Abstract
Multi-modal DNNs have been demonstrated to outperform the best uni-modal DNNs by fusing information from different modalities. However, the performance improvement of multi-modal DNNs is always associated with an incredible increase in computational cost (e.g., network parameters, MAC operations, etc.) to handle more modalities, which ultimately makes them impractical for many real-world applications where computing capability is limited.
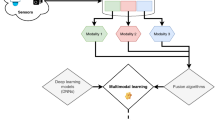
In this paper, we propose MMExit, a multi-modal exit architecture that allows for computing appropriate modalities and layers to predict results for different data samples. To this end, we define a novel metric called utility of exit (UoE) to measure the correlations of performance and computational cost for different exits. We then use an equivalent modality serialization method to map the two-dimensional exit space into an equivalent linear space and rank the exits according to their UoE to achieve fast and adaptive inference. To train the MMExit network, we devise a joint loss function which synthesizes the features of different modalities and layers. Our results show that MMExit can slash up to 48.72% of MAC operations with the best performance compared to SOTA multi-modal architectures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, M.S., Chauhan, D.S., Ghosal, D., Poria, S., Ekbal, A., Bhattacharyya, P.: Multi-task learning for multi-modal emotion recognition and sentiment analysis. In: NAACL-HLT (2019)
Arevalo, J., Solorio, T., Montes-y Gómez, M., González, F.A.: Gated multimodal units for information fusion. In: ICLR (2017)
Bach, F.R., Lanckriet, G.R., Jordan, M.I.: Multiple kernel learning, conic duality, and the SMO algorithm. In: ICML (2004)
Bhattacharjee, A., et al.: MIME: adapting a single neural network for multi-task inference with memory-efficient dynamic pruning. In: DAC (2022)
Castro, S., Hazarika, D., Pérez-Rosas, V., Zimmermann, R., Mihalcea, R., Poria, S.: Towards multimodal sarcasm detection (an _obviously_ perfect paper). In: ACL (2019)
Choi, K., Yang, H.: A GPU architecture aware fine-grain pruning technique for deep neural networks. In: Sousa, L., Roma, N., Tomás, P. (eds.) Euro-Par 2021. LNCS, vol. 12820, pp. 217–231. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85665-6_14
Cui, W., et al.: DVABatch: diversity-aware multi-entry multi-exit batching for efficient processing of DNN services on GPUs. In: USENIX ATC (2022)
Han, Y., Huang, G., Song, S., Yang, L., Wang, H., Wang, Y.: Dynamic neural networks: a survey. TPAMI 44, 7436–7456 (2021)
Hasan, M.K., et al.: Humor knowledge enriched transformer for understanding multimodal humor. In: AAAI (2021)
Hou, X., et al.: Architecting efficient multi-modal AIoT systems. In: ISCA (2023)
Hou, X., et al.: Characterizing and understanding end-to-end multi-modal neural networks on GPUs. In: IEEE CAL (2022)
Huang, G., Chen, D., Li, T., Wu, F., van der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Multi-scale dense networks for resource efficient image classification. In: ICLR (2018)
Jayakumar, S.M., et al.: Multiplicative interactions and where to find them. In: ICLR (2020)
Kim, W., Son, B., Kim, I.: ViLT: vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In: ICML (2021)
Laskaridis, S., Kouris, A., Lane, N.D.: Adaptive inference through early-exit networks: design, challenges and directions. In: MobiSys (2021)
Liang, P.P., et al.: MultiBench: multiscale benchmarks for multimodal representation learning. In: NeurIPS (2021)
Liu, J., Hou, X., Tang, F.: Fine-grained machine teaching with attention modeling. In: AAAI (2020)
Liu, Z., Shen, Y., Lakshminarasimhan, V.B., Liang, P.P., Zadeh, A., Morency, L.P.: Efficient low-rank multimodal fusion with modality-specific factors. In: ACL (2018)
Neverova, N., Wolf, C., Taylor, G.W., Nebout, F.: Multi-scale deep learning for gesture detection and localization. In: Agapito, L., Bronstein, M.M., Rother, C. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8925, pp. 474–490. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16178-5_33
Peng, X., Wei, Y., Deng, A., Wang, D., Hu, D.: Balanced multimodal learning via on-the-fly gradient modulation. In: CVPR (2022)
Pham, H., Liang, P.P., Manzini, T., Morency, L.P., Póczos, B.: Found in translation: learning robust joint representations by cyclic translations between modalities. In: AAAI (2019)
Scardapane, S., Scarpiniti, M., Baccarelli, E., Uncini, A.: Why should we add early exits to neural networks? Cogn. Comput. 12, 954–966 (2020)
Sze, V., Chen, Y.H., Yang, T.J., Emer, J.S.: Efficient processing of deep neural networks. In: Synthesis Lectures on Computer Architecture (2020)
Teerapittayanon, S., McDanel, B., Kung, H.T.: BranchyNet: fast inference via early exiting from deep neural networks. In: ICPR (2016)
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., Erhan, D.: Show and tell: lessons learned from the 2015 MSCOCO image captioning challenge. TPAMI 39, 652–663 (2016)
Zadeh, A., Chen, M., Poria, S., Cambria, E., Morency, L.P.: Tensor fusion network for multimodal sentiment analysis. In: EMNLP (2017)
Zhang, C., Yang, Z., He, X., Deng, L.: Multimodal intelligence: representation learning, information fusion, and applications. JSTSP 14, 478–493 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the National Key R &D Program of China under grant No.2021ZD0110104, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No.62122053. It was also partially supported by ACCESS - AI Chip Center for Emerging Smart Systems, InnoHK funding, Hong Kong SAR. We thank all the anonymous reviewers for their valuable feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hou, X. et al. (2023). MMExit: Enabling Fast and Efficient Multi-modal DNN Inference with Adaptive Network Exits. In: Cano, J., Dikaiakos, M.D., Papadopoulos, G.A., Pericàs, M., Sakellariou, R. (eds) Euro-Par 2023: Parallel Processing. Euro-Par 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14100. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-39698-4_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-39698-4_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-39697-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-39698-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)