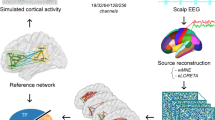
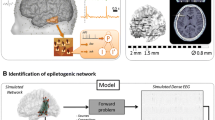
Abstract
Source localization consists in defining exact position of the brain generators for a time course obtained from a surface electrophysiological signal (EEG, MEG), in order to determine with a high precision the epileptogenic zones. We applied diverse inverse problem techniques to obtain this resolution. These techniques present various hypotheses and specific epileptic network connectivity. We proposed here to rate the performance of issued inverse problem in identifying epileptic zone. Then, we used four methods of inverse problem to explain cortical areas and neural generators of excessive discharges. We computed network connectivity of each technique. We applied a pre processing chain to assess the rate of epileptic gamma oscillation connectivity among MEG of each technique. Wavelet Maximum Entropy on the Mean (wMEM) proved a high matching between MEG network connectivity based on Correlation, Coherence, Granger Causality (GC) and Phase Locking Value (PLV) between active sources, followed by Dynamical Statistical Parametric Mapping (dSPM), standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA), and Minimum norm estimation (MNE). The problem techniques studied are at least able to find theoretically part of seizure onset zone. wMEM and dSPM represent the most powerful connection of all techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mamelak, A.N., Akhtari, M., Sutherling, W.W., Lopez, N.: Mamelak 4mm between 2 dipoles.pdf, vol. 97, pp. 865–873 (2002)
David, O., Garnero, L., Cosmelli, D., Varela, F.J.: Estimation of neural dynamics from MEG/EEG cortical current density maps: application to the reconstruction of large-scale cortical synchrony. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49(9), 975–987 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2002.802013
Horwitz, B.: The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage 19(2), 466–470 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00112-5
Darvas, F., Pantazis, D., Kucukaltun-Yildirim, E., Leahy, R.M.: Mapping human brain function with MEG and EEG: methods and validation. Neuroimage 23(SUPPL. 1), 289–299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.014
Gross, J., Kujala, J., Hämäläinen, M., Timmermann, L., Schnitzler, A., Salmelin, R.: Dynamic imaging of coherent sources: studying neural interactions in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98(2), 694–699 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.98.2.694
Peled, A., Geva, A.B., Kremen, W.S., Blankfeld, H.M., Esfandiarfard, R., Nordahl, T.E.: Functional connectivity and working memory in schizophrenia: an EEG study. Int. J. Neurosci. 106(1–2), 47–61 (2001). https://doi.org/10.3109/00207450109149737
Kaminski, M.J., Blinowska, K.J.: A new method of the description of the information flow in the brain structures. Biol. Cybern. 65(3), 203–210 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198091
Nawel, J., Abir, H., Ichrak, B., Amal, N., Chokri, B.A.: A comparison of inverse problem methods for source localization of epileptic meg spikes. In: Proceedings - 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, BIBE 2019, pp. 867–870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBE.2019.00161
Jmail, N., Gavaret, M., Bartolomei, F., Chauvel, P., Badier, J.-M., Bénar, C.-G.: Comparison of brain networks during interictal oscillations and spikes on magnetoencephalography and intracerebral EEG. Brain Topogr. 29(5), 752–765 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0501-7
Hadriche, A., ElBehy, I., Hajjej, A., Jmail, N.: Evaluation of techniques for predicting a build up of a seizure. In: Abraham, A., Gandhi, N., Hanne, T., Hong, T.-P., Nogueira Rios, T., Ding, W. (eds.) ISDA 2021. LNNS, vol. 418, pp. 816–827. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-96308-8_76
Hadriche, A., Jmail, N.: A build up of seizure prediction and detection Software: a review. J. Clin. Images Med. Case Reports 2(2), 1–2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.52768/2766-7820/1087
Delorme, A., Makeig, S.: EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 134(1), 9–21 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009
Tadel, F., Baillet, S., Mosher, J.C., Pantazis, D., Leahy, R.M.: Brainstorm: a user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 1–13 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/879716
Hincapié, A.S., et al.: MEG connectivity and power detections with minimum norm estimates require different regularization parameters. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 12–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3979547
Borchers, B., Uram, T., Hendrickx, J.M.H.: Tikhonov regularization of electrical conductivity depth profiles in field soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 61(4), 1004–1009 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100040002x
Pascual-Marqui, R.D., Esslen, M., Kochi, K., Lehmann, D.: Functional imaging with low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (LORETA): a review. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 24(SUPPL. C), 91–95 (2002)
McDonald, C.R., et al.: Distributed source modeling of language with magnetoencephalography: application to patients with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 50(10), 2256–2266 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02172.x
Chowdhury, R.A., Lina, J.M., Kobayashi, E., Grova, C.: MEG source localization of spatially extended generators of epileptic activity: comparing entropic and hierarchical Bayesian approaches. PLoS ONE 8(2), e55969 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055969
Lina, J.M., Chowdhury, R., Lemay, E., Kobayashi, E., Grova, C.: Wavelet-based localization of oscillatory sources from magnetoencephalography data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(8), 2350–2364 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2012.2189883
Tass, P., et al.: Tass1998, pp. 1–4 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.3291
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by 20PJEC0613 “Hatem Ben Taher Tunisian Project”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Necibi, A., Hadriche, A., Jmail, N. (2023). Assessment of Epileptic Gamma Oscillations’ Networks Connectivity. In: Abraham, A., Pllana, S., Casalino, G., Ma, K., Bajaj, A. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 716. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35501-1_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-35500-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-35501-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)