020)
Almanee, S., Wu, X., Huai, Y., Chen, Q.A., Garcia, J.: scenoRITA: generating less-redundant, safety-critical and motion sickness-inducing scenarios for autonomous vehicles. CoRR abs/2112.09725. arXiv: 2112.09725 (2021)
Ding, W., Chen, B., Li, B., Eun, K.J., Zhao, D.: Multimodal safety-critical scenarios generation for decision-making algorithms evaluation. IEEE Rob. Autom. Lett. 6, 1551–1558 (2021)
Parashar, P., Cosgun, A., Nakhaei, A., Fujimura, K.: Modeling preemptive behaviors for uncommon hazardous situations from demonstrations. CoRR abs/1806.00143. arXiv: 1806.00143 (2018)
Demetriou, A., Alfsvåg, H., Rahrovani, S., Chehreghani, M.: A deep learning framework for generation and analysis of driving scenario trajectories. CoRR abs/2007.14524. arXiv: 2007.14524 (2020)
Nishiyama, D., et al.: Discovering avoidable planner failures of autonomous vehicles using counterfactual analysis in behaviorally diverse simulation. In: Proceedings of 23rd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Zhong, Z., et al.: A survey on scenario-based testing for automated driving systems in high-fidelity simulation. CoRR abs/2112.00964. arXiv: 2112.00964 (2021)
Ding, W., Xu, M., Zhao, D.: CMTS: a conditional multiple trajectory synthesizer for generating safety-critical driving scenarios. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4314–4321. IEEE (2020)
Sun, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, W.: Building narrative scenarios for human-autonomous vehicle interaction research in simulators. In: Cassenti, D.N., Scataglini, S., Rajulu, S.L., Wright, J.L. (eds.) AHFE 2020. AISC, vol. 1206, pp. 150–156. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51064-0_20
Karunakaran, D., Worrall, S., Nebot, E.: Efficient falsification approach for autonomous vehicle validation using a parameter optimisation technique based on reinforcement learning (2020). arXiv: 2011.07699
Karunakaran, D., Worrall, S., Nebot, E.M.: Efficient statistical validation with edge cases to evaluate highly automated vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2020)
Ding, W., Chen, B., Xu, M., Zhao, D.: Learning to collide: an adaptive safety-critical scenarios generating method. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 2243–2250. IEEE (2020)
Wang, J., et al.: AdvSim: generating safety-critical scenarios for self-driving vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9909–9918 (2021)
Hamdi, A., Mueller, M., Ghanem, B.: SADA: semantic adversarial diagnostic attacks for autonomous applications. In: Proceedings of Thirty-Fourth Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 10901–10908. AAAI Press (2020)
Gupta, P., Coleman, D., Siegel, J.: Towards safer self-driving through great PAIN (Physically Adversarial Intelligent Networks). CoRR abs/2003.10662. arXiv: 2003.10662 (2020)
Wen, M., Park, J., Cho, K.: A scenario generation pipeline for autonomous vehicle simulators. HCIS 10, 24 (2020)
Koren, M., Kochenderfer, M.J.: Efficient autonomy validation in simulation with adaptive stress testing. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, pp. 4178–4183. IEEE (2019)
Muktadir, G.M., Whitehead, J.: Adversarial jaywalker modeling for simulation-based testing of autonomous vehicle systems. In: Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 1697–1702. IEEE (2022)
Ding, W., Lin, H., Li, B., Zhao, D.: CausalAF: causal autoregressive flow for safety-critical driving scenario generation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR (2022, to appear)
Abeysirigoonawardena, Y., Shkurti, F., Dudek, G.: Generating adversarial driving scenarios in high-fidelity simulators. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 8271–8277. IEEE (2019)
Priisalu, M., Pirinen, A., Paduraru, C., Sminchisescu, C.: Generating scenarios with diverse pedestrian behaviors for autonomous vehicle testing. In: Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR, vol. 164, pp. 1247–1258 (2021)
Priisalu, M., Paduraru, C., Pirinen, A., Sminchisescu, C.: Semantic synthesis of pedestrian locomotion. In: Ishikawa, H., Liu, C.-L., Pajdla, T., Shi, J. (eds.) ACCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12623, pp. 470–487. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69532-3_29
Yang, Z., et al.: SurfelGAN: synthesizing realistic sensor data for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11115–11124. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Li, W., et al.: AADS: Augmented autonomous driving simulation using data-driven algorithms. Sci. Rob. 4, eaaw0863 (2019)
Saadatnejad, S., Li, S., Mordan, T., Alahi, A.: A shared representation for photorealistic driving simulators. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23, 13835–13845 (2022)
Lee, S., et al.: Visuomotor understanding for representation learning of driving scenes. In: Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference, p. 262. BMVA Press (2019)
Wu, Y., Gao, R., Park, J., Chen, Q.: Future video synthesis with object motion prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5538–5547. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE (2020)
Li, Z., et al.: READ: large-scale neural scene rendering for autonomous driving. CoRR abs/2205.05509. arXiv: 2205.05509 (2022)
Makansi, O., Çiçek, Ö., Buchicchio, K., Brox, T.: Multimodal future localization and emergence prediction for objects in egocentric view with a reachability prior. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4353–4362. IEEE (2020)
Sun, J., Averbuch-Elor, H., Wang, Q., Snavely, N.: Hidden footprints: learning contextual walkability from 3D human trails. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12363, pp. 192–207. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_12
Fang, J., et al.: Behavioral intention prediction in driving scenes: a survey. CoRR abs/2211.00385. arXiv: 2211.00385 (2022)
Rasouli, A., Tsotsos, J.K.: Autonomous vehicles that interact with pedestrians: a survey of theory and practice. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 21, 900–918 (2019)
Hanselmann, N., Renz, K., Chitta, K., Bhattacharyya, A., Geiger, A.: KING: generating safety-critical driving scenarios for robust imitation via kinematics gradients. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) Proceedings of the 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 13698, pp. 335–352. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19839-7_20
Wan, Z., et al.: Too afraid to drive: systematic discovery of semantic DoS vulnerability in autonomous driving planning under physical-world attacks. In: The Proceedings of the 29th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium. The Internet Society (2022)
Mockus, J.: On Bayes methods for seeking an extremum. Avtomatika i Vychislitelnaja Technika 3, 53–62 (1972)
Dai, Q., Xu, X., Guo, W., Huang, S., Filev, D.: Towards a systematic computational framework for modeling multi-agent decision-making at micro level for smart vehicles in a smart world. Robot. Auton. Syst. 144, 103859 (2021)
Rempe, D., Philion, J., Guibas, L.J., Fidler, S., Litany, O.: Generating useful accident-prone driving scenarios via a learned traffic prior. In: Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 17305–17315 (2022)
Serrano, S.M., Llorca, D.F., Daza, I.G., Sotelo, M.Á.: Insertion of real agents behaviors in CARLA autonomous driving simulator. In: da Silva, H.P., Vanderdonckt, J., Holzinger, A., Constantine, L.L. (eds.) Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer-Human Interaction Research and Applications, pp. 23–31. SCITEPRESS (2022)
Vasquez, R., Farooq, B.: Multi-objective autonomous braking system using naturalistic dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, pp. 4348–4353 (2019)
Schmitt, P., et al.: nuReality: a VR environment for research of pedestrian and autonomous vehicle interactions. CoRR abs/2201.04742. arXiv: 2201.04742 (2022)
Li, C., Cheng, C., Sun, T., Chen, Y., Yan, R.: ComOpT: combination and optimization for testing autonomous driving systems. In: Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 7738–7744. IEEE (2022)
Boloor, A., et al.: Attacking vision-based perception in end-to-end autonomous driving models. J. Syst. Architect. 110, 101766 (2020)
Machiraju, H., Balasubramanian, V.N.: A little fog for a large turn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision 2020, pp. 2902–2911 (2020)
Cao, Y., et al.: Adversarial sensor attack on LiDAR-based perception in autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 2267–2281. Association for Computing Machinery (2019)
Fursa, I., et al.: Worsening perception: real-time degradation of autonomous vehicle perception performance for simulation of adverse weather conditions. SAE Int. J. Connected Autom. Veh. 5, 87–100 (2022)
Kim, E., et al.: Querying labelled data with scenario programs for sim-to-real validation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 ACM/IEEE 13th International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems, pp. 34–45 (2022)
Spooner, J., Palade, V., Cheah, M., Kanarachos, S., Daneshkhah, A.: Generation of pedestrian crossing scenarios using Ped-Cross Generative Adversarial Network. Appl. Sci. 11, 471 (2021)
Dagdanov, R., Eksen, F., Durmus, H., Yurdakul, F., Ure, N.K.: DeFIX: detecting and fixing failure scenarios with reinforcement learning in imitation learning based autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 4215–4220. IEEE (2022)
Williams, R.J.: Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 8, 229–256 (1992)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y. (eds.) Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Hydén, C.: Traffic conflicts technique: state-of-the-art. Traffic Saf. Work Video Process. 37, 3–14 (1996)
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., Lopez, A., Koltun, V.: CARLA: an open urban driving simulator. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR, vol. 78, pp. 1–16 (2017)
Chandra, S., Bharti, A.K.: Speed distribution curves for pedestrians during walking and crossing. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 104, 660–667 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Research Council Consolidator grant SEED, CNCS-UEFISCDI PCCF-2016-0180, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF) Smart Systems Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Priisalu, M., Paduraru, C., Smichisescu, C. (2023). Varied Realistic Autonomous Vehicle Collision Scenario Generation. In: Gade, R., Felsberg, M., Kämäräinen, JK. (eds) Image Analysis. SCIA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13886. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31438-4_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31438-4_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-31437-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-31438-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)