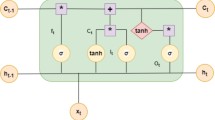
Abstract
Air pollution is a worldwide issue that affects the lives of many people in urban areas. It is considered that the air pollution may lead to heart and lung diseases. A careful and timely forecast of the air quality could help to reduce the exposure risk for affected people. In this paper, we use a data-driven approach to predict air quality based on historical data. We compare three popular methods for time series prediction: Exponential Smoothing (ES), Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Long short-term memory (LSTM). Considering prediction accuracy and time complexity, our experiments reveal that for short-term air pollution prediction ES performs better than ARIMA and LSTM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadi, M., et al.: Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: 12th \(\{\)USENIX\(\}\) Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (\(\{\)OSDI\(\}\) 16), pp. 265–283 (2016)
Alsouda, Y., Pllana, S., Kurti, A.: A machine learning driven IoT solution for noise classification in smart cities. In: Machine Learning Driven Technologies and Architectures for Intelligent Internet of Things (ML-IoT), pp. 1–6. Euromicro (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1809.00238
Alsouda, Y., Pllana, S., Kurti, A.: IoT-based Urban Noise Identification Using Machine Learning: Performance of SVM, KNN, Bagging, and Random Forest. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Omni-Layer Intelligent Systems. COINS 2019, New York, NY, USA, pp. 62–67. ACM (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3312614.3312631
Amaral, V., et al.: Programming languages for data-intensive HPC applications: a systematic mapping study. Parallel Comput. 91, 102584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parco.2019.102584
Amjad, M., Shah, D.: Trading bitcoin and online time series prediction. In: NIPS 2016 Time Series Workshop, pp. 1–15 (2017)
Benkner, S., et al.: PEPPHER: efficient and productive usage of hybrid computing systems. IEEE Micro 31(5), 28–41 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2011.67
Das, P.K., A, D.V., Meher, S., Panda, R., Abraham, A.: A systematic review on recent advancements in deep and machine learning based detection and classification of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. IEEE Access 10, 81741–81763 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3196037
Gulli, A., Pal, S.: Deep Learning with Keras. Packt Publishing Ltd (2017)
Le, D.: Real-time air pollution prediction model based on spatiotemporal big data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.00432 (2018)
Le Borgne, Y.A., Santini, S., Bontempi, G.: Adaptive model selection for time series prediction in wireless sensor networks. Signal Process. 87(12), 3010–3020 (2007)
Longcore, T., Rich, C.: Ecological light pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2(4), 191–198 (2004)
Massaron, L., Boschetti, A.: Regression Analysis with Python. Packt Publishing Ltd. (2016)
Memeti, S., Pllana, S.: Accelerating DNA Sequence Analysis Using Intel(R) Xeon Phi(TM). In: 2015 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA. vol. 3, pp. 222–227 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/Trustcom.2015.636
Memeti, S., Pllana, S.: Optimization of heterogeneous systems with AI planning heuristics and machine learning: a performance and energy aware approach. Computing 103(12), 2943–2966 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-021-01017-6
Ochando, L.C., Julián, C.I.F., Ochando, F.C., Ferri, C.: Airvlc: an application for real-time forecasting urban air pollution. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Mining Urban Data, vol. 1392, pp. 72–79. MUD 2015, CEUR-WS.org, Aachen, DE (2015)
Petrushevski, S.: Air pollution in Skopje from 2008 to 2018 (2018). https://www.kaggle.com/cokastefan/pm10-pollution-data-in-skopje-from-2008-to-2018
Pllana, S., Xhafa, F.: Programming Multicore and Many-core Computing Systems. Wiley, Hoboken (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119332015
Qin, X., Mahmassani, H.S.: Adaptive calibration of dynamic speed-density relations for online network traffic estimation and prediction applications. Transp. Res. Record 1876(1), 82–89 (2004)
Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N.: Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. John Wiley & Sons (2016)
Shaban, K.B., Kadri, A., Rezk, E.: Urban air pollution monitoring system with forecasting models. IEEE Sensors J. 16(8), 2598–2606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2016.2514378
Siami-Namini, S., Namin, A.S.: Forecasting economics and financial time series: Arima vs. lstm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.06386 (2018)
Smith, T.G.: pmdarima: Arima estimators for Python (2017)
Subramanian, V.N.: Data analysis for predicting air pollutant concentration in smart city uppsala (2016)
Viebke, A., Memeti, S., Pllana, S., Abraham, A.: CHAOS: a parallelization scheme for training convolutional neural networks on Intel Xeon Phi. J. Supercomput. 75(1), 197–227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-017-1994-x
Yang, D., Wang, J., Yan, X., Liu, H.: Subway air quality modeling using improved deep learning framework. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 163, 487–497 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.05.055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Talamanova, I., Pllana, S. (2023). Data-driven Real-time Short-term Prediction of Air Quality: Comparison of ES, ARIMA, and LSTM. In: Abraham, A., Pllana, S., Casalino, G., Ma, K., Bajaj, A. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 716. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-35500-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-35501-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)