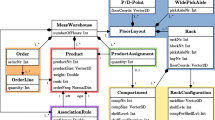
Abstract
The efficiency of warehouse operations can be measured by various indicators, but the main one is the lead time, which is heavily influenced by the order picking, as this is the most time- and labor-intensive process in the warehouse operation. In order to reduce lead times, many researchers are working on the topic of Storage Location Assignment Problem (SLAP) The optimized SLA is designed to improve picking efficiency, so that the picker does not have to travel long distances unnecessarily in a picker-to-parts system. During the optimization process, it is necessary to evaluate the SLA in an appropriate way, on the basis of which it is possible to measure whether the objectives are approximated by the results or not. It is also very important to evaluate regularly the SLA during the period after optimization to get an up-to-date information about the assignment of the storage items. The results of regular evaluations can be used to check whether the SLA is effective and lead times are good or whether optimization and reassignment is necessary. Based on studies and experience, SLAs are reassessed and optimized following significant inefficiencies, resulting in relocation tasks and additional work and costs for warehouses. The authors’ research concept includes avoiding large-scale relocation tasks by continuously review the SLA. While other studies evaluate the optimized SLA by running picking lists, but it usually would be necessary to get information about the assignment of the entire warehouse. Furthermore, since assigning thousands of items to thousands of positions is a huge combinational problem, evolutionary algorithm would be necessary to apply. It is also requiring time-effective and generalized individual evolution method to make us possible tactical SLA optimization.
The aim of this paper is to describe a novel generalized SLA evaluation method where each of the located items is evaluated to obtain a more accurate optimization result. Furthermore, unlike other research, the aim is to ensure that the optimization concept and the evaluation method are not only specified for one warehouse but can be used in other warehouses as well.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Koster, R.B.M., Le-Duc, T., Roodbergen, K.J.: Design and control of warehouse order picking: a literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 182(2), 481–501 (2007)
van Gils, T., Caris, A., Ramaekers, K., Braekers, K., de Koster, R.B.M.: Designing efficient order picking systems: the effect of real-life features on the relationship among planning problems. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 125(January), 47–73 (2019)
van Gils, T., Ramaekers, K., Caris, A., de Koster, R.B.M.: Designing efficient order picking systems by combining planning problems: state-of-the-art classification and review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 267(1), 1–15 (2018)
de Koster, R.B.M., Le-Duc, T., Roodbergen, K.J.: Design and control of warehouse order picking: a literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 129(2), 396–411 (2019)
Görbe, P., Bódis, T., Botzheim, J.: A conceptual framework for adaptive storage location assignment considering order characteristics. Eur. J. Sci. Technol. (April), 610–614 (2020)
Görbe, P., Bódis, T., Földesi, P.: Trade-offs in warehousing storage location reassignment. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. (1742–7967 1742–7975): 1(1), 1 (2023)
Frazelle, E.H.: Stock location assignment and order picking productivity. Doctoral Dissertation, Georgia Institute of Technology (1989)
Kübler, P., Glock, C.H., Bauernhansl, T.: A new iterative method for solving the joint dynamic storage location assignment, order batching and picker routing problem in manual picker-to-parts warehouses. Comput. Ind. Eng. 147, 106645 (2020)
Zhang, Y.: Correlated storage assignment strategy to reduce travel distance in order picking. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49(2), 30–35 (2016)
Zhang, R.Q., Wang, M., Pan, X.: New model of the storage location assignment problem considering demand correlation pattern. Comput. Ind. Eng. 129, 210–219 (2019)
Silva, A., Coelho, L.C., Darvish, M., Renaud, J.: Integrating storage location and order picking problems in warehouse planning. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 140(July), 102003 (2020)
Li, Y., Méndez-Mediavilla, F.A., Temponi, C., Kim, J., Jimenez, J.A.: A heuristic storage location assignment based on frequent itemset classes to improve order picking operations. Appl. Sci. (Switzerland) MDPI AG 11(4), 1–15 (2021)
Trindade, M.A.M., Sousa, P.S.A., Moreira, M.R.A.: Improving order-picking operations with precedence constraints through efficient storage location assignment: evidence from a retail company, U Porto. J. Eng. 7(3), 34–52 (2021)
Park, C., Seo, J.: Comparing heuristic algorithms of the planar storage location assignment problem. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 46(1), 171–185 (2010)
Pan, J.C.H., Shih, P.H., Wu, M.H., Lin, J.H.: A storage assignment heuristic method based on genetic algorithm for a pick-and-pass warehousing system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 81, 1–13 (2015)
Öncan, T.: MILP formulations and an iterated local search algorithm with Tabu thresholding for the order batching problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 243(1), 142–155 (2015)
Wang, M., Zhang, R.Q., Fan, K.: Improving order-picking operation through efficient storage location assignment: a new approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 139(October 2019), 106186 (2020)
Li, J., Moghaddam, M., Nof, S.Y.: Dynamic storage assignment with product affinity and ABC classification—a case study. Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 84(9–12), 2179–2194 (2016)
Dijkstra, A.S., Roodbergen, K.J.: Exact route-length formulas and a storage location assignment heuristic for picker-to-parts warehouses. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 102, 38–59 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Görbe, P., Bódis, T. (2023). Generalized Objective Function to Ensure Robust Evaluation for Evolutionary Storage Location Assignment Algorithms. In: Nguyen, N.T., et al. Advances in Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1864. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41774-0_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41774-0_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-41773-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-41774-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)