Abstract
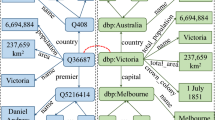
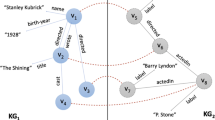
Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have recently gained attention for representing knowledge about a particular domain and play a central role in a multitude of AI tasks like recommendations and query answering. Recent works have revealed that KG embedding methods used to implement these tasks often exhibit direct forms of bias (e.g., related to gender, nationality, etc.) leading to discrimination. In this work, we are interested in the impact of indirect forms of bias related to the structural diversity of KGs in entity alignment (EA) tasks. In this respect, we propose an exploration-based sampling algorithm, SUSIE, that generates challenging benchmark data for EA methods, with respect to structural diversity. SUSIE requires setting the value of a single hyperparameter, which affects the connectivity of the generated KGs. The generated samples exhibit similar characteristics to some of the most challenging real-world KGs for EA tasks. Using our sampling, we demonstrate that state-of-the-art EA methods, like RREA, RDGCN, MultiKE and PARIS, exhibit different robustness to structurally diverse input KGs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
As opposed to strongly connected components, where edge directions matter.
- 3.
According to the sampling taxonomy proposed in [34].
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
References
Airlines dataset. https://archive.org/download/kasabi. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Locah dataset. http://data.archiveshub.ac.uk/. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Mem-e dataset from oaei 2022. http://oaei.ontologymatching.org/2022/knowledgegraph/index.html. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Memory-alpha dataset. http://memory-alpha.wikia.com/. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Restaurants dataset from oaei 2010. http://oaei.ontologymatching.org/2010/im/. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Star trek expanded universe dataset. http://stexpanded.wikia.com/. Accessed 02 Mar 2023
Biemer, P.P., et al.: Total Survey Error in Practice. Wiley, Hoboken (2017)
Bose, A.J., Hamilton, W.L.: Compositional fairness constraints for graph embeddings. In: ICML, vol. 97, pp. 715–724 (2019)
Bourli, S., Pitoura, E.: Bias in knowledge graph embeddings. In: ASONAM, pp. 6–10 (2020)
Buyl, M., Bie, T.D.: DeBayes: a Bayesian method for debiasing network embeddings. CoRR abs/2002.11442 (2020)
Chaurasiya, D., et al.: Entity alignment for knowledge graphs: progress, challenges, and empirical studies. CoRR abs/2205.08777 (2022)
Chen, M., Wei, Z., Huang, Z., Ding, B., Li, Y.: Simple and deep graph convolutional networks. CoRR abs/2007.02133 (2020)
Chen, M., Tian, Y., Chang, K., Skiena, S., Zaniolo, C.: Co-training embeddings of knowledge graphs and entity descriptions for cross-lingual entity alignment. In: IJCAI, pp. 3998–4004 (2018)
Cheng, W., Wang, C., Xiao, B., Qian, W., Zhou, A.: On statistical characteristics of real-life knowledge graphs. In: Zhan, J., Han, R., Zicari, R.V. (eds.) BPOE 2015. LNCS, vol. 9495, pp. 37–49. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-29006-5_4
Choudhary, M., Laclau, C., Largeron, C.: A survey on fairness for machine learning on graphs. CoRR abs/2205.05396 (2022)
Christophides, V., Efthymiou, V., Stefanidis, K.: Entity Resolution in the Web of Data. Morgan & Claypool Publishers (2015)
Dong, Y., Kang, J., Tong, H., Li, J.: Individual fairness for graph neural networks: a ranking based approach. In: KDD, pp. 300–310 (2021)
Dong, Y., Ma, J., Chen, C., Li, J.: Fairness in graph mining: a survey. CoRR abs/2204.09888 (2022)
Dwork, C., Hardt, M., Pitassi, T., Reingold, O., Zemel, R.S.: Fairness through awareness. In: Innovations in Theoretical Computer Science, pp. 214–226 (2012)
Efthymiou, V., Stefanidis, K., Christophides, V.: Big data entity resolution: from highly to somehow similar entity descriptions in the web. In: IEEE BigData, pp. 401–410 (2015)
Efthymiou, V., Stefanidis, K., Pitoura, E., Christophides, V.: FairER: entity resolution with fairness constraints. In: CIKM, pp. 3004–3008 (2021)
Fanourakis, N., Efthymiou, V., Kotzinos, D., Christophides, V.: Knowledge graph embedding methods for entity alignment: an experimental review. CoRR abs/2203.09280 (2022)
Fisher, J.: Measuring social bias in knowledge graph embeddings. CoRR abs/1912.02761 (2019)
Fisher, J., Mittal, A., Palfrey, D., Christodoulopoulos, C.: Debiasing knowledge graph embeddings. In: EMNLP, pp. 7332–7345 (2020)
Guo, Q., et al.: A survey on knowledge graph-based recommender systems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 34(8), 3549–3568 (2022)
Huang, X., Cheng, H., Li, R., Qin, L., Yu, J.X.: Top-K structural diversity search in large networks. VLDB J. 34, 319–343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-015-0379-0
Huang, X.L., Tiwari, M., Shah, S.: Structural diversity in social recommender systems. In: RecSys (2013)
Jeong, J., Yun, J., Keam, H., Park, Y., Park, Z., Cho, J.: div2vec: diversity-emphasized node embedding. In: RecSys (2020)
Kang, J., He, J., Maciejewski, R., Tong, H.: InFoRM: individual fairness on graph mining. In: KDD, pp. 379–389 (2020)
Kang, J., Zhu, Y., Xia, Y., Luo, J., Tong, H.: RawlsGCN: towards Rawlsian difference principle on graph convolutional network. CoRR abs/2202.13547 (2022)
Karakasidis, A., Pitoura, E.: Identifying bias in name matching tasks. In: EDBT, pp. 626–629 (2019)
Keidar, D., Zhong, M., Zhang, C., Shrestha, Y.R., Paudel, B.: Towards automatic bias detection in knowledge graphs. In: EMNLP, pp. 3804–3811 (2021)
Khajehnejad, A., Khajehnejad, M., Babaei, M., Gummadi, K.P., Weller, A., Mirzasoleiman, B.: CrossWalk: fairness-enhanced node representation learning. In: AAAI, pp. 11963–11970 (2022)
Leskovec, J., Faloutsos, C.: Sampling from large graphs. In: SIGKDD, pp. 631–636 (2006)
Li, J., Song, D.: Uncertainty-aware pseudo label refinery for entity alignment. In: WWW, pp. 829–837 (2022)
Li, P., Wang, Y., Zhao, H., Hong, P., Liu, H.: On dyadic fairness: exploring and mitigating bias in graph connections. In: ICLR (2021)
Luo, Y., Yang, B., Xu, D., Tian, L.: A survey: complex knowledge base question answering. In: ICICSE, pp. 46–52 (2022)
Mao, X., Wang, W., Xu, H., Wu, Y., Lan, M.: Relational reflection entity alignment. In: CIKM, pp. 1095–1104 (2020)
Martínez-Plumed, F., Ferri, C., Nieves, D., Hernández-Orallo, J.: Missing the missing values: the ugly duckling of fairness in machine learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 36(7), 3217–3258 (2021)
Masrour, F., Wilson, T., Yan, H., Tan, P., Esfahanian, A.: Bursting the filter bubble: fairness-aware network link prediction. In: AAAI, pp. 841–848 (2020)
Molokwu, B.C., Shuvo, S.B., Kar, N.C., Kobti, Z.: Node classification in complex social graphs via knowledge-graph embeddings and convolutional neural network. In: Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V., et al. (eds.) ICCS 2020. LNCS, vol. 12142, pp. 183–198. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50433-5_15
Nathani, D., Chauhan, J., Sharma, C., Kaul, M.: Learning attention-based embeddings for relation prediction in knowledge graphs. In: ACL, pp. 4710–4723 (2019)
Obraczka, D., Schuchart, J., Rahm, E.: EAGER: embedding-assisted entity resolution for knowledge graphs. CoRR abs/2101.06126 (2021)
Quy, T.L., Roy, A., Iosifidis, V., Zhang, W., Ntoutsi, E.: A survey on datasets for fairness-aware machine learning. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 12(3), e1452 (2022)
Rahman, T.A., Surma, B., Backes, M., Zhang, Y.: Fairwalk: towards fair graph embedding. In: IJCAI, pp. 3289–3295 (2019)
Rossi, A., Barbosa, D., Firmani, D., Matinata, A., Merialdo, P.: Knowledge graph embedding for link prediction: a comparative analysis. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 15(2), 14:1–14:49 (2021)
Sanz-Cruzado, J., Pepa, S.M., Castells, P.: Structural novelty and diversity in link prediction. In: WWW, pp. 1347–1351 (2018)
Saxena, A., Fletcher, G., Pechenizkiy, M.: HM-EIICT: fairness-aware link prediction in complex networks using community information. J. Comb. Optim. 44(4), 2853–2870 (2021)
Sinha, A., Cazabet, R., Vaudaine, R.: Systematic biases in link prediction: comparing heuristic and graph embedding based methods. In: Aiello, L.M., Cherifi, C., Cherifi, H., Lambiotte, R., Lió, P., Rocha, L.M. (eds.) COMPLEX NETWORKS 2018. SCI, vol. 812, pp. 81–93. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05411-3_7
Suchanek, F.M., Abiteboul, S., Senellart, P.: PARIS: probabilistic alignment of relations, instances, and schema. PVLDB 5(3), 157–168 (2011)
Sun, Z., et al.: A benchmarking study of embedding-based entity alignment for knowledge graphs. Proc. VLDB Endow. 13(11), 2326–2340 (2020)
Tang, X., et al.: Investigating and mitigating degree-related biases in graph convolutional networks. In: CIKM, pp. 1435–1444 (2020)
Trisedya, B.D., Qi, J., Zhang, R.: Entity alignment between knowledge graphs using attribute embeddings. In: AAAI, pp. 297–304 (2019)
Ugander, J., Backstrom, L., Marlow, C., Kleinberg, J.M.: Structural diversity in social contagion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109(16), 5962–5966 (2012)
Wang, S.: On the analysis of large integrated knowledge graphs for economics, banking and finance. In: EDBT/ICDT Workshops, vol. 3135 (2022)
Wu, Y., Liu, X., Feng, Y., Wang, Z., Yan, R., Zhao, D.: Relation-aware entity alignment for heterogeneous knowledge graphs. In: IJCAI, pp. 5278–5284 (2019)
Zhang, Q., Sun, Z., Hu, W., Chen, M., Guo, L., Qu, Y.: Multi-view knowledge graph embedding for entity alignment. In: IJCAI 2019 (2019)
Zhang, R., Trisedya, B.D., Li, M., Jiang, Y., Qi, J.: A benchmark and comprehensive survey on knowledge graph entity alignment via representation learning. VLDB J. 31(5), 1143–1168 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-022-00747-z
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhu, J.J.H., Wang, X., Pentland, A.S.: The strength of structural diversity in online social networks. CoRR abs/1906.00756 (2019)
Acknowledgement
The work of N. Fanourakis and V. Efthymiou was funded from the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) and the General Secretariat for Research and Technology (GSRT), under GA No 969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fanourakis, N., Efthymiou, V., Christophides, V., Kotzinos, D., Pitoura, E., Stefanidis, K. (2023). Structural Bias in Knowledge Graphs for the Entity Alignment Task. In: Pesquita, C., et al. The Semantic Web. ESWC 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13870. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33455-9_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33455-9_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-33454-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-33455-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)