Abstract
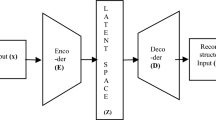
Weakly-supervised video anomaly detection uses video-level labels to avoid annotating all frames or segments in the training video. This problem is typically considered as a multiple instance learning problem, the training process aims to learn how to score both abnormal segments and normal segments, and the score of abnormal segments is higher than the score of normal segments. The features are extracted from videos before the training or testing process. Although many models have been proposed and obtained good results, improving the performance of the problem remains a challenge. This study proposes a convolutional autoencoder based approach to reconstruct features, with an assumption that the reconstructed features contain important information early bound to the objective of normal or abnormal video classification (minimizing the cost function). The work is validated on the ShanghaiTech Campus dataset and has produced results that outperform state-of-the-art methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravanbakhsh, M., Nabi, M., Sangineto, E., Marcenaro, L., Regazzoni, C., Sebe, N.: Abnormal event detection in videos using generative adversarial nets. arXiv:1708.09644 (2017)
Hasan, M., Choi, J., Neumann, J.K.A., Davis, L.S.: Learning temporal regularity in video sequences. arXiv:1604.04574 (2016)
Smeureanu, S., Ionescu, R.T., Popescu, M., Alexe, B.: Deep appearance features for abnormal behavior detection in video. In: Battiato, S., Gallo, G., Schettini, R., Stanco, F. (eds.) ICIAP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10485, pp. 779–789. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68548-9_70
Sultani, W., Chen, C., Shah, M.: Real-world Anomaly detection in surveillance videos. arXiv:1801.04264 (2018)
Degardin, B.: Weakly and partially supervised learning frameworks for anomaly detection (2020). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.30613.65769
Tian, Y., Pang, G., Chen, Y., Singh, R., Verjans, J.W., Carneiro, G.: Weakly-supervised video anomaly detection with robust temporal feature magnitude learning. arXiv:2101.10030 (2021)
Deshpande, K., Punn, N.S., Sonbhadra, S.K., Agarwal, S.: Anomaly detection in surveillance videos using transformer based attention model. arXiv:2206.01524 (2022)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27, 3 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/3422622
Georgescu, M., Barbalau, A., Ionescu, R.T., Khan, F.S., Popescu, M., Shah, M.: Anomaly detection in video via self-supervised and multi-task learning. arXiv:2011.07491 (2020)
Georgescu, M., Ionescu, R.T., Khan, F.S., Popescu, M., Shah, M.: A background-agnostic framework with adversarial training for abnormal event detection in video. arXiv:2021.3074805 (2020)
Wu, P., et al.: Not only look, but also listen: learning multimodal violence detection under weak supervision. arXiv:2007.04687 (2020)
Liu, Z., et al.: Video Swin Transformer. arXiv:2106.13230 (2021)
Kay, W., et al.: The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv:1705.06950 (2017)
Carreira, J., Noland, E., Hillier, C., Zisserman, A.: A short note about kinetics-600. arXiv:1808.01340 (2018)
Goyal, R., et al.: The “Something Something” video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, pp. 5843–5851 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.622
Miech, A., Alayrac, J., Smaira, L., Laptev, I., Sivic, J., Zisserman, A.: End-to-end learning of visual representations from uncurated instructional videos. ArXiv. /abs/1912.06430 (2019)
Miech, A., Zhukov, D., Alayrac, J., Tapaswi, M., Laptev, I., Sivic, J.: HowTo100M: learning a text-video embedding by watching hundred million narrated video clips. ArXiv. /abs/1906.03327 (2019)
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., Paluri, M.: A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. ArXiv. /abs/1711.11248 (2017)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo Vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. ArXiv. /abs/1705.07750 (2017)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. arXiv:1412.0767 (2014)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: An image is worth 16 × 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ArXiv. /abs/2010.11929 (2020)
Liu, Z., et al.: Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. ArXiv. /abs/2103.14030 (2021)
Neimark, D., Bar, O., Zohar, M., Asselmann, D.: Video transformer network. ArXiv. /abs/2102.00719 (2021)
Arnab, A., Dehghani, M., Heigold, G., Sun, C., Lučić, M., Schmid, C.: ViViT: a video vision transformer. ArXiv. /abs/2103.15691 (2021)
Michelucci, U.: An introduction to autoencoders. arXiv:2201.03898 (2022)
Liu, W., Luo, W., Lian, D., Gao, S.: Future frame prediction for anomaly detection – a new baseline. arXiv:1712.09867 (2017)
Zhong, J., Li, N., Kong, W., Liu, S., Li, T.H., Li, G.: Graph convolutional label noise cleaner: train a plug-and-play action classifier for anomaly detection. arXiv:1903.07256 (2019)
Wan, B., Fang, Y., Xia, X., Mei, J.: Weakly supervised video anomaly detection via center-guided discriminative learning. In: Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, United Kingdom, pp. 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME46284.2020.9102722
Zhang, J., Qing, L., Miao, J.: Temporal convolutional network with complementary inner bag loss for weakly supervised anomaly detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, pp. 4030–4034 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803657
Feng, J., Hong, F., Zheng, W.: MIST: multiple instance self-training framework for video anomaly detection. arXiv:2104.01633 (2021)
Wu, J.-C., Hsieh, H.-Y., Chen, D.-J., Fuh, C.-S., Liu, T.-L.: Self-supervised sparse representation for video anomaly detection. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds.) ECCV 2022. LNCS, vol. 13673, pp. 729–745. Springer, Heidelberg (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19778-9_42
Hung, P.D., Kien, N.N.: SSD-MobileNet implementation for classifying fish species. In: Vasant, P., Zelinka, I., Weber, G.W. (eds.) ICO 2019. AISC, vol. 1072, pp. 399–408. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33585-4_40
Hung, P.D., Su, N.T., Diep, V.T.: Surface classification of damaged concrete using deep convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 29, 676–687 (2019)
Hung, P.D., Su, N.T.: Unsafe construction behavior classification using deep convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 31, 271–284 (2021)
Duy, L.D., Hung, P.D.: Adaptive graph attention network in person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 32, 384–392 (2022)
Su, N.T., Hung, P.D., Vinh, B.T., Diep, V.T.: Rice leaf disease classification using deep learning and target for mobile devices. In: Al-Emran, M., Al-Sharafi, M.A., Al-Kabi, M.N., Shaalan, K. (eds.) ICETIS 2021. LNNS, vol. 299, pp. 136–148. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82616-1_13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hieu, P.N.D., Hung, P.D. (2023). A Convolutional Autoencoder Approach for Weakly Supervised Anomaly Video Detection. In: Nguyen, N.T., et al. Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 14162. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41456-5_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41456-5_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-41455-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-41456-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)