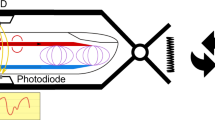
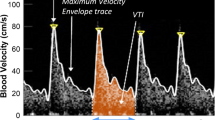
Abstract
Continuous monitoring of cardiac function is highly desirable for long-term assessment of cardiovascular health, detection of acute cardiac dysfunction. Information from volume flow rate may be important in a variety of different clinical circumstances, such as stroke, arteriovenous malformation, cardiac failure. The main aim of the work was review of non-invasive measurements of carotid blood flow methods and devices. There are various types of methods and devices for monitoring blood flow in the carotid artery, however, so far no mobile recorder of the appropriate quality of registration has been developed. The most promising solutions are wireless wearable patches that, when applied to the skin of the neck, will not be a burden during measurements. This is important when measurements are to be made, during extreme activities, such as in pilots. As a result of the conducted research, there is a presumption that carotid blood flow measurements methods has great potential to be a useful tool in the diagnosis of the pilot's predisposition, at the same time performing a warning function, the so-called alerters, before the imminent overload loss of consciousness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, H., Huang, H., Li, M., et al.: A wearable cardiac ultrasound imager. Nature 613, 667–675 (2023)
Houte, J., Mooi, F.J., Montenij, L.J., Meijs, L.P.B., Suriani, I., Conjaerts, B.C.M., Houterman, S., Bouwman, A.R.: Correlation of carotid doppler blood flow with invasive cardiac output measurements in cardiac surgery patients. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth., 36(4), 1081–1091 (2022)
Goldman, L.: Cecil medicine. Saunders Elsevier, (2008)
Likittanasombut, P., Reynolds, P., Meads, D., Tegeler, C.: Volume flow rate of common carotid artery measured by Doppler method and Color Velocity Imaging Quantification (CVI-Q). J. Neuroimaging 16(1), 34–38 (2006)
Eicke, B.M., Tegeler, C.H.: Ultrasonic quantification of blood flow volume. In: Tegeler, C.H., Babikian, V.L., Gomez, C.R. (eds.) Neurosonology. Missouri: Mosby-Year Book, Inc., St. Louis, MO, pp. 101−110 (1996)
Houte, J., Raaijmaakers, A.E., Mooi, F.J., Meijs, L.P.B., Boer, E.C., Suriani, I., Houterman, S., Montenij, L.J., Bouwman, A.R.: Evaluating corrected carotid flow time as a non-invasive parameter for trending cardiac output and stroke volume in cardiac surgery patients. J. Ultrasound, (2022)
Girotto, V., Teboul, J.L., Beurton, A., et al.: Carotid and femoral Doppler do not allow the assessment of passive leg raising effects. Ann Intensive Care 8, 67 (2018)
Suriani, I., Houte, J., Boer, E.C., Knippenberg, L., Manzari, S., Mischi, M., Bouwman, R.A.: Carotid Doppler ultrasound for non-invasive haemodynamic monitoring: a narrative review. Physiol Meas. 43(10), (2023)
Brandt, A.H. et al.: A comparison study of vector velocity, spectral Doppler and magnetic resonance of blood flow in the common carotid artery Ultrasound Med. Biol. 44, 1751–61 (2018)
Bussmann, B.M., Sharma, S., McGregor, D., Hulme, W., Harris, T.: Observational study in healthy volunteers to define interobserver reliability of ultrasound haemodynamic monitoring techniques performed by trainee doctors Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 26, 217–223 (2019)
Cencetti, S., Lagi, A., Cipriani, M., Fattorini, L., Bandinelli, G., Bernardi, L.: Autonomic control of the cerebral circulation during normal and impaired peripheral circulatory control. Heart 82, 365–372 (1999)
Mnich, K.: The methods of survey blood fl ow in human body, Works of the Strata Mechanics Research Institute PAN, Tom 6, nr 3–4, s. 171–184 (2004), in Polish
Kuwabara, K., Higuchi, Y., Ogasawara, T., Koizumi, H., Haga, T.: Wearable blood flowmeter appcessory with low-power laser Doppler signal processing for daily-life healthcare monitoring. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 6274–6277 (2014)
Traczyk, W.: Human functional diagnostics. Medical Publisher, Warszawa (1999). in Polish
Noszczyk, W.: Surgery of peripheral arteries and veins. Medical Publisher, Warszawa (1998). in Polish
Du, Y., Shen, Y.: V Flow a novel visualization of blood flow. Mindray Healthc. Reach., (2016)
Filipczyński, L.: Blood flows, Polish Academy of Sciences PAN. Warszawa- Poznań (1980), in Polish
Steinmetz, M.P.: Nutritional care of the spinal cord–injured patient, calorimetry: measurement of energy expenditures. Benzel’s Spine Surg., (2017)
Priebe, L.: Methods of thermal blood flow measurement. Bibl Radiol. 6, 33–44 (1975)
Xingting, L., Xingyu, C., et al.: The thermal behavior of blood flow in the arteries with various radii and various stenosis angles using non-Newtonian Sisko model. Alex. Eng. J. 61(9), 7195–7201 (2022)
Sel, K., Osman, D., Jafari, R.: Non-invasive cardiac and respiratory activity assessment from various human body locations using bioimpedance. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2, 210–217 (2021)
Bu, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., et al.: Comparison of carotid blood flow measured by ultrasound and cardiac output in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Research Square, (2022)
Cheong, I., Otero, C.V., Sosa, F.A., Tort, O.B., Merlo, P.M., Tamagnone, F.M.: Carotid flow as a surrogate of the left ventricular stroke volume. J. Clin. Monit. Comput, (2022)
Du, Y,. Ding, H., He, L., Yiu, B.Y.S., Deng, L., Yu, A.C.H., Zhu, L.: Quantitative blood flow measurements in the common carotid artery: A comparative study of high-frame-rate ultrasound vector flow imaging, pulsed wave doppler, and phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostics (Basel), 12(3), 690 (2022)
Kenny, J.S.: Assessing fluid intolerance with doppler ultrasonography: a physiological framework. Med Sci (Basel) 10(1), 12 (2022)
Kenny, J.S., Elfarnawany, M., Yang, Z., Eibl, A.M., Eibl, J.K., Kim, C.H., Johnson, B.D.: A wireless ultrasound patch detects mild-to-moderate central hypovolemia during lower body negative pressure. J. Trauma. Acute. Care. Surg, 93(2S Suppl 1), S35-S40 (2022).
Kenny, J.S., Barjaktarevic, I., Mackenzie, D.C., Elfarnawany, M., Yang, Z., Eibl, A.M., Eibl, J.K., Kim, C.H., Johnson, B.D.: Carotid artery velocity time integral and corrected flow time measured by a wearable Doppler ultrasound detect stroke volume rise from simulated hemorrhage to transfusion. BMC Res Notes 15(1), 7 (2022)
Kenny, J.S., Munding, C.E., Eibl, J.K., Eibl, A.M., Long, B.F., Boyes, A., Yin, J., Verrecchia, P., Parrotta, M., Gatzke, R., Magnin, P.A., Burns, P.N., Foster, F.S., Demore, C.E.M.: A novel, hands-free ultrasound patch for continuous monitoring of quantitative Doppler in the carotid artery. Sci Rep. 11(1), 7780 (2021).
Wang, C., Qi, B., Lin, M., Zhang, Z., Makihata, M., Liu, B., Zhou, S., Huang, Y.H., Hu, H., Gu, Y., Chen, Y., Lei, Y., Lee, T., Chien, S., Jang, K.I., Kistler, E.B., Xu, S.: Continuous monitoring of deep-tissue hemodynamics with stretchable ultrasonic phased arrays. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5(7), 749–758 (2021)
Wang, F., Jin, P., Feng, Y., Fu, J., Wang, P., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, A., Feng, X.: Flexible doppler ultrasound device for the monitoring of blood flow velocity. Sci Adv. 7(44), (2021).
Hu, H., Zhu, X., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Li, X., Lee, S., Huang, Z., Chen, R., Chen, Z., Wang, C., Gu, Y., Chen, Y., Lei, Y., Zhang, T., Kim, N., Guo, Y., Teng, Y., Zhou, W., Li, Y., Nomoto, A., Sternini, S., Zhou, Q., Pharr, M., Scalea, FL., Xu, S.: Stretchable ultrasonic transducer arrays for three-dimensional imaging on complex surfaces. Sci Adv., 4(3), (2018)
Shen, H., Li, S., Wang, Y., Qin, K.R.: Effects of the arterial radius and the center-line velocity on the conductivity and electrical impedance of pulsatile flow in the human common carotid artery. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 57(2), 441–451 (2019)
Campen, C.L.M.C., Verheugt, F.W.A., Visser, F.C.: Cerebral blood flow changes during tilt table testing in healthy volunteers, as assessed by Doppler imaging of the carotid and vertebral arteries. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract., 3, 91–95 (2018)
Jalil, B., Thompson, P., Cavallazzi, R., Marik, P., Mann, J., El-Kersh, K., Guardiola, J., Saad, M.: Comparing changes in carotid flow time and stroke volume induced by passive leg raising. Am. J. Med. Sci. 355(2), 168–173 (2018)
Webb, R.C., Ma, Y., Krishnan, S., Li, Y., Yoon, S., Guo, X., Feng, X., Shi, Y., Seidel, M., Cho, N.H., Kurniawan, J., Ahad, J., Sheth, N., Kim, J., Taylor, J.G., Darlington, T., Chang, K., Huang, W., Ayers, J., Gruebele, A., Pielak, R.M., Slepian, M.J., Huang, Y., Gorbach, A.M., Rogers, J.A.: Epidermal devices for noninvasive, precise, and continuous mapping of macrovascular and microvascular blood flow. Sci Adv. 1(9), (2015)
Sobotnicka, E., Sobotnicki, A., Czerw, M., Badura, G., Sobiech, M., Krej, M., Puchalska, L., Dziuda, Ł.: A multiparameter examination system to assess self-regulatory mechanisms of the cardiovascular system under simulated hypergravity conditions. In: 2018 Baltic URSI Symposium (URSI), pp. 87–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.23919/URSI.2018.8406698
Sobotnicka, E., Sobotnicki, A., Czerw, M., Badura, G., Sobiech, M., Krej, M., Puchalska, L., Dziuda L.:Tests for pilots under simulated hypergravity conditions—technological challenges and research methodology. In: 2018 25th International conference “mixed design of integrated circuits and system” (MIXDES), pp. 465–470 (2018). https://doi.org/10.23919/MIXDES.2018.8436651
Sobotnicka, E., Sobotnicki, A., Czerw, M., Badura, G., Krej, M., Puchalska, L., Kowalczuk, K., Gaździński, S., Dziuda Ł.: Methods to assess self-regulatory mechanisms of the cardiovascular system under simulated hypergravity conditions. In: 2019 MIXDES—26th International conference mixed design of integrated circuits and systems. pp. 407–412(2019). https://doi.org/10.23919/MIXDES.2019.87871529
Funding
This work was supported by the resources of the National Centre of Research and Development, Poland, within the framework of the Program for National Defense and Security, Project DOB-BIO-12–05-001–2022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sobotnicka, E., Mocha, J., Sobotnicki, A., Gałecka, J., Gacek, A. (2024). Measurement of Blood Flow in the Carotid Artery as one of the Elements of Assessing the Ability for Pilots in the Gravitational Force Conditions–Review of Available Solutions. In: Strumiłło, P., Klepaczko, A., Strzelecki, M., Bociąga, D. (eds) The Latest Developments and Challenges in Biomedical Engineering. PCBEE 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 746. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38430-1_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-38430-1_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-38429-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-38430-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)