Abstract
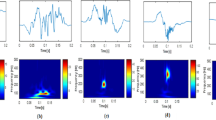
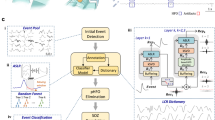
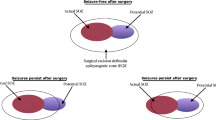
High frequency oscillations (HFOs) have been presented as a promising clinical biomarker of regions responsible of epileptic seizure onset zone (soz) and thus a potential aid to guide epilepsy surgery. Visual identification of HFOs in long-term continuous intracranial EEG (iEEG) is cumbersome, due to their low amplitude and short duration. The objective of our study is to improve and automate HFO detection by developing analysis tools based on an unsupervised clustering method. First, we used a temporal basis set from Jmail et al. 2017 while exploiting the time-frequency content of iEEG data. Subsequently, we used a CNN (resnet 18) feature extractor. Then, we applied the clustering method based on reducing the events dimension per frame while preserving the distance between points when displaying from high-dimensional space to a low-dimensional one. The clustering method (Deep Cluster) is based on a standard k-means clustering algorithm. This algorithm successfully isolated HFOs from artifacts, peaks and peaks with ripples. Using this algorithm, we were able to locate the seizure onset area.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zentner, J.: Surgical treatment of epilepsies. In: Sutter, B., Schröttner, O. (eds.) Advances in Epilepsy Surgery and Radiosurgery, pp. 27–35. Springer Vienna, Vienna (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6117-3_3
Hadriche, A., ElBehy, I., Hajjej, A., Jmail, N.: Evaluation of techniques for predicting a build up of a seizure. In: Abraham, A., Gandhi, N., Hanne, T., Hong, T.-P., Nogueira Rios, T., Ding, W. (eds.) ISDA 2021. LNNS, vol. 418, pp. 816–827. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96308-8_76
Hadriche, A,, Behy, I., Necibi, A., Kachouri, A., Ben Amar, C., Jmail, N.: Assessment of Effective Network Connectivity among MEG None Contaminated Epileptic Transitory Events. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6406362
Nawel, J., Abir, H., Ichrak, B., Amal, N., Chokri, B.A.: A comparison of inverse problem methods for source localization of epileptic meg spikes. In: 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), pp. 867–870 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBE.2019.00161
Jmail, N., Gavaret, M., Wendling, F., Kachouri, A., Hamadi, G., Badier, J.M.: A comparison of methods for separation of transient and oscillatory signals in EEG. J. Neurosci. Methods 193, 273–289 (2011)
Zelmann, R., Mari, F., Jacobs, J., Zijlmans, M., Dubeau, F., Gotman, J.: A comparison between detectors of high frequency oscillations. Clinical Neurophysiol. 123(1), 106–116 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.06.006
Engel, J., Bragin, A., Staba, R., Mody, I.: High-frequency oscillations: what is normal and what is not? Epilepsia 50(4), 598–604 (2009)
Schevon, C.A., Trevelyan, A.J., Schroeder, C.E., Goodman, R.R., McKhann, G., Emerson, R.G.: Spatial characterization of interictal high frequency oscillations in epileptic neocortex. Brain 132(Pt 11), 3047–3059 (2009)
Worrell, G.A., et al.: High-frequency oscillations in human temporal lobe: simultaneous microwire
Blanco, J.A., et al.: Unsupervised classification of high-frequency oscillations in human neocortical epilepsy and control patients. J. Neurophysiol. 104(5), 2900–2912 (2010)
Andrew, B.G., Greg W., Eric, A,M., Dennis, D., Brian, L.: Human and automated detection of high-frequency oscillations in clinical intracranial EEG Regcordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 118(5), 1134–1143 (2007)
Akiyama, T., et al.: Focal cortical high-frequency oscillations trigger epileptic spasms: confirmation by digital video subdural EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol.
Crépon, B., et al.: Mapping interictal oscillations greater than 200 Hz recorded with intracranial macroelectrodes in human epilepsy. Brain 133(Pt 1), 33–45 (2010)
Burnos, S., et al.: Human intracranial high frequency oscillations (HFOs) detected by automatic time-frequency analysis. PLoS One 9(4), e94381 (2014)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning, vol. 43. MIT Press (2016)
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Leland, M., Healy, J., Melville, J.: Umap: uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.03426 (2018)
David, M.C., et al.: t-SNE-CUDA: GPU-accelerated t-SNE and its applications to modern data. Preprint arXiv arXiv:1807.11824 (2018)
Benchmarks for popular CNN models. https://github.com/jcjohnson/cnn-benchmarks
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by 20PJEC0613 “Hatem Ben Taher Tunisian Project”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sadek, Z., Hadriche, A., Jmail, N. (2023). Clustering of High Frequency Oscillations HFO in Epilepsy Using Pretrained Neural Networks. In: Abraham, A., Pllana, S., Casalino, G., Ma, K., Bajaj, A. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 716. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-35500-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-35501-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)