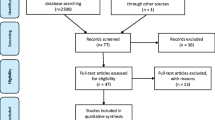
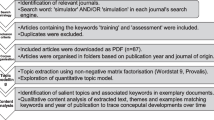
Abstract
Developing objective assessment approach in maritime simulator training can be a highly challenging task due to the complexity of simulating realistic scenarios, capturing relevant performance indicators and establishing good assessment protocols. This study provides a synthesis of simulation scenario contexts, data collection tools, and data analysis approaches in published simulator training studies. A systematic literature review (SLR) approach was followed for identifying the relevant studies for in-depth content analysis. The findings reveal that the reviewed studies focused on full-mission simulator-based assessment using collected data from various tools including surveys, eye-tracking, ECG, video or voice recording etc. The findings hold relevance in the development of learning analytics for facilitating objective assessment in maritime simulator training.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobayashi, H.: Use of simulators in assessment, learning and teaching of mariners. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 4, 57–75 (2005)
Juszkiewicz, W., Żukowska, A.: The use of the K-sim polaris simulator in the process of automatic assessment of navigator competence in the aspect of anticollision activities. Appl. Sci. 13(2), 915 (2023)
Munim, Z.H., Kim, T.-E.: A review of learning analytics dashboard and a novel application in maritime simulator training. In: Proceedings of the AHFE Conference (2023)
Macke, J., Genari, D.: Systematic literature review on sustainable human resource management. J. Clean. Prod. 208, 806–815 (2019)
Jiménez, J.I.A.: Modelling the relationship between performance and ship-handling simulator. J. Marit. Res. 17(3), 68–73 (2020)
Atik, O.: Eye tracking for assessment of situational awareness in bridge resource management training. J. Eye Mov. Res. 12(3) (2019).https://doi.org/10.16910/jemr.12.3.7
Hjelmervik, K., Nazir, S., Myhrvold, A.: Simulator training for maritime complex tasks: an experimental study. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 17(1), 17–30 (2018)
Liu, Y., et al.: Psychophysiological evaluation of seafarers to improve training in maritime virtual simulator. Adv. Eng. Inform. 44, 101048 (2020)
Orlandi, L., Brooks, B.: Measuring mental workload and physiological reactions in marine pilots: building bridges towards redlines of performance. Appl. Ergon. 69, 74–92 (2018)
Orlandi, L., Brooks, B., Bowles, M.: A comparison of marine pilots’ planning and manoeuvring skills: uncovering mental models to assess shiphandling and explore expertise. J. Navig. 68(5), 897–914 (2015)
Sanfilippo, F.: A multi-sensor fusion framework for improving situational awareness in demanding maritime training. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 161, 12–24 (2017)
Saus, E.-R., Johnsen, B.H., Eid, J., Thayer, J.F.: Who benefits from simulator training: personality and heart rate variability in relation to situation awareness during navigation training. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28(4), 1262–1268 (2012)
Sellberg, C., Lundin, M., Säljö, R.: Assessment in the zone of proximal development: simulator-based competence tests and the dynamic evaluation of knowledge-in-action. Classroom Discourse 13(4), 365–385 (2022)
Türkistanli, T.T., Kuleyin, B.: Game-based learning for better decision-making: a collision prevention training for maritime transportation engineering students. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 30(3), 917–933 (2022)
Wahl, A., Kongsvik, T., Antonsen, S.: Balancing safety I and safety II: learning to manage performance variability at sea using simulator-based training. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 195, 106698 (2020)
Xue, H., Batalden, B.-M., Sharma, P., Johansen, J.A., Prasad, D.K.: Biosignal-based driving skill classification using machine learning: a case study of maritime navigation. Appl. Sci. 11(20), 9765 (2021)
Fan, S., Yang, Z.: Towards objective human performance measurement for maritime safety: a new psychophysiological data-driven machine learning method. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 233, 109103 (2023)
Funding
This research is funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101060107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Munim, Z.H., Krabbel, H., Haavardtun, P., Kim, TE., Bustgaard, M., Thorvaldsen, H. (2023). Scenario Design, Data Measurement, and Analysis Approaches in Maritime Simulator Training: A Systematic Review. In: Kubincová, Z., Caruso, F., Kim, Te., Ivanova, M., Lancia, L., Pellegrino, M.A. (eds) Methodologies and Intelligent Systems for Technology Enhanced Learning, Workshops - 13th International Conference. MIS4TEL 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 769. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42134-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42134-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-42133-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-42134-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)